No products in the cart.
Thiamine, 50 µg/ml 1 ml 10 pcs
€1.32 €1.00
Description
Thiamine influences the conduction of nerve excitation in synapses, has ganglioblocking and curare-like properties. It is of great importance for the function of the nervous system, the digestive system, cardiac activity, and the endocrine system.
The source of thiamine for humans is food. In the absence or insufficient intake with food or with various conditions that prevent its absorption and assimilation, a person develops symptoms of hypo- and avitaminosis B1.
B1 avitaminosis, called beri- beri, runs either with paralysis and exhaustion or with heart damage and edema.
Form of release
Form of release
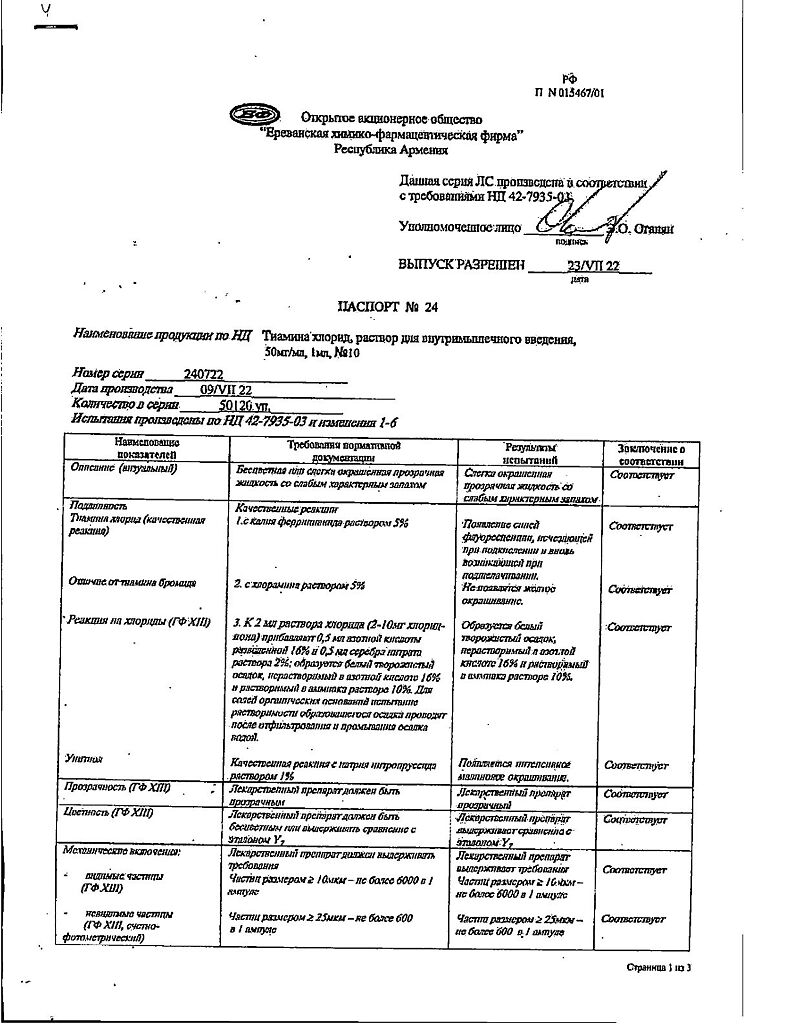
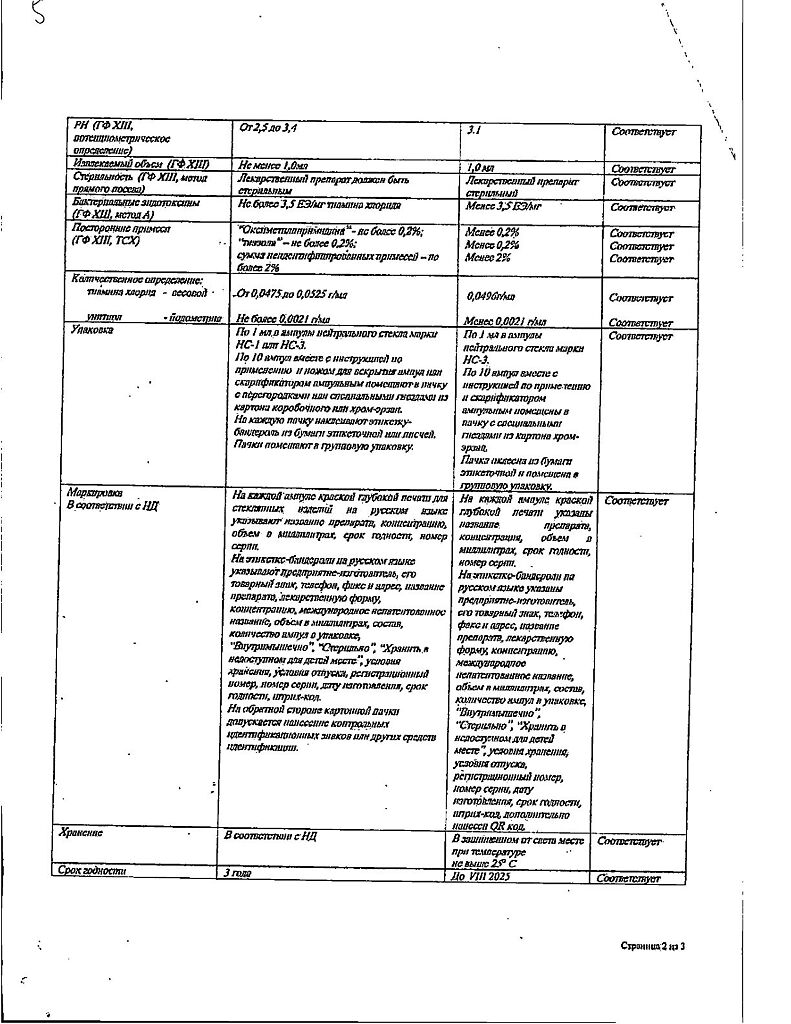
Solution for injection
Additional information
| Conditions of storage | Store in a dry place at a temperature not exceeding 25°C, out of the reach of children. |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Yerevan CFF, Armenia |
| Medication form | solution |
| Brand | Yerevan CFF |
Other forms…
Buy Thiamine, 50 µg/ml 1 ml 10 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.