No products in the cart.
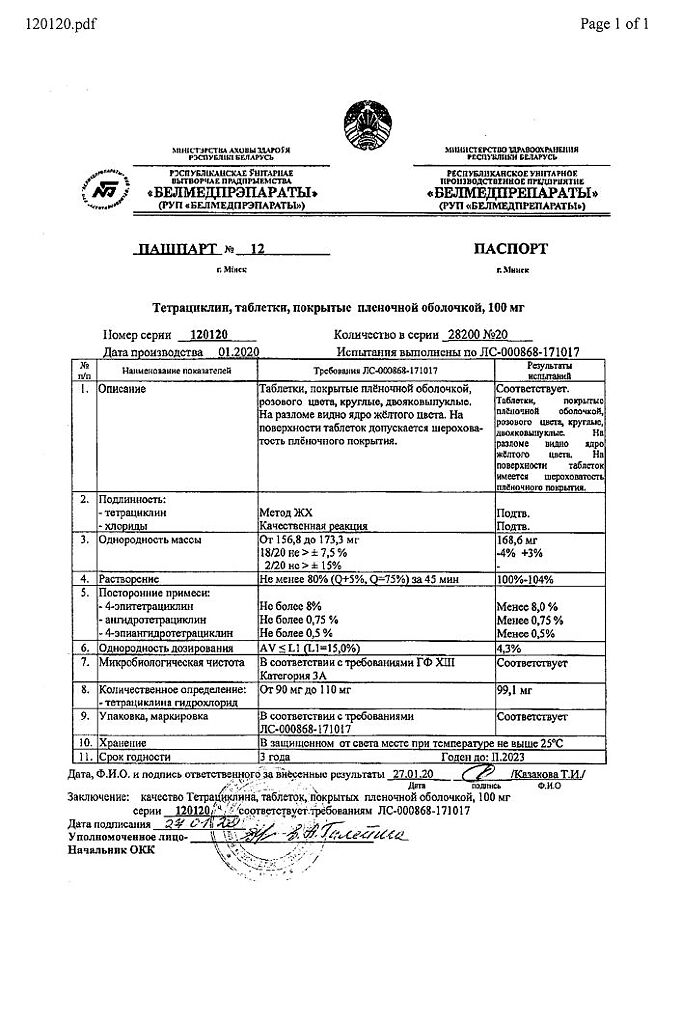
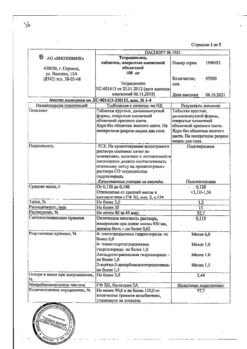
Tetracycline, 100 mg 20 pcs.
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Tetracycline is active against Gram-positive microorganisms: Staphylococcus spp. (including Staphylococcus aureus, including penicillinase-producing strains), Streptococcus pneumoniae, Listeria spp, Bacillus anthracis, Clostridium spp., Actinomyces israelii; Gram-negative microorganisms: Haemophilus influenzae, Haemophilus ducreyi, Bordetella pertussis, Escherichia coli, Enterobacter spp. (including Enterobacter aerogenes), Acinetobacter spp, Klebsiella spp., Salmonella spp., Shigella spp., Yersinia pestis, Francisella tularensis, Bartonella bacilliformis, Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio fetus, Rickettsia spp., Borrelia burgdorferi, Brucella spp. (in combination with streptomycin); when contraindicated to use penicillins – Clostridium spp, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Actinomyces spp.; also active against Calymmatobacterium granulomatis, Chlamydia trachomatis, Chlamydia psittaci, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Treponema spp. Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus spp., Serratia spp., most strains of Bacteroides spp. and fungi, viruses, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus faecalis are resistant to tetracycline.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption – 75-77%, the binding to plasma proteins – 55-65%, decreased with food. Time to reach maximum plasma concentration (TCmax) when administered orally is 2-3 hours (it may take 2-3 days to reach therapeutic concentration). During the next 8 hours, the concentration gradually decreases. Maximum drug concentration in plasma is 1.5-3.5 mg/l (a concentration of 1 mg/l is sufficient to achieve therapeutic effect).
In the body it is distributed unevenly: the maximum drug concentration is determined in the liver, kidneys, lungs and in organs with well developed reticulo-endothelial system – spleen, lymph nodes. The concentration in bile is 5-10 times higher than in blood serum. In thyroid and prostate tissues tetracycline concentration corresponds to that found in plasma; in pleural, ascitic fluid, saliva, milk of lactating women – 60-100% concentration in plasma. In large amounts it is accumulated in bone tissue, tumor tissues, dentin and enamel of milk teeth.
It penetrates poorly through the blood-brain barrier. With intact cerebral membranes in cerebrospinal fluid it is not determined or detected in insignificant amounts (5-10% of the concentration in plasma). In patients with diseases of the central nervous system, especially in inflammatory processes in the brain membranes, the concentration in cerebrospinal fluid is 8-36% of the plasma concentration. It penetrates through the placental barrier and into breast milk. Volume of distribution is 1.3-1.6 l/kg.
It is slightly metabolized in the liver. The half-life of the drug (T1/2) is 6-11 hours, with anuria 57-108 hours. In urine it is found in high concentration 2 hours after the drug intake and retained for 6-12 hours; during the first 12 hours up to 10-20% of dose is excreted by kidneys.
In smaller amounts (5-10% of the total dose) it is excreted with bile in the intestine, where there is partial reverse absorption, which promotes prolonged circulation of the active substance in the body (intestine-hepatic circulation). Excretion through the intestine is 20-50%. With hemodialysis it is removed slowly.
