No products in the cart.
Trajenta, 5 mg 30 pcs.
€51.62 €43.02
Description
Trajenta is an inhibitor of the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4), which is involved in the inactivation of the hormones incretins glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide type 1 (GFP-1). These hormones are degraded by the enzyme DPP-4. Incretins maintain glucose concentration at the necessary physiological level.
In a 24-hour period, basal concentrations of GIP and GFP-1 are at low levels, which rise rapidly in response to food intake.
The hormones activate insulin biosynthesis and production by pancreatic beta cells when blood glucose concentrations are normal or high. GFP-1 decreases the production of glucagon by pancreatic alpha cells, resulting in reduced glucose production in the liver.
Indications
Indications
Monotherapy in patients with inadequate glycemic control only against the background of exercise and diet, with contraindications to metformin or with its intolerance due to renal failure;
Two-component combination treatment with metformin, thiazolidine or sulfonylurea derivatives in case of insufficient effectiveness of exercise, diet therapy and monotherapy with these drugs;
Three-component combination therapy with sulfonylurea derivatives and metformin in case of ineffectiveness of physical exercise, diet therapy and combination treatment with these drugs.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Trajenta is an inhibitor of the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4), which is involved in the inactivation of the incretin hormones glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide type 1 (GLP-1). These hormones are destroyed by the enzyme DPP-4. Incretins maintain glucose concentrations at the required physiological level.
During the day, basal concentrations of GIP and GLP-1 are at low levels, which quickly increase in response to food intake.
Hormones activate the biosynthesis of insulin and its production by beta cells of the pancreas under conditions of normal or high blood glucose concentrations. GLP-1 reduces the production of glucagon by the alpha cells of the pancreas, resulting in decreased glucose production in the liver.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Tragenta is contraindicated in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus or for the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis.
The incidence of hypoglycemia when linagliptin was used as monotherapy was comparable to placebo.
In clinical studies, it was reported that the incidence of hypoglycemia when linagliptin was used in combination with drugs that are not considered to cause hypoglycemia (metformin, thiazolidinedione derivatives) was similar to the corresponding effect of placebo.
Sulfonylureas are known to cause hypoglycemia. Therefore, when using linagliptin in combination with sulfonylurea derivatives, caution should be exercised. If necessary, it is possible to reduce the dose of sulfonylurea derivatives.
No specific clinical studies have been conducted on the use of linagliptin in combination with insulin.
The use of linagliptin does not increase the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.
Linagliptin in combination therapy with other oral hypoglycemic drugs has been used in patients with severe renal failure.
Linagliptin provided a significant reduction in glycosylated hemoglobin concentrations and fasting glucose concentrations.
No dose adjustment is required when used in patients with impaired renal function, liver function or in elderly patients.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery
No studies have been conducted on the effect of Tragenta on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery. However, due to the possible development of dizziness, caution must be exercised when operating vehicles and machinery.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Linagliptin
Composition
Composition
1 tablet contains:
Active ingredient:
linagliptin 5 mg;
Excipients:
mannitol – 130.9 mg,
pregelatinized starch – 18 mg,
corn starch – 18 mg,
copovidone – 5.4 mg,
magnesium stearate – 2.7 mg;
Shell composition:
opadry pink (02F34337) – 5 mg (hypromellose 2910 – 2.5 mg, titanium dioxide (E171) – 1.25 mg, talc – 875 mcg, macrogol 6000 – 250 mcg, iron dye red oxide (E172) – 125 mcg).
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
The use of linagliptin during pregnancy and breastfeeding is contraindicated.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Individual intolerance to Trajent components, type 1 diabetes mellitus, diabetic ketoacidosis
Side Effects
Side Effects
The following side effects were observed with linagliptin monotherapy:
From the immune system: hypersensitivity reactions.
From the respiratory system: cough.
From the digestive system: pancreatitis.
Infectious diseases: nasopharyngitis.
When using linagliptin with metformin:
From the immune system: hypersensitivity reactions.
From the respiratory system: cough.
From the digestive system: pancreatitis.
Infectious diseases: nasopharyngitis.
When using linagliptin with sulfonylurea derivatives:
From the immune system: hypersensitivity reactions.
Metabolic disorders: hypertriglyceridemia.
From the respiratory system: cough.
From the digestive system: pancreatitis.
