No products in the cart.
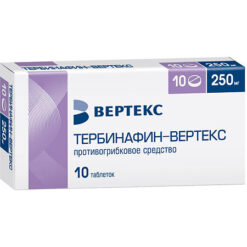
Terbinafin-Vertex, tablets 250 mg 30 pcs
€25.53 €21.27
Description
Terbinafine belongs to the group of allilamines, has a broad spectrum of antifungal action. In low concentrations it has fungicidal effect on dermatophytes Trychophyton spp. (T. rubrum, T. mentagrophytes, T. tonsurans, T.verrucosum, T.violaceum), Microsporum canis, Epidermophyton floccosum, mold fungi (e.g. Scopulariopsis brevicaulis), yeasts, mainly Candida albicans.
It has fungicidal or fungistatic effect on Candida spp. fungi and their mycelial forms depending on a fungus species.
Terbinafine disrupts an early stage of biosynthesis of the main component of the cell membrane of fungus ergosterol by inhibiting the enzyme squalene epoxidase.
When administered orally it is not effective in treating discolorous lichen caused by Pityrosporum ovale, Pityrosporum orbiculare, Malassezia furfur.
Pharmacokinetics
When administered orally it is well absorbed by more than 70%, absolute bioavailability due to the “first pass” effect is approximately 50%. After a single oral administration in a dose of 250 mg time of maximum concentration in plasma (ÒÑmax) is about 1.5 h; maximum concentration (Ñmax) is 1.3 µg/ml.
Area under curve “Concentration – time” (AUC) – 4.56 µh×m/ml, in concurrent usage with food AUC is increased by 20%. With prolonged use Cmax increases by 25%, AUC – 2.3 times. Effective elimination half-life (T1/2) is about 30 hours, terminal T1/2 – 200-400 hours (indicates prolonged excretion from the skin and adipose tissue).
Equilibrium concentration (Css) is independent of age. The plasma concentration of terbinafine is independent of sex. Binding with plasma proteins is more than 99%. Rapidly distributed in tissues, penetrates into dermal layer of skin and nail plates.
It penetrates into the secretion of sebaceous glands and accumulates in high concentrations in hair follicles, in the hair, skin and subcutaneous tissue. It is subject to significant metabolism; the resulting metabolites have no antifungal activity. 70% is excreted by kidneys.
It does not accumulate in the body. The age of patients does not affect the pharmacokinetics of terbinafine, but elimination may be reduced with liver and kidney damage, leading to high concentrations of terbinafine in the blood.
Excreted with breast milk.
Indications
Indications
Mycoses of the scalp (trichophytia, microsporia).
– Fungal diseases of the skin and nails (onychomycosis) caused by Trychophyton spp. (T. rubrum, T. mentagrophytes, T. verrucosum, T. violaccum), Microsporum spp. (M. canis, M. gypseum) and Epidermophyton floccosum.
– Severe, widespread dermatomycosis of smooth skin of the trunk and extremities, requiring systemic treatment.
– Candidiasis of the skin and mucous membranes.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Terbinafine belongs to the group of allylamines and has a wide spectrum of antifungal action. At low concentrations it has a fungicidal effect on dermatophytes Trychophyton spp. (T. rubrum, T. mentagrophytes, T. tonsurans, T. verrucosum, T. violaceum), Microsporum canis, Epidermophyton floccosum, molds (eg Scopulariopsis brevicaulis), yeasts, mainly Candida albicans.
For fungi Candida spp. and their mycelial forms have a fungicidal or fungistatic effect depending on the type of fungus.
Terbinafine disrupts the early stage of biosynthesis of the main component of the cell membrane of the fungus, ergosterol, by inhibiting the enzyme squalene epoxidase.
When administered orally, it is not effective in the treatment of pityriasis versicolor caused by Pityrosporum ovale, Pityrosporum orbiculare, Malassezia furfur.
Pharmacokinetics
When taken orally, more than 70% is well absorbed; absolute bioavailability due to the “first pass” effect is about 50%. After a single oral dose of 250 mg, the time to reach maximum plasma concentration (TCmax) is about 1.5 hours; maximum concentration (Cmax) – 1.3 µg/ml.
The area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) is 4.56 mcg/ml; when taken with food, the AUC increases by 20%. With long-term use, Cmax increases by 25%, AUC by 2.3 times. The effective half-life (T1/2) is about 30 hours, terminal T1/2 is 200-400 hours (indicates long-term elimination from the skin and adipose tissue).
