No products in the cart.
Termicon, tablets 250 mg 14 pcs
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group antifungal agent
ATC code D01BA02
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics:terbinafine belongs to the group of allilamines, has a wide range of antifungal action. At low concentrations it has a fungicidal effect on dermatophytes (T. rubrum, T. mentagrophytes, T. tonsurans,
T. verrucosum, T. violaceum), Microsporumcanis, Epidermophyton floccosum, molds (e.g. Aspergillus, Cladosporium, Scopulariopsisbrevicalius), yeasts, mainly Candidaalbicans, and some dimorphic fungi. Candida fungi and its mycelial forms have fungicidal or fungistatic effect depending on the fungus species.
Terbinafine disrupts the early stage of biosynthesis of the main component of the cell membrane of the fungus ergosterol by inhibiting the enzyme squalene epoxidase.
If administered orally, it is not effective in the treatment of variegated herpes caused by Malasseziafurfur.
Pharmacokinetics: Oral administration is well absorbed; half of the dose is absorbed after 0.8 hours; after 4.6 hours half of the dose is distributed in the body. One to two hours after a single oral dose of 250 mg, maximum blood plasma concentration reaches 0.97 mcg/ml. Bioavailability is 80%. Food intake does not affect the bioavailability of terbinafine.
Terbinafine binds intensively with plasma proteins (99%), quickly spreads in the tissues, penetrates into the dermal layer of the skin and nail plates. It penetrates into the secretion of sebaceous glands and accumulates in high concentrations in hair follicles, hair, skin and subcutaneous tissue.
The elimination half-life is 16-18 h, the terminal phase elimination half-life is 200-400 h.
It is biotransformed in the liver to inactive metabolites; 80 % of the dose taken is excreted in the urine as metabolites, the rest (22 %) – in the faeces. It does not accumulate in the body. Age of patients does not affect the pharmacokinetics of terbinafine, however, elimination may be reduced with kidney or liver damage, leading to high concentrations of terbinafine in blood.
It is excreted with the breast milk.
Indications
Indications
Skin and nail mycoses caused by Trychophyton (T. rubrum, mentagrophytes, verrucosum, violaceum), Microsporum (M. canis, M. gypseum) and Epidermophytonfloccosum.
Onychomycoses.
Severe, widespread dermatomycoses of smooth skin of the trunk and extremities that require systemic treatment.
Candidoses of the skin and mucous membranes.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
The active ingredient:
Excipients:
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
The duration of treatment and dosing regimen is set on an individual basis and depends on the localization of the process and the severity of the disease.
The drug is used orally, regardless of meals, with water. It is desirable to use the drug at the same time.
Adults:
The usual dose: 250 mg (1 tablet) once a day.
Onychomycosis: duration of therapy is about 6-12 weeks.
In onychomycosis of the hands, 6 weeks of treatment is enough in most cases.
In onychomycosis of the feet, 12 weeks of treatment is sufficient in most cases. Some patients with reduced nail growth may require longer treatment.
The optimal clinical effect is seen several months after mycological cure and discontinuation of therapy. This is determined by the period of time it takes for the healthy nail to grow back.
Fungal skin infections: duration of treatment in case of interfinger, plantar or “toe” localization of infection is 2-6 weeks, in mycosis of other body areas: shins – 2-4 weeks, trunk – 4 weeks, in mycosis caused by Candida – 2-4 weeks, in mycosis of head caused by Micisporumcanis – more than 4 weeks.
In children:
The single dose depends on body weight and is: for children with a body weight of 20 to 40 kg – 125 mg (1/2 tablet 250 mg); with a body weight over 40 kg – 250 mg.
The drug is prescribed once a day.
The duration of treatment of mycoses of the scalp is about 4 weeks; in case of infection with Micisporumcanis it may be longer.
Interaction
Interaction
Inhibits CYP2D6 isoenzyme and interferes with the metabolism of such drugs as tricyclic antidepressants and selective serotonin uptake blockers (e.g. Desipramine, fluvoxamine), β1-blockers (metoprolol, propranololol), antiarrhythmic agents (flecainide, propafenone), MAO-B-inhibitors (selegiline) and antipsychotics (e.g., chlorpromazine, haloperidol).
