No products in the cart.
Description
Hepatitis, HIV infection
Treatment of HIV-1 infection as part of combination antiretroviral therapy in adults.
Indications
Indications
Treatment of HIV-1 infection as part of combination antiretroviral therapy in adults.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Tenofovir
Composition
Composition
Active substances:
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate 300.0 mg
Contraindications
Contraindications
Tenofovir is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to any component of the drug.
With caution
Renal failure with creatinine clearance less than 50 ml/min, including patients on hemodialysis. When creatinine clearance is less than 30 ml/min, the use of the drug should be avoided; If other treatment is not available, renal function should be carefully monitored and the interval between drug administrations should be adjusted.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Below are adverse reactions with a suspected (possible) connection with the drug, which are listed by system-organ class in descending order of their severity, with the following frequency: very often (> 1/10) and often (> 1/100, 1/10000, < 1/1000), very rarely
Metabolic and nutritional disorders: very often – hypophosphatemia.
From the nervous system: very often – dizziness.
From the gastrointestinal tract: very often – diarrhea, vomiting, nausea; often – flatulence.
Combination retroviral therapy has been associated with metabolic disorders such as hypertriglyceridemia, hypercholesterolemia, insulin resistance, hyperglycemia and hyperlactatemia; redistribution of subcutaneous tissue (lipodystrophy).
Cases of osteonecrosis have been reported, especially in patients with risk factors or during long-term combination antiviral therapy. Frequency unknown.
Post-marketing experience
Metabolic and nutritional disorders: rarely – lactic acidosis, frequency unknown – hypokalemia
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: very rarely – dyspnea.
From the gastrointestinal tract: rarely – pancreatitis.
From the hepatobiliary system: rarely – increased transaminase activity; very rarely – hepatitis, frequency unknown – liver steatosis.
From the skin and subcutaneous tissues: rarely – rash.
From the musculoskeletal system: frequency unknown – rhabdomyolysis, osteomalacia, muscle weakness, myopathy.
From the urinary system: rarely – acute renal failure, proximal renal tubulopathy (including Fanconi syndrome), hypercreatininemia; very rarely – acute tubular necrosis; frequency unknown – nephritis (including acute interstitial), nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.
General disorders and changes at the injection site: very rarely – asthenia.
Interaction
Interaction
Didanosine: increased concentrations of didanosine when used together; they should be used with caution and monitored for signs of didanosine toxicity (eg, pancreatitis, neuropathy). The combination of tenofovir with didanosine is not recommended; If warranted, dose reduction or discontinuation of didanosine therapy should be considered. Tenofovir is combined with reduced doses of didanosine (for example, patients weighing > 60 kg are prescribed didanosine 250 mg once daily; < 60 kg - 200 mg once daily). On the other hand, such a low-dose combination may be characterized by low antiviral activity and insufficient increase in the number of CO4 lymphocytes, as indicated by the high rate of treatment failure when using this combination with the addition of efavirenz or nevirapine.Atazanavir: Decreased atazanavir concentrations when coadministered and increased tenofovir concentrations. It is necessary to use tenofovir with atazanavir only with additional enhancement of the latter’s action with ritonavir.Lopinavir/ritonavir: Increased concentrations of tenofovir when used together.Darunavir: Increases tenofovir concentrations by 20-25%. The drugs should be used in standard doses, and the nephrotoxic effects of tenofovir should be carefully monitored. Tenofovir is primarily eliminated from the body through the kidneys; coadministration of tenofovir with drugs that decrease renal function or reduce/abstain active tubular secretions may increase serum concentrations of tenofovir and/or increase concentrations of other drugs eliminated through the kidneys.
Ganciclovir, valganciclovir, and cidofovir compete with tenofovir for active renal tubular secretion, resulting in increased levels of tenofovir or the concomitantly administered drug; Caution for possible side effects is required. Nephrotoxic drugs may also increase tenofovir serum concentrations.
Overdose
Overdose
In case of overdose, the patient should be examined to identify possible signs of intoxication. If necessary, standard supportive therapy is used.
Tenofovir is effectively removed by hemodialysis with an extraction rate of approximately 54%. After taking 300 mg tenofovir, a 4-hour hemodialysis procedure removes approximately 10% of the tenofovir dose taken.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Drug technology, Russia
Additional information
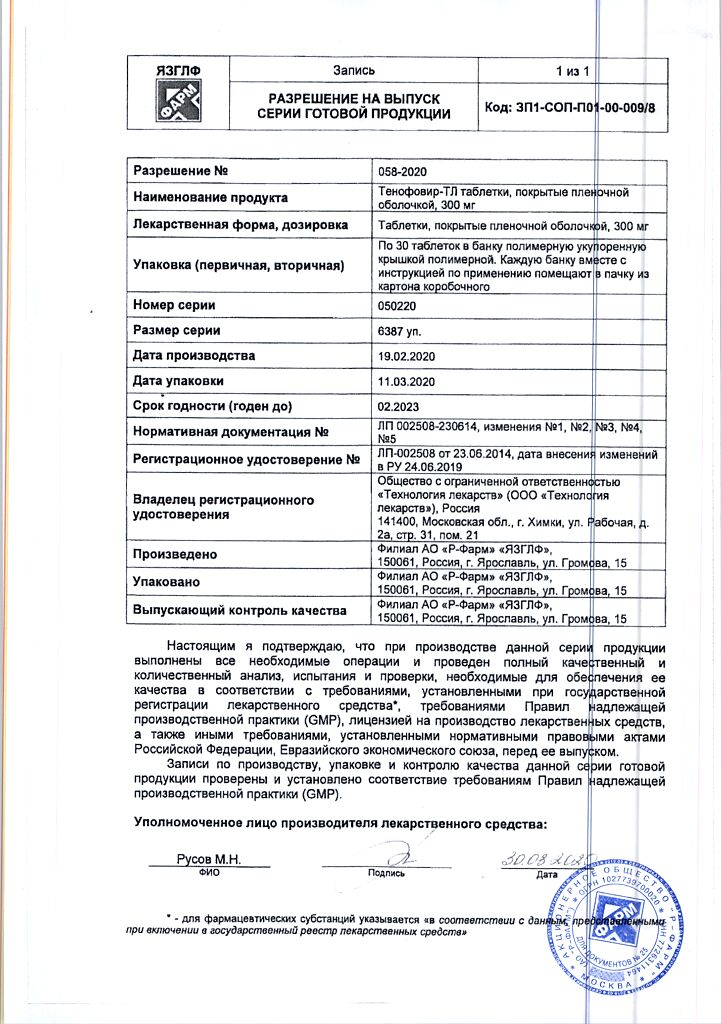
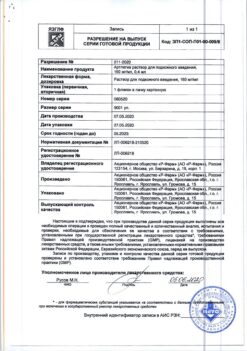
| Manufacturer | Drug Technology, Russia |
|---|---|
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Drug Technology |
Related products
Buy Tenofovir TL, 300 mg 30 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.