No products in the cart.
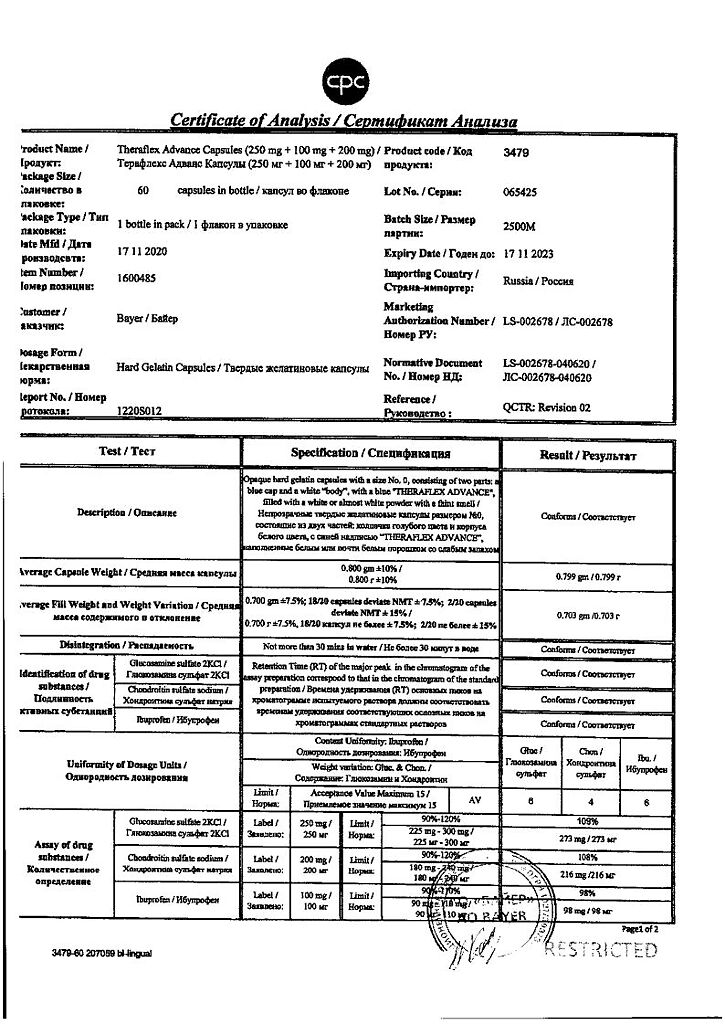
Theraflex Advance, 250 mg+100 mg+200 mg capsules 60 pcs
€52.19 €43.49
Description
Tereflex Advans – stimulates the regeneration of cartilage tissue, analgesic, anti-inflammatory.
Pharmacodynamics
Tereflex Advance is a combination drug that contains chondroitin sulfate, glucosamine sulfate and ibuprofen as the active ingredients.
Chondroitin sulfate is involved in the construction and repair of cartilage tissue, protects it from breakage and improves joint mobility.
Glucosamine sulfate activates the synthesis of proteoglycans, hyaluronic and chondroitin acids and other substances that make up the joint membranes, intra-articular fluid and cartilage tissue.
Ibuprofen is a derivative of propionic acid and has analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effect due to non-selective blockade of COX-1 and COX-2.
The glucosamine sulfate and chondroitin sulfate contained in the drug potentiate the analgesic effect of ibuprofen.
Pharmacokinetics
The bioavailability of glucosamine when taken orally is 25% (first-pass effect through the liver), the highest concentrations are found in the liver, kidney and joint cartilage. About 30% of the dose taken persists in bone and muscle tissue for a long time. It is excreted mainly with urine unchanged, partially with feces. T1/2 is 68 hours.
More than 70% of chondroitin sulfate is absorbed in the digestive tract. Bioavailability is about 13%. When a single oral administration of an average therapeutic dose, Cmax in plasma is observed after 3-4 hours, in the synovial fluid – after 4-5 hours. Absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, the drug accumulates in synovial fluid. It is excreted by the kidneys.
