No products in the cart.
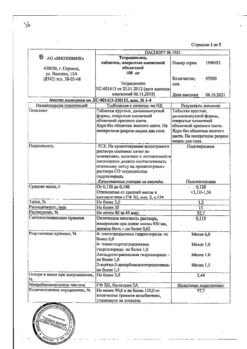
Tetracycline, 100 mg 20 pcs.
€6.31 €5.52
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Antibiotic, tetracycline
ATCode
J01AA07
Pharmacodynamics:
Bacteriostatic antibiotic from the tetracycline group. It disrupts formation of the complex between transporter RNA and ribosome which leads to suppression of protein synthesis.
Active against Gram-positive microorganisms – Staphylococcus spp. (including Staphylococcus aureus including penicillinase producing strains) Streptococcus spp. (some strains ‘including Streptococcus pneumoniae) Listeria monocytogenes Bacillus anthracis Clostridium spp. Actinomyces spp. Propionibacterium acnes Bacillus fusifonnis;
– Gram-negative microorganisms – Haemophilus influenzae Haemophilus ducreyi Bordetella pertussis Escherichia coli Enterobacter spp. (including Enterobacter aerogenes) Klebsiella spp. Neisseria gonorrhoeae Shigella spp. Yersinia pestis Bartonella bacilliformis Vibrio cholerae Vibrio fetus Rickettsia prawazekii-Rickettsia reckettsn Rickettsia akari Borrelia Vinceni Borrelia “recurrentis Borrelia burgdorferi Brucella spp. (in combination with streptomycin); Calymmatobacterium granulomatis’ Francisella tularensis Treponema pallidum Treponema pertenue;
– when contraindicated for the administration of penicillins – Clostridiumspp. Neisseria gonorrhoeae Actinomyces spp.;
– active against Chlamydia trachomatis; Chlamydia psittaci Entamoeba histolytica;
– microorganisms resistant to tetracycline: Pseudomonas aeruginosa Proteus spp.
– Serratia spp. most strains of Bacteroides. spp. and beta-haemolytic viruses fungi; Streptococcus groupA (including 44% of Streptococcus pyogenes strains and 74% of Streptococcus faecalis strains). Pharmacokinetics:
Absorption – 75-77% when ingested decreases binding to plasma proteins – 55-65%.
The time to reach maximum concentration when taken orally is 2-3 h (it may take 2-3 days to reach therapeutic concentration). Over the next 8 hours the concentration gradually decreases. Maximum concentration is 15 g. 35 mg/l (a concentration of 1mg/l is sufficient to achieve therapeutic effect).
In the body it is distributed unevenly: the maximum concentration is contained in the liver kidneys lungs and in organs with a well developed reticuloendothelial system – spleen lymph nodes. The concentration in bile is 5-10 times higher than in blood serum. In thyroid and prostate tissues tetracycline content is the same as in plasma; in pleural ascitic fluid saliva milk of lactating women – 60-100% concentration in plasma. In large amounts it accumulates in bone tissue tumor tissues in dentin and enamel of milk teeth. It penetrates poorly through the blood-brain barrier. In intact cerebral membranes in the cerebrospinal fluid is not determined or detected in insignificant amounts (5-10% of the concentration in plasma). In patients with diseases of the central nervous system, especially with inflammatory processes in the brain membranes, the concentration in the cerebrospinal fluid is 8-36% of the plasma concentration. It penetrates through the placental barrier and into the breast milk. The volume of distribution is 13-16 l/kg.
It is slightly metabolized in the liver. Elimination half-life is 6-11 hours with anuria 57-108 hours. It is found in high concentration in urine within 2 hours after intake and is maintained for 6-12 hours; during the first 12 hours up to 10-20% of dose is excreted by kidneys. Smaller amount (5-10% of total dose) is excreted with bile in intestine where partial reverse absorption occurs, which promotes prolonged circulation of active substance in organism (intestine-hepatic circulation).
The intestinal excretion is 20-50%. With hemodialysis it is removed slowly.