Indications
Indications
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
Active substance:
Tetracycline hydrochloride – 0.1 g.
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Ingestion with plenty of fluid.
Adults – 0.3 – 0.5 g every 6 hours (4 times a day) or 0.5-1 g every 12 hours (2 times a day). The maximum daily dose is 4 g. The course of treatment is 5-10 days.
In children over 8 years of age – 6.25 to 12.5 mg/kg every 6 hours or 12.5 to 25 mg/kg every 12 hours.
In acne: 0.5 to 2 g/day in divided doses. If condition improves (usually after 3 weeks), the dose is gradually reduced to a maintenance dose of 0.1 to 1 g. Adequate remission of acne can be achieved by using the drug every other day or by intermittent therapy.
Brucellosis – 0.5 g every 6 hours for 3 weeks, simultaneously with intramuscular administration of streptomycin at a dose of 1 g every 12 hours for 1 week and once daily for 2 weeks.
Uncomplicated gonorrhea – initial single dose of 1.5 g, then 0.5 g every 6 hours for 4 days (total dose of 9 g).
Syphilis – 0.5 g every 6 hours for 15 days (early syphilis) or 30 days (late syphilis).
Uncomplicated urethral, endocervical and rectal infections caused by Chlamydia trachomatis – 0.5 g every 6 hours for at least 7 days.
Lyme disease (early stage only) – 1.0 to 1.5 g daily for 10 to 14 days.
Listeriosis – 0.2 – 0.3 g every 6 hours for 7 – 10 days.
Actinomycosis – 3 g daily for the first 10 days, then 0.5 g every 6 hours for the last 18 days.
Chlamydia – 1.5 to 2 g per day for 10 days (“fresh” forms) and 15 to 20 days (chronic, complicated forms).
In inguinal granuloma, venereal lymphogranuloma – 0.5 g every 6 hours for 3 – 4 weeks.
Psittacosis – 0.5 g every 6 hours (relief and disappearance of symptoms occurs after 24 to 48 hours). Treatment is continued for 7-14 days after normalization of body temperature in order to prevent relapse.
Vesicular rickettsiosis – 0.8 – 1.2 g per day for 8 – 10 days.
Tularemia – 1.5 – 2 g per day. After normalization of temperature the treatment is continued for 5-7 days more.
Frambiesia – 0.5 g every 6 hours for 14 days.
Pestilence – up to 6 g per day. If the condition improves, the dose is reduced to 2 g per day until the temperature normalizes, but for at least 3 days. Contact persons should be given a course of 0.3 g every 6 hours.
Interaction
Interaction
Due to the suppression of intestinal microflora, reduces the prothrombin index (requires reducing the dose of indirect anticoagulants).
Decreases the effectiveness of bactericidal antibiotics that disrupt cell wall synthesis (penicillins, cephalosporins).
Decreases the effectiveness of estrogen-containing oral contraceptives and increases the risk of breakthrough bleeding; retinol – the risk of developing increased intracranial pressure.
Absorption is reduced by antacids containing aluminum, magnesium and calcium, iron preparations and colestyramine.
Chymotrypsin increases concentration and duration of circulation.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
Possible development of photosensitization requires limitation of insolation.
Long-term use requires periodic monitoring of renal, hepatic and hematopoietic function.
May mask the manifestations of syphilis; therefore, if there is a possibility of mixed infection, serological testing should be performed monthly for 4 months.
All tetracyclines form persistent complexes with calcium ions in any bone-forming tissue. Because of this, taking it during the period of tooth development can cause long-term yellow-gray-brown staining of teeth, as well as enamel hypoplasia.
B and K vitamins and brewer’s yeast should be prescribed to prevent hypovitaminosis.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles or potentially dangerous machinery
There are no data on the effect on reaction rate when driving vehicles or operating machinery.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Side effects
Side effects
Digestive system disorders: decreased appetite, vomiting, diarrhea, nausea, glossitis, esophagitis, gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulceration, hypertrophy of papillae of the tongue, dysphagia, hepatotoxic effect, pancreatitis, intestinal disbacteriosis, enterocolitis, increased activity of “liver” transaminases, antibiotic-induced diarrhea.
Central nervous system disorders: increased intracranial pressure, headache, toxic effects on the central nervous system (dizziness or unsteadiness).
Hematopoietic disorders: hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, eosinophilia.
More urinary system disorders: azotemia, hypercreatininemia, nephrotoxic effect.
Allergic and immunopathological reactions: maculopapular rash, skin hyperemia, angioedema, anaphylactoid reactions, drug-induced systemic lupus erythematosus, photosensitization.
Others: superinfection, candidiasis, hypovitaminosis of B vitamins, hyperbilirubinemia, discoloration of tooth enamel in children, stomatitis.
An overdose of the drug may increase the above-described side effects.
The treatment is symptomatic.
Overdose
Overdose
The dose-dependent side effects may increase.
Treatment: symptomatic therapy.
Pregnancy use
Pregnancy use
Contraindicated in pregnancy (tetracyclines pass through the placenta, accumulate in the bones and dental buds of the fetus, disrupting their mineralization, can cause severe disorders of bone development). The FDA fetal category of action is D.
Breast-feeding should be stopped for the period of treatment (tetracyclines penetrate into the breast milk and may have a negative effect on the development of baby’s bones and teeth, and cause photosensitization reactions, candidiasis of the mouth and vagina in infants).
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
| Weight | 0.037 kg |
|---|---|
| Shelf life | 3 years |
| Conditions of storage | In a dry place, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C |
| Manufacturer | Belmedpreparaty, Belarus |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Belmedpreparaty |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Tetracycline, 100 mg 20 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.