Drugs which are inducers of CYP450 enzymes (e.g. rifampicin) may accelerate excretion of terbinafine.
Drugs – CYP450 inhibitors (e.g. cimetidine) can slow down the metabolism and excretion of terbinafine from the body. With the simultaneous use of these drugs it may be necessary to adjust the dose of terbinafine.
The menstrual cycle may be disrupted if terbinafine and oral contraceptives are used at the same time.
Limits caffeine clearance by 21% and prolongs its half-life by 31%.
It does not affect clearance of phenazone, digoxin, warfarin.
When co-administered with ethanol or drugs with hepatotoxic effects, there is a risk of drug-induced liver damage.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
If terbinafine is used irregularly or is discontinued prematurely, it can lead to a recurrence of the disease.
The duration of therapy may also be affected by factors such as the presence of underlying medical conditions and the condition of the nails at the start of treatment.
If the condition has not improved after 2 weeks of treatment, the causative agent and its sensitivity to the medication must be reassessed.
The systemic use in onychomycosis is reasonable only in case of total lesion of the majority of nails, the presence of significant subnail hyperkeratosis, the failure of previous local therapy.
In the treatment of onychomycosis, the clinical response is usually observed in a few months after mycological cure and cessation of the treatment, due to the speed of regrowth of healthy nails. Removal of the nail plates is not required when treating onychomycosis of the hands for 3 weeks and onychomycosis of the feet for 6 weeks.
In the presence of severe renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance less than 50 ml/min or creatinine in the blood more than 300 µmol/l), in liver function disorders the dose of terbinafine should be reduced by half.
The clearance of terbinafine may be reduced in the presence of liver disease.
In case of reduced liver function, half the adult dose is prescribed.
Hepatic function tests should be performed before starting terbinafine tablets. Hepatotoxicity may occur in patients with or without previous liver disease.
A periodic liver function tests are recommended during therapy (4-6 weeks after the start of treatment). Treatment with terbinafine should be immediately discontinued in case of increased activity of “liver tests”.
Patients receiving terbinafine should be warned to immediately inform the treating physician if symptoms such as persistent nausea, decreased appetite, fatigue, vomiting, pain in the right subcostal area, jaundice, dark urine or light stool occur while taking the drug.
If these symptoms occur, the drug should be stopped immediately and liver function testing should be performed.
Serious skin reactions (including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) have rarely been reported with terbinafine.
Prescribing terbinafine to psoriasis patients requires extra caution because in very rare cases terbinafine may trigger a psoriasis flare.
When using terbinafine tablets very rare cases of changes in the cellular composition of the blood (neutropenia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia) were noted. In case of development of qualitative or quantitative changes in blood cells the cause of the disorders should be determined and the issue of reducing the dose of the drug or, if necessary, discontinuing therapy with terbinafine should be considered.
Terbinafine has been shown to inhibit metabolism mediated by the 2D6 isoenzyme (CYP2D6).
Therefore, it is necessary to monitor patients receiving concomitant treatment with drugs predominantly metabolized with participation of this enzyme (such as tricyclic antidepressants, beta-adrenoblockers, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, antiarrhythmic drugs of class IC and type B monoamine oxidase inhibitors) in case the drug used simultaneously has a low therapeutic concentration range.
In treatment with terbinafine, general rules of hygiene should be followed to prevent the possibility of reinfection through underwear and shoes. During treatment (after 2 weeks) and at the end of treatment, antifungal treatment of shoes, socks and stockings should be performed.
The effect of terbinafine on the ability to drive vehicles and operate mechanisms has not been studied. If dizziness develops during therapy with the drug, patients should not drive motor transport and/or operate machinery.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Severe, chronic or active liver disease.
The use of terbinafine in patients with impaired renal function (creatinine clearance less than 50 ml/min or serum creatinine concentration greater than 300 µmol/L) is not recommended, because the use of the drug in this category of patients has not been adequately studied.
With caution
Hepatic disorders, inhibition of medullary hematopoiesis, cutaneous lupus erythematosus or systemic lupus erythematosus, psoriasis.
Side effects
Side effects
The drug Termicon® is generally well tolerated. Side effects are usually mild to moderate and transient.