Ibuprofen is well absorbed from the stomach. Tmax is about 1 h. Ibuprofen is approximately 99% bound to plasma proteins. It is slowly distributed in synovial fluid and excreted more slowly than from plasma. Ibuprofen is metabolized in the liver mainly by hydroxylation and carboxylation of the isobutyl group.
The CYP2C9 isoenzyme is involved in metabolism of the drug. After absorption about 60% of pharmacologically inactive R-form of ibuprofen is slowly transformed into active S-form. Ibuprofen has biphasic elimination kinetics. T1/2 from plasma is 2-3 hours. Up to 90% of the dose can be detected in the urine as metabolites and their conjugates. Less than 1% is excreted unchanged in the urine and to a lesser extent in the bile. Ibuprofen is completely eliminated in 24 hours.
Indications
Indications
Osteoarthritis of large joints; spinal osteochondrosis accompanied by moderate pain syndrome.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
1 capsule contains:
Active substances:
glucosamine sulfate – 250 mg;
chondroitin sulfate sodium – 200 mg;
Ibuprofen – 100 mg;
Associates:
MCC, 30.78 mg;
Corn starch, 19.69 mg;
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Ingestion with a small amount of water.
Adults: 2 capsules 3 times a day after meals.
The duration of treatment without medical advice should not exceed 3 weeks.
Continue use should be coordinated with the physician.
Interaction
Interaction
Microsomal oxidation inducers (phenytoin, ethanol, barbiturates, rifampicin, phenylbutazone, tricyclic antidepressants) increase the production of hydroxylated active metabolites of ibuprofen, increasing the risk of severe hepatotoxic reactions.
Microsomal oxidation inhibitors reduce the risk of hepatotoxic effects.
Decreases hypotensive activity of vasodilators (including BCC and ACE inhibitors), natriuretic and diuretic activity of furosemide and hydrochlorothiazide.
Decreases the effectiveness of uricosuric drugs, increases the effect of indirect anticoagulants, antiaggregants, fibrinolytics (increased risk of hemorrhagic complications), ulcerogenic effect with bleeding of GCS, NSAIDs, colchicine, estrogen, ethanol, increases the effect of oral hypoglycemic drugs and insulin.
Antacids and colestiramine decrease absorption of ibuprofen.
Enhances blood concentrations of digoxin, lithium drugs and methotrexate.
Caffeine increases the analgesic effect.
When simultaneously prescribed, ibuprofen decreases anti-inflammatory and antiplatelet effects of acetylsalicylic acid (the incidence of acute coronary failure may increase in patients receiving low doses of acetylsalicylic acid as an antiplatelet agent after starting ibuprofen).
When administered simultaneously with anticoagulant and thrombolytic drugs (alteplase, streptokinase, urokinase) the risk of bleeding increases.
Cefamandole, cefoperazone, cefotetan, valproic acid, plikamycin increase the frequency of hypoprothrombinemia.
Myelotoxic drugs increase manifestations of hematotoxicity.
Cyclosporine and gold drugs increase the effect of ibuprofen on PG synthesis in the kidneys, which is manifested by increased nephrotoxicity.
Ibuprofen increases the plasma concentration of cyclosporine and the likelihood of its hepatotoxic effects.
Like drugs that block tubular secretion decrease excretion and increase the plasma concentration of ibuprofen.
The drug’s glucosamine may decrease the effectiveness of hypoglycemic agents, doxorubicin, teniposide, etoposide.
Glucosamine increases absorption of tetracyclines and reduces the effect of semi-synthetic penicillins and chloramphenicol.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
During long-term treatment it is necessary to monitor peripheral blood picture and functional state of the liver and kidneys.
In case of symptoms of gastropathy, close monitoring is indicated, including esophagogastroduodenoscopy, blood tests with determination of hemoglobin, hematocrit, stool analysis for occult blood.