The steady-state concentration (Css) does not depend on age. The concentration of terbinafine in plasma does not depend on gender. Communication with plasma proteins is more than 99%. It is quickly distributed in tissues, penetrates the dermal layer of the skin and nail plates.
Penetrates into the secretions of the sebaceous glands and accumulates in high concentrations in the hair follicles, hair, skin and subcutaneous tissue. Subject to significant metabolism, the resulting metabolites do not have antifungal activity. 70% is excreted by the kidneys.
Does not accumulate in the body. The age of patients does not affect the pharmacokinetics of terbinafine, however, elimination may be reduced in cases of liver and kidney damage, leading to high concentrations of terbinafine in the blood.
Excreted in breast milk.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Irregular use or early termination of treatment increases the risk of relapse.
The duration of therapy can be influenced by factors such as the presence of concomitant diseases, the condition of the nails with onychomycosis at the beginning of the course of treatment.
If after 2 weeks of treatment of a skin infection there is no improvement in the condition, it is necessary to re-determine the causative agent of the disease and its sensitivity to the drug.
Systemic use for onychomycosis is justified only in the case of total damage to most nails, the presence of severe subungual hyperkeratosis, and the ineffectiveness of previous local therapy.
When treating onychomycosis, a laboratory-confirmed clinical response is usually observed several months after mycological cure and cessation of treatment, which is due to the rate of regrowth of a healthy nail.
Removal of nail plates is not required when treating onychomycosis of the hands for 3 weeks and onychomycosis of the feet for 6 weeks.
In the presence of liver disease, the clearance of terbinafine may be reduced. During treatment, it is necessary to monitor the activity of liver transaminases in the blood serum.
In rare cases, cholestasis and hepatitis occur after 3 months of treatment. If signs of liver dysfunction occur (weakness, persistent nausea, decreased appetite, excessive abdominal pain, jaundice, dark urine or discolored stools), the drug should be discontinued.
Prescribing terbinafine to patients with psoriasis requires caution, because in very rare cases, terbinafine can cause an exacerbation of psoriasis.
When treating with terbinafine, general hygiene rules should be observed to prevent the possibility of re-infection through underwear and shoes. During treatment (after 2 weeks) and at the end it is necessary to carry out antifungal treatment of shoes, socks and stockings.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
There is no data on the effect of Terbinafine on the ability to drive vehicles and machines.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Terbinafine
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient:
terbinafine hydrochloride 281.25 mg (corresponding to 250 mg terbinafine base);
Excipients:
colloidal silicon dioxide 3.9 mg,
magnesium stearate 3.9 mg,
hypromellose 11.7 mg,
microcrystalline cellulose 44.4 mg,
sodium carboxymethyl starch, type “A” 44.85 mg.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
There are no data on the safety of terbinafine during pregnancy. Therefore, terbinafine should be used during pregnancy only if the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the possible risk to the fetus.
Lactation period
Terbinafine is excreted in breast milk. Its use during breastfeeding is contraindicated.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients;
Acute or chronic liver diseases;
Children under 2 years of age (efficacy and safety have not been established);
Lactation period.
With caution: pregnancy; renal failure; alcoholism, suppression of bone marrow hematopoiesis, tumors, metabolic diseases, occlusive vascular diseases of the extremities.
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the digestive tract: often: feeling of fullness in the stomach, nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea, loss of appetite; in isolated cases (0.1-1%) – disturbance of taste sensations, including their loss (recovery occurs within several weeks after cessation of treatment); rarely (0.01-0.1%) – hepatotoxic effect (increased activity of “liver” enzymes, liver failure).
From the central nervous system: often: headache, dizziness.
From the hematopoietic system: very rarely (<0.01%) neutropenia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia.From the immune system: rarely: anaphylactoid reactions, including angioedema, exacerbation of systemic lupus erythematosus.From the skin and subcutaneous tissue: often: rash, urticaria; very rare: psoriasis-like skin rashes, exacerbation of psoriasis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, hair loss, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis.From the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue: often: arthralgia, myalgia.General disorders: very rare: fatigue.
