No products in the cart.
Terbinafin, cream 1% 30 g
€10.04 €8.78
Description
Terbinafine belongs to the group of allilamines and has a broad spectrum of antifungal action. In low concentrations it has fungicidal effect on dermatophytes Trychophyton (T. rubrum, T. mentagrophytes, T. tonsurans, T.verrucosum, T.violaceum), Microsporum canis, Epidermophyton floccosum, mold fungi (e.g. Scopulariopsis brevicaulis), yeasts, mainly Candida albicans.
On Candida spp. fungi and their mycelial forms has fungicidal or fungistatic action depending on the fungus species.
Terbinafine disrupts the early stage of biosynthesis of the main component of the cell membrane of the fungus ergosterol by inhibiting the enzyme squaleneepoxidase.
In oral administration it is not effective in the treatment of variegated herpes caused by Pityrosporum ovale, Pityrosporum orbiculare, Malassezia furfur.
Pharmacokinetics
In oral administration it is well absorbed; in 0.8 hours half of the dose is absorbed; in 4.6 hours half of the dose is dispersed in the body. One to two hours after a single oral dose of 250 mg, maximum blood plasma concentration reaches 0.97 mcg/ml. Bioavailability is 80%. Food intake does not affect the bioavailability of terbinafine.
Terbinafine is intensively bound to blood plasma proteins (99%), rapidly distributed in the tissues, penetrates the dermal layer of the skin and nail plates. It penetrates into the secretion of the sebaceous glands and accumulates in high concentrations in the hair follicles, hair, skin and subcutaneous tissue.
The elimination half-life is 16-18 h, the terminal phase elimination half-life is 200-400 h.
Biotransformed in the liver to inactive metabolites. The kidneys excrete 80% of the taken dose as metabolites, the rest (20%) is excreted through the intestines.
It does not cumulate in the body. The age of patients does not affect the pharmacokinetics of terbinafine, but elimination may be reduced with renal or liver damage, leading to high concentrations of terbinafine in the blood.
Excreted with the breast milk.
Indications
Indications
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
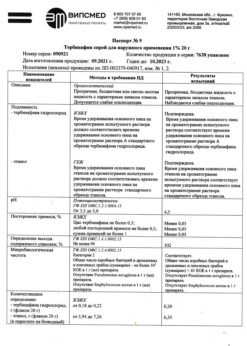
1 g of the cream contains:
The active substances:
terbinafine hydrochloride 10 mg;
Excipients:
benzyl alcohol,
polysorbate 60 (tween 60),
sorbitan monostearate,
cetyl alcohol,
isopropyl myristate,
cetyl palmitate,
sodium hydroxide,
purified water.
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Adults and children over 12 years of age: Apply a thin layer, rubbing gently, 1 or 2 times a day on the affected skin and the surrounding area.
The duration of treatment depends on the indication and the severity of the disease.
The course of treatment is on average 2-4 weeks.
The duration and number of times of application: dermatomycosis of the trunk, shins, feet – 1 time a day for 1 week; cutaneous candidiasis – 1-2 times a day for 1-2 weeks; lichen permosa – 1-2 times a day for 2 weeks.
Interaction
Interaction
There are no known drug interactions for terbinafine ointment/cream.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
If terbinafine is used irregularly or if treatment is stopped prematurely, it may lead to a recurrence of the disease. If after 2 weeks of treatment of skin infection there is no improvement of the condition, it is necessary to determine again the causative agent and its sensitivity to the drug.
The systemic use in onychomycosis is justified only in case of lesion of the majority of nails, the presence of marked subnail hyperkeratosis, the ineffectiveness of previous local therapy. When treating onychomycosis, the clinical response, confirmed by the laboratory, is usually observed in a few months after mycological cure and cessation of treatment, due to the speed of healthy nail regrowth. Removal of nail plates is not required when treating onychomycosis of the hands for 3 weeks and onychomycosis of the feet for 6 weeks.
In the presence of liver disease clearance of terbinafine may be reduced. During treatment it is necessary to monitor the activity of “hepatic” transaminases in the blood serum.
In rare cases after 3 months of treatment cholestasis and hepatitis occur. If signs of liver dysfunction appear (weakness, persistent nausea, decreased appetite, excessive abdominal pain, jaundice, darkened urine or discolored feces) the drug should be stopped.
Prescribing terbinafine to psoriasis patients requires caution because in very rare cases terbinafine may provoke an exacerbation of psoriasis. During treatment with terbinafine, general rules of hygiene should be followed to prevent the possibility of reinfection through underwear and shoes. During treatment (after 2 weeks) and at the end of treatment, antifungal treatment of shoes, socks and stockings should be performed.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Caution should be exercised when:
Side effects
Side effects
For external use: itching and burning of the skin, hyperemia at the site of application, allergic reactions possible.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, pain in the epigastric region, rapid urination, rash.
Treatment: measures to eliminate the drug (gastric lavage, intake of activated charcoal); if necessary – symptomatic supportive therapy.
Pregnancy use
Pregnancy use
Terbinafine has not been found to have teratogenic properties in experimental studies.
The use of the drug in pregnancy is possible in cases where the estimated benefit to the mother exceeds the possible risk to the fetus. Terbinafine is excreted with the breast milk.
If it is necessary to use the drug during lactation, the question of stopping breastfeeding should be addressed.
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
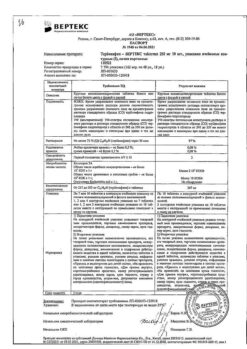
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C |
| Manufacturer | Vertex, Russia |
| Medication form | exterior cream |
| Brand | Vertex |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Terbinafin, cream 1% 30 g with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.