If simultaneous use of additional NSAIDs and analgesic agents is necessary, the physician should consider the presence of ibuprofen in the drug. If prolonged use of additional NSAIDs is necessary, the drug Teraflex without ibuprofen should be used.
If it is necessary to determine 17-ketosteroids, the drug should be discontinued 48 hours before the study.
The intake of alcohol is not recommended during treatment.
Impact on ability to drive vehicles and other mechanisms requiring increased concentration
Patients should refrain from activities requiring increased attention, rapid mental and motor reactions.
Synopsis
Synopsis
Contraindications
Contraindications
Side effects
Side effects
When using the drug Teraflex Advance nausea, abdominal pain, flatulence, diarrhea, constipation, allergic reactions are possible. These reactions disappear after discontinuation of the drug.
Possible adverse reactions associated with ibuprofen present in the drug should be considered. When ibuprofen preparations are used in higher doses than those contained in Teraflex Advance, the following adverse reactions may occur.
Gastrointestinal disorders: NSAID gastropathy (abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, heartburn, decreased appetite, diarrhea, flatulence, constipation; rarely – ulceration of the GI mucosa, which in some cases is complicated by perforation and bleeding); irritation or dryness of the oral mucosa, pain in the mouth, ulceration of the gum mucosa, aphthous stomatitis, pancreatitis.
Hepatobiliary system: hepatitis.
Respiratory system: shortness of breath, bronchospasm.
Senses: hearing disorders (decreased hearing, ringing or tinnitus), vision disorders (toxic optic nerve damage, blurred vision or double vision, scotoma, dry and irritated eyes, edema of conjunctiva and eyelids of allergic origin).
CNS and peripheral nervous system disorders: headache, dizziness, insomnia, anxiety, nervousness and irritability, psychomotor agitation, drowsiness, depression, confusion, hallucinations; aseptic meningitis is rare (more often in patients with autoimmune diseases).
Systemic diseases: heart failure, tachycardia, increased BP.
Urinary system disorders: acute renal failure, allergic nephritis, nephrotic syndrome (edema), polyuria, cystitis.
Allergic reactions: skin rash (usually erythematous or urticaria), skin itching, Quincke’s edema, anaphylactoid reactions, anaphylactoid shock, bronchospasm or dyspnea, fever, erythema multiforme exudative (including Stevens-John syndrome).Stevens-Johnson syndrome), toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell’s syndrome), eosinophilia, allergic rhinitis.
Hematopoietic disorders: anemia (including hemolytic, aplastic), thrombocytopenia and thrombocytopenic purpura, agranulocytosis, leukopenia.
Laboratory parameters: bleeding time may increase, serum glucose concentration may decrease, creatinine clearance may decrease; hematocrit or hemoglobin may decrease; serum creatinine concentration may increase; hepatic transaminase activity may increase.
Pregnancy use
Pregnancy use
It is contraindicated in pregnancy and lactation.
Additional information
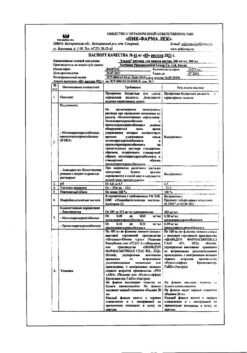
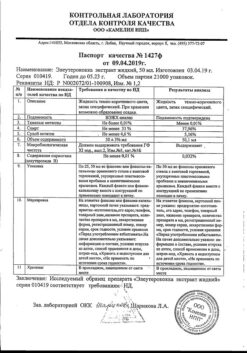
| Weight | 0.090 kg |
|---|---|
| Shelf life | 2 years. |
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. |
| Manufacturer | Contract Pharmacal Corporation, USA |
| Medication form | capsules |
| Brand | Contract Pharmacal Corporation |
Related products
Buy Theraflex Advance, 250 mg+100 mg+200 mg capsules 60 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.