The following gradations were used to assess the incidence of side effects of the drug: “very frequently” (â¥1/10), “frequently” (from â¥1/100 < 1/10), “infrequently” (â¥1/1000 < 1/100), “rarely” (â¥1/10000 < 1/1000), “very rarely” (< 1/10000) including individual reports.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: infrequent – anemia; very rare – neutropenia, agranulocytosis, pancytopenia, thrombocytopenia.
Disorders of the immune system: very rarely – anaphylactoid reactions (including angioedema), cutaneous and systemic lupus erythematosus (or their exacerbation).
Psychiatric disorders: often – depression; rarely – anxiety.
Nervous system disorders: very often – headache; often – dizziness, impairment of sense of taste, up to their loss (usually recovery occurs within a few weeks after stopping the treatment). In some cases, against the background of terbinafine use, emaciation has been noted. There have been isolated reports of cases of prolonged disorders of taste sensation; paresthesias and hypoesthesias are infrequent.
Visual organ disorders: infrequent – visual disturbances.
Hearing and labyrinth disorders: infrequent – tinnitus.
Hepatic and biliary tract disorders: rare – hepatobiliary dysfunction (predominantly of cholestatic nature), including liver failure, including very rare cases of severe liver failure (some with fatal outcome or requiring liver transplantation; in most cases when liver failure developed, patients had serious systemic diseases and causal connection of liver failure with taking terbinafine was doubtful), hepatitis, jaundice, cholestasis, increased activity of “liver” enzymes.
Digestive system disorders: very often – bloating, decreased appetite, dyspepsia, nausea, mild abdominal pain, diarrhea.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: very common – rash, urticaria; infrequent – photosensitivity reactions; very rare – Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, erythema multiforme, toxic skin rash, exfoliative dermatitis, bullous dermatitis, psoriasis-like skin rash or exacerbation of psoriasis, alopecia.
Muscular and connective tissue disorders: very often arthralgia and myalgia.
General disorders: often – feeling of fatigue; infrequently – increase in body temperature.
Laboratory and instrumental data: infrequent – weight loss (secondary to impaired taste).
Based on spontaneous reports received in the post-registration period and literature data, the following adverse events have been identified, the frequency of which cannot be determined due to the imprecise number of patients.
Immune system disorders: anaphylactic reactions, serum sickness-like syndrome.
Visual organ disorders:visual impairment.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders:drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (rash, edema, fever and enlarged lymph nodes).
Hearing and labyrinth disorders: hearing loss, hearing impairment.
Vascular disorders: vasculitis.
Nervous system disorders: loss of sense of smell, including for a long period of time, decreased sense of smell.
Digestive system disorders: pancreatitis.
Muscular and connective tissue disorders: rhabdomyolysis.
General disorders: flu-like syndrome.
Laboratory and instrumental findings: increased serum creatine phosphokinase activity.
If you notice any side effects of the drug, tell your doctor.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: nausea, vomiting, pain in the lower abdomen, epigastric region.
Treatment: gastric lavage followed by administration of activated charcoal and/or symptomatic therapy.
Pregnancy use
Pregnancy use
The experimental data do not suggest the presence of adverse events with regard to fertility and fetal toxicity. Since clinical experience with terbinafine in pregnant women is very limited, the drug should not be used during pregnancy unless the expected benefits of therapy exceed the potential risk to the fetus.
Terbinafine is excreted with breast milk, so women receiving terbinafine orally should not breastfeed.