Infectious diseases: nasopharyngitis.
When using linagliptin with pioglitazone:
From the immune system: hypersensitivity reactions.
Metabolic disorders: hyperlipidemia.
From the respiratory system: cough.
From the digestive system: pancreatitis.
Infectious diseases: nasopharyngitis.
Other: weight gain.
When using linagliptin with insulin:
From the immune system: hypersensitivity reactions.
From the respiratory system: cough.
From the digestive system: pancreatitis, constipation.
Infectious diseases: nasopharyngitis.
When using linagliptin with metformin and sulfonylureas:
From the immune system: hypersensitivity.
Metabolic disorders: hypoglycemia.
From the respiratory system: cough.
From the digestive system: pancreatitis.
Infectious diseases: nasopharyngitis.
When using linagliptin with metformin and pioglitazone:
From the immune system: hypersensitivity reactions.
Metabolic disorders: hyperlipidemia.
From the respiratory system: cough.
From the digestive system: pancreatitis.
Infectious diseases: nasopharyngitis.
Other: weight gain.
Post-marketing experience:
From the immune system: angioedema, urticaria.
From the digestive system: acute pancreatitis.
From the skin: rash.
Interaction
Interaction
In vitro assessment of drug interactions
Linagliptin is a weak competitive inhibitor of the CYP3A4 isoenzyme.
Linagliptin does not inhibit other CYP isoenzymes and is not an inducer.
Linagliptin is a substrate for P-glycoprotein and inhibits to a small extent P-glycoprotein-mediated transport of digoxin.
In vivo assessment of drug interactions
Linagliptin does not have a clinically significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of metformin, glibenclamide, simvastatin, pioglitazone, warfarin, digoxin and oral contraceptives, which has been proven in vivo, and is based on the low ability of linagliptin to lead to drug interactions with substrates for CYP3A4, CYP2C9, CYP2C8, P-glycoprotein and organic transport molecules cations.
Metformin. Combined use of metformin (multiple daily doses of 850 mg 3 times a day) and linagliptin at a dose of 10 mg 1 time a day. (above the therapeutic dose) in healthy volunteers did not lead to clinically significant changes in the pharmacokinetics of linagliptin or metformin. Thus, linagliptin is not an inhibitor of organic cation transport.
Sulfonylurea derivatives. The pharmacokinetics of linagliptin (5 mg) did not change when combined with glibenclamide (single dose of glyburide 1.75 mg) and repeated oral administration of linagliptin (5 mg each). However, there was a clinically insignificant decrease in the AUC and Cmax values of glibenclamide by 14%. Because glibenclamide is metabolized primarily by CYP2C9, these data also support the conclusion that linagliptin is not a CYP2C9 inhibitor. Clinically significant interactions are not expected with other sulfonylureas (for example, glipizide and glimepiride), which, like glibenclamide, are mainly metabolized by CYP2C9.
Thiazolidinediones. Combined use of several doses of linagliptin 10 mg/day. (above the therapeutic dose) and pioglitazone 45 mg/day. (multiple doses), which is a substrate for CYP2C8 and CYP3A4, did not have a clinically significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of linagliptin or pioglitazone, or the active metabolites of pioglitazone. This indicates that linagliptin in vivo is not an inhibitor of CYP2C8-mediated metabolism and supports the conclusion that linagliptin does not have a significant inhibitory effect on CYP3A4 in vivo.
Ritonavir. Co-administration of linagliptin (single dose 5 mg orally) and ritonavir (multiple doses of 200 mg orally), an active inhibitor of P-glycoprotein and the CYP3A4 isoenzyme, increased the AUC and Cmax values of linagliptin by approximately 2-fold and 3-fold, respectively. However, these changes in linagliptin pharmacokinetics were not considered significant. Therefore, clinically significant interactions with other P-gp and CYP3A4 inhibitors are not expected and no dose adjustment is required.
Rifampicin. Repeated co-administration of linagliptin and rifampicin, an active inducer of P-glycoprotein and the CYP3A4 isoenzyme, led to a decrease in the AUC and Cmax values of linagliptin by 39.6% and 43.8%, respectively, and to a decrease in the inhibition of basal dipeptidyl peptidase-4 activity by approximately 30%. Thus, the clinical efficacy of linagliptin when used in combination with active P-glycoprotein inducers is expected to be maintained, although it may not be fully realized.