Indications
Indications
Infectious and inflammatory diseases caused by microorganisms sensitive to tetracycline: pneumonia and respiratory tract infections caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae respiratory tract infections caused by Haemophilus influenzae and Klebsiella spp. bacterial infections of the genitourinary organs infections of the skin and soft tissues ulcerative-necrotic gingivostomatitis conjunctivitis acne actinomycosis intestinal amebiasis anthrax brucellosis bartonellosis chancroid-cholera chlamydia uncomplicated gonorrhea inguinal granuloma. venereal lymphogranuloma listeriosis plague psittacosis vesicular rickettsiosis Rocky Mountain spotted fever typhus relapsing fever syphilis trachoma tularemia yaws botulism tetanus gas gangrene food poisoning whooping cough dysentery vibriosis Lyme disease.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group
antibiotic, tetracycline
ATX code
J01AA07
Pharmacodynamics:
Bacteriostatic antibiotic from the tetracycline group. It disrupts the formation of a complex between transport RNA and the ribosome, which leads to suppression of protein synthesis.
Active against gram-positive microorganisms – Staphylococcus spp. (including Staphylococcus aureus including penicillinase-producing strains) Streptococcus spp. (some strains including Streptococcus pneumoniae) Listeria monocytogenes Bacillus anthracis Clostridium spp. Actinomyces spp. Propionibacterium acnes Bacillus fusifonnis;
– gram-negative microorganisms – Haemophilus influenzae Haemophilus ducreyi Bordetella pertussis Escherichia coli Enterobacter spp. (including Enterobacter aerogenes) Klebsiella spp. Neisseria gonorrhoeae Shigella spp. Yersinia pestis Bartonella bacilliformis Vibrio cholerae Vibrio fetus Rickettsia prawazekii-Rickettsia reckettsn Rickettsia akari Borrelia Vinceni Borrelia “recurrentis Borrelia burgdorferi Brucella spp. (in combination with streptomycin); Calymmatobacterium granulomatis’ Francisella tularensis Treponema pallidum Treponema pertenue;
– in case of contraindications to the prescription of penicillins – Clostridium spp. Neisseria gonorrhoeae Actinomyces spp.;
– active against Chlamydia trachomatis; Chlamydia psittaci Entamoeba histolytica;
– microorganisms resistant to tetracycline: Pseudomonas aeruginosa Proteus spp.
Serratia spp. most Bacteroides strains. spp. and fungal viruses beta-hemolytic; Group A streptococci (including 44% of Streptococcus pyogenes strains and 74% of Streptococcus faecalis strains).
Pharmacokinetics:
Absorption – 75-77%; when eating, the connection with plasma proteins decreases – 55-65%.
The time to reach maximum concentration after oral administration is 2-3 hours (2-3 days may be required to achieve therapeutic concentrations). Over the next 8 hours, the concentration gradually decreases. The maximum concentration is 15 g. 35 mg/l (a concentration of 1 mg/l is sufficient to achieve a therapeutic effect).
It is distributed unevenly in the body: in maximum concentration it is found in the liver, kidneys, lungs and in organs with a well-developed reticuloendothelial system – the spleen and lymph nodes. The concentration in bile is 5-10 times higher than in blood serum. In the tissues of the thyroid and prostate glands, the content of tetracycline is the same as in plasma; in pleural ascitic fluid, saliva, and milk of lactating women – 60-100% of the concentration in plasma. It accumulates in large quantities in bone tissue, tumor tissues in dentin and enamel of baby teeth. Penetrates poorly through the blood-brain barrier. With intact meninges, it is not detected in the cerebrospinal fluid or is detected in small quantities (5-10% of the plasma concentration). In patients with diseases of the central nervous system, especially with inflammatory processes in the membranes of the brain, the concentration in the cerebrospinal fluid is 8-36% of the concentration in the plasma. Penetrates through the placental barrier and into breast milk. Volume of distribution -13-16 l/kg.
Slightly metabolized in the liver. The half-life is 6-11 hours with anuria – 57-108 hours. It is found in urine in high concentration 2 hours after administration and persists for 6-12 hours; in the first 12 hours, up to 10-20% of the dose is excreted by the kidneys. In smaller quantities (5-10% of the total dose) it is excreted with bile into the intestine where partial reabsorption occurs, which promotes long-term circulation of the active substance in the body (enterohepatic circulation).