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
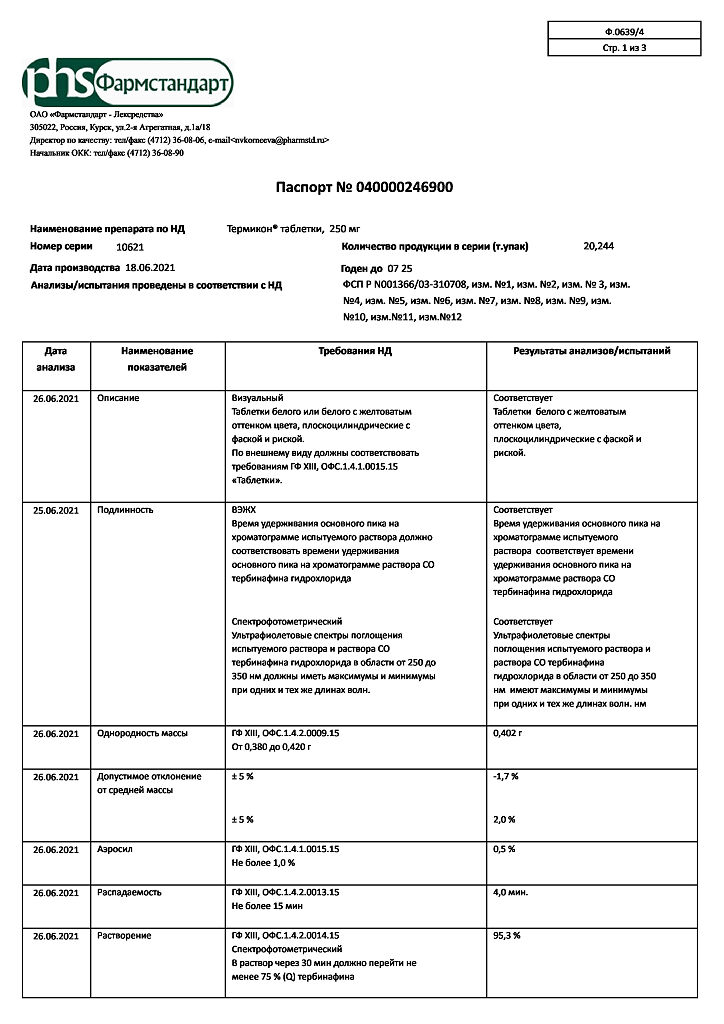
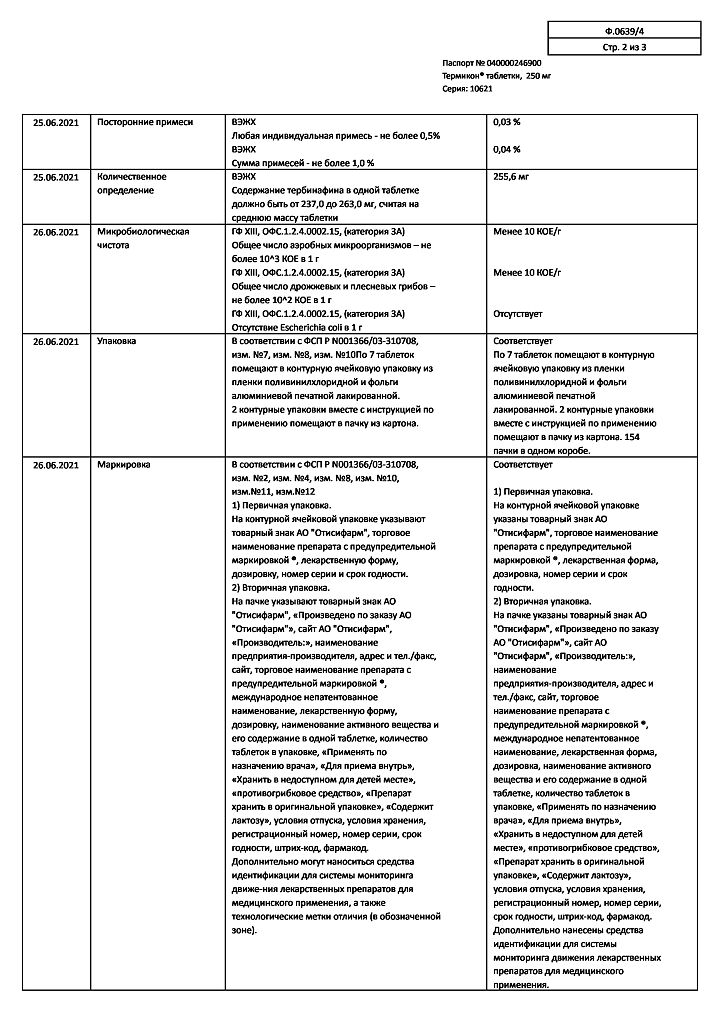
| Shelf life | 4 years. Do not use after the expiration date printed on the package. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a light-protected place, in a well-capped container, at a temperature not exceeding 30 °C |
| Manufacturer | Pharmstandard-Leksredstva, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Pharmstandard-Leksredstva |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Termicon, tablets 250 mg 14 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.