Digoxin. Combined repeated use of linagliptin (5 mg/day) and digoxin (0.25 mg/day) in healthy volunteers did not affect the pharmacokinetics of digoxin. Thus, linagliptin is not an inhibitor of P-glycoprotein-mediated transport in vivo.
Warfarin. Linagliptin, administered repeatedly at a dose of 5 mg/day, did not change the pharmacokinetics of warfarin, which is a substrate for CYP2C9, indicating that linagliptin does not have the ability to inhibit CYP2C9.
Simvastatin. Linagliptin was used repeatedly in healthy volunteers at a dose of 10 mg/day. (above the therapeutic dose), had a minimal effect on the pharmacokinetic parameters of simvastatin, which is a sensitive substrate for CYP3A4. After taking linagliptin at a dose of 10 mg together with simvastatin, used at a daily dose of 40 mg for 6 days, the AUC value of simvastatin increased by 34% and the Cmax value by 10%. Thus, linagliptin is a weak inhibitor of CYP3A4-mediated metabolism. Dose changes when taken concomitantly with drugs that are metabolized by CYP3A4 are considered inappropriate.
Oral contraceptives. Co-administration of linagliptin at a dose of 5 mg with levonorgestrel or ethinyl estradiol did not change the pharmacokinetics of these drugs.
Overdose
Overdose
During controlled clinical studies in healthy volunteers, a single dose of linagliptin 600 mg (120 times the recommended dose) was well tolerated.
There is no experience with the use of linagliptin in doses exceeding 600 mg.
In case of overdose, it is recommended to use usual supportive measures, for example, removal of unabsorbed Trajenta from the gastrointestinal tract, clinical monitoring and symptomatic treatment.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
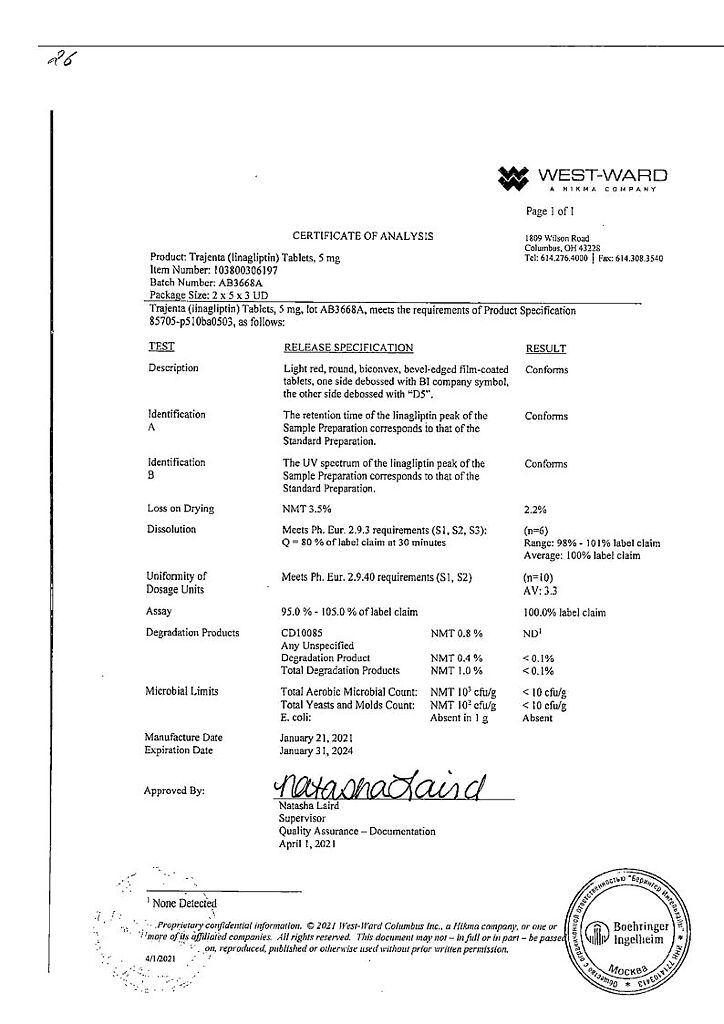
At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
West Word Columbus Inc., USA
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C |
| Manufacturer | West Ward Columbus Inc. |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | #Н/Д |
Related products
Buy Trajenta, 5 mg 30 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.