Interaction
Interaction
Inhibits the CYP2D6 isoenzyme and disrupts the metabolism of drugs such as tricyclic antidepressants and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (for example, desipramine, fluvoxamine), beta-blockers (metoprolol, propranolol), antiarrhythmics (flecainide, propafenone), monoamine oxidase B inhibitors (for example, selegiline) and antipsychotics (for example, chlorpromazine, haloperidol) agents.
Drugs that induce cytochrome P450 isoenzymes (for example, rifampicin) can accelerate the metabolism and elimination of terbinafine from the body. Medicines that are inhibitors of cytochrome P450 isoenzymes (for example, cimetidine) can slow down the metabolism and elimination of terbinafine from the body. If these drugs are used concomitantly, a dose adjustment of terbinafine may be required.
Menstrual irregularities are possible when taking terbinafine and oral contraceptives simultaneously.
Terbinafine reduces the clearance of caffeine by 21% and prolongs its half-life by 31%. Does not affect the clearance of phenazone, digoxin, warfarin.
When used together with ethanol or drugs that have hepatotoxic effects, there is a risk of developing drug-induced liver damage.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: nausea, vomiting, headache, dizziness, pain in the epigastric region, in the lower abdomen, frequent urination.
Treatment: gastric lavage followed by the use of activated carbon and/or symptomatic therapy.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Vertex, Russia
Additional information
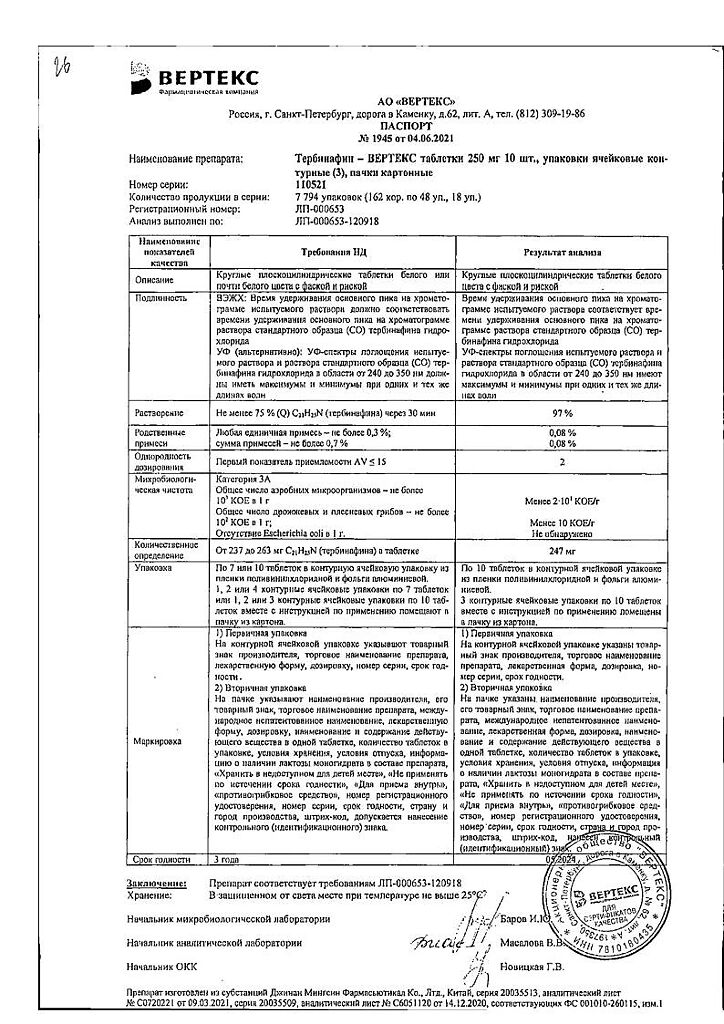
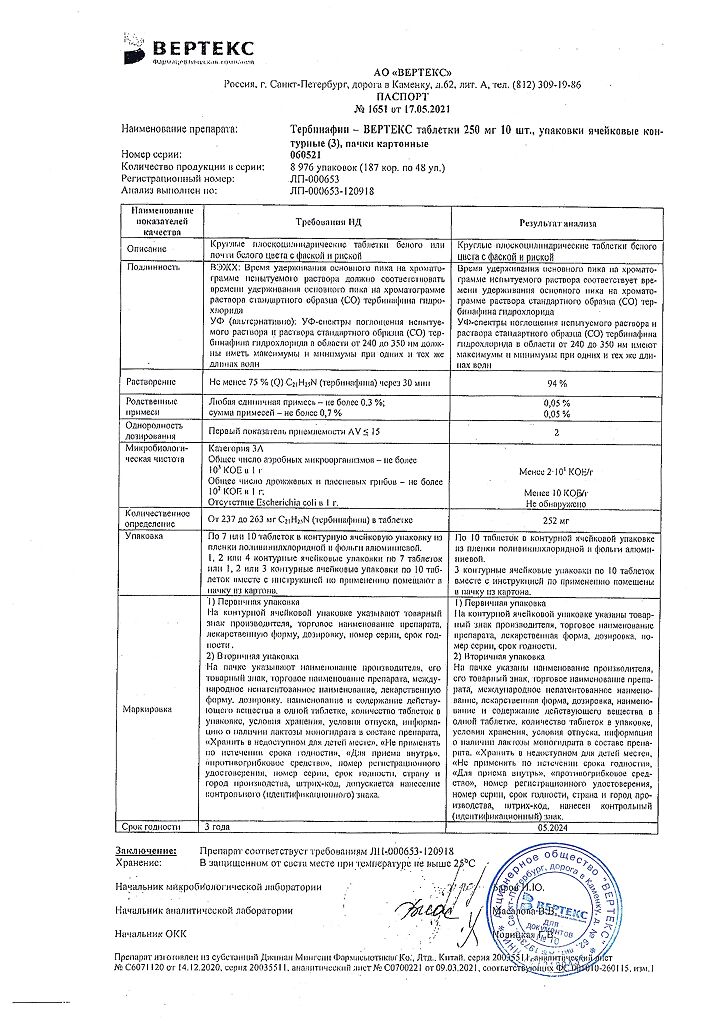
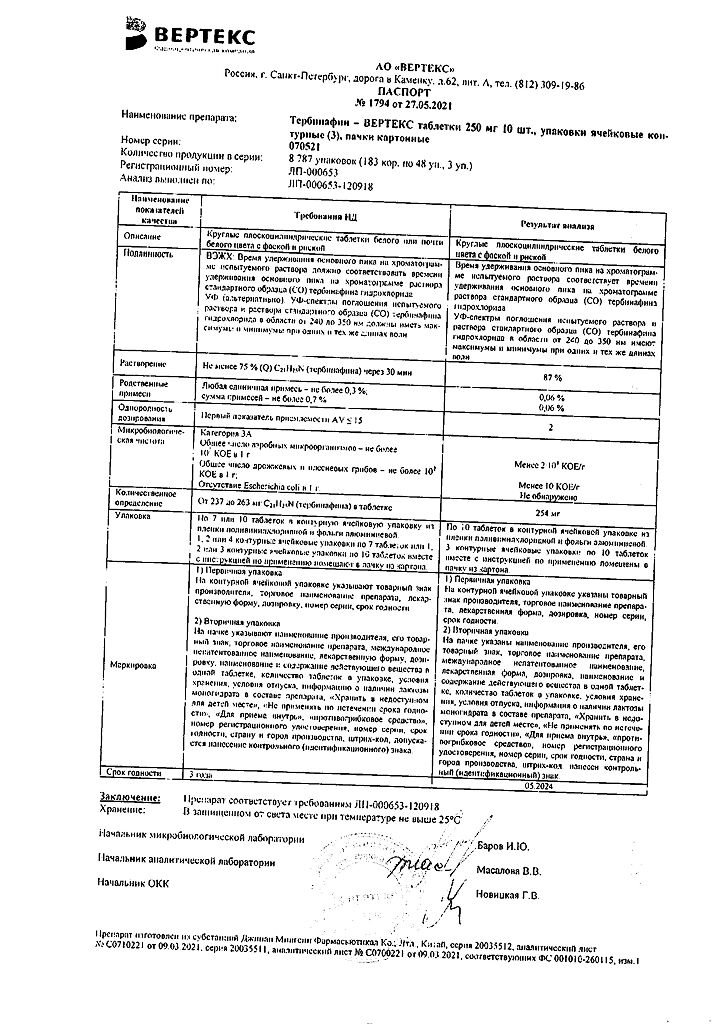
| Manufacturer | Vertex, Russia |
|---|---|
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Vertex |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Terbinafin-Vertex, tablets 250 mg 30 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.