Excretion through the intestines is 20-50%. During hemodialysis it is removed slowly.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Due to the possible development of photosensitivity, it is necessary to limit insolation.
With long-term use, periodic monitoring of the function of the kidneys, liver and hematopoietic organs is necessary.
It can mask the manifestations of syphilis, and therefore, if a mixed infection is possible, monthly serological analysis is necessary for 4 months.
All tetracyclines form stable complexes with calcium in any bone-forming tissue. In this regard, taking it during the period of tooth development can cause long-term staining of the teeth in a yellow-gray-brown color, as well as enamel hypoplasia.
To prevent hypovitaminosis, vitamins B and K should be prescribed brewer’s YEAST.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles. Wed and fur.:
During the treatment period, it is necessary to refrain from driving vehicles and engaging in potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Tetracycline
Composition
Composition
1 tablet contains:
Active substance: Tetracycline hydrochloride in terms of active substance – 100 mg.
Excipients: sucrose (refined sugar) – 7.1 mg, calcium stearate monohydrate – 1.26 mg, magnesium hydrosilicate (talc) – 1.26 mg, gelatin – 0.54 mg, potato starch – 15.84 mg.
Film shell: hypromellose (hydroxypropyl methylcellulose) – 1.332 mg, liquid paraffin (vaseline oil) – 0.25 mg, polysorbate-80 (Tween-80) – 0.388 mg, azoru bin dye (acid red 2 C) – 0.03 mg.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Contraindicated during pregnancy (tetracyclines pass through the placenta and accumulate in the bones and dental buds of the fetus, disrupting their mineralization and can cause severe disturbances in the development of bone tissue).
FDA category of effect on the fetus is D.
During treatment, it is necessary to stop breastfeeding (tetracyclines pass into breast milk and can adversely affect the development of the child’s bones and teeth and also cause photosensitivity reactions to oral and vaginal candidiasis in infants).
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to tetracycline and components of the drug pregnancy breastfeeding period children’s age (up to 8 years) leukopenia sucrase/isomaltase deficiency fructose intolerance glucose-galactose malabsorption renal failure liver dysfunction.
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the digestive system: loss of appetite vomiting diarrhea nausea glossitis esophagitis gastritis ulceration of the stomach and duodenum hypertrophy of the papillae of the tongue dysphagia hepatotoxic effect pancreatitis intestinal dysbiosis enterocolitis increased activity of “liver” transaminases antibiotic-associated diarrhea.
From the central nervous system: increased intracranial pressure, headache, toxic effect on the central nervous system (dizziness or instability).
From the hematopoietic organs: hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, eosinophilia.
From the urinary system, azotemia, hypercreatininemia, nephrotoxic effect.
Allergic and immunopathological reactions: maculopapular rash; skin hyperemia angioedema anaphylactoid reactions drug systemic lupus erythematosus photosensitivity.
Other: superinfection candidiasis hypovitaminosis of B vitamins hyperbilirubinemia discoloration of tooth enamel in children stomatitis.
Interaction
Interaction
Due to the suppression of intestinal microflora, it reduces the prothrombin index (requires a reduction in the dose of indirect anticoagulants).
Reduces the effectiveness of bactericidal antibiotics that disrupt cell wall synthesis (penicillins, cephalosporins).
Reduces the effectiveness of estrogen-containing oral contraceptives and increases the risk of breakthrough bleeding; retinol – risk of developing increased intracranial pressure.
Absorption is reduced by antacids containing aluminum; magnesium and calcium, iron preparations and cholestyramine.
Chymotrypsin increases the concentration and duration of circulation.
Overdose
Overdose
In case of an overdose of the drug, the above-described side effects may increase.
Treatment is symptomatic.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a dry place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years. Do not use after the expiration date indicated on the package.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Ozon, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years. Do not use after the expiration date stated on the package. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry place at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. Store out of the reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Ozon, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Ozon |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Tetracycline, 100 mg 20 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.