No products in the cart.
Symbicort Turbuhaler, 160+4, 5 mcg/dose 120 doses
€59.71 €49.75
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group: bronchodilator combined (beta2-adrenomimetic selective + local glucocorticosteroid)
ATX code: R03AK07
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Simbicort® contains budesonide and formoterol, which have different mechanisms of action and have an additive effect in reducing the frequency of exacerbations of bronchial asthma. The special properties of budesonide and formoterol make it possible to use their combination to relieve attacks/symptoms with an anti-inflammatory effect, or as maintenance therapy for bronchial asthma.
Budesonide. Budesonide is a glucocorticosteroid that has a rapid (within hours) and dose-dependent anti-inflammatory effect on the airways after inhalation, reducing the severity of symptoms and the frequency of exacerbations of bronchial asthma. When prescribing inhaled budesonide, there is a lower incidence of serious adverse effects than when using systemic glucocorticosteroids. It reduces the severity of bronchial mucosal edema, mucus production, sputum formation and airway hyperresponsiveness. The exact mechanism of anti-inflammatory action of glucocorticosteroids is unknown.
Formoterol. Formoterol is a selective b2-adrenoreceptor agonist, after inhalation of which there is rapid and prolonged relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle in patients with reversible airway obstruction. The dose-dependent bronchodilator effect occurs within 1-3 minutes after inhalation and persists for at least 12 hours after a single dose.
Simbicort® Turbukhaler®: Budesonide + Formoterol Bronchial asthma
Clinical effectiveness of Simbicort® as an anti-inflammatory attack/symptom therapy: For anti-inflammatory seizure/symptom control (therapy A) and as maintenance therapy and for anti-inflammatory seizure/symptom control (therapy B)
. A total of 7 double-blind clinical trials enrolled 20140 patients with bronchial asthma, 7831 of whom were randomized to therapy with Symbicort® for attack/symptom control with anti-inflammatory effects and with or without maintenance therapy (therapy B) (therapy A).
In two studies (SYGMA 1 and SYGMA 2) involving 8064 patients with mild bronchial asthma, 3384 patients received Symbicort® for attack/symptom control with anti-inflammatory action (therapy A) for 12 months.
In the SYGMA 2 study, Symbicort® 160/4.5 mcg when used on-demand in response to symptoms (for attack/symptom management with anti-inflammatory action – therapy A) was comparable to maintenance dose budesonide (1 inhaled 200 mcg/dose twice daily) combined with a short-acting beta2-adrenomimetic on demand with respect to the frequency of severe exacerbations. Prevention of severe exacerbations was achieved with a 75% reduction in median steroid load and without the need for adherence to maintenance therapy with inhaled glucocorticosteroids. In the SYGMA 1 trial, Symbicort® for anti-inflammatory attack/symptoms provided a statistically significant and clinically meaningful 64% reduction in the annual incidence of severe exacerbations compared to on-demand use of a short-acting beta2-adrenomimetic. The reduction in the annual incidence of moderate to severe exacerbations was 60%.
. In the SYGMA 1 study, Symbicort® 160/4.5 mcg on-demand was superior to short-acting beta2-adrenomimetic on-demand with respect to bronchial asthma symptom control, showing an average of 34.4% and 31.1% of weeks with good bronchial asthma control, respectively, but was less effective compared with maintenance dose budesonide (1 inhaled 200 mcg/dose twice daily) in combination with an on-demand short-acting beta2-adrenomimetic, with a mean of 34.4% and 44.4% weeks with good bronchial asthma control, respectively. Symbicort® for anti-inflammatory attack/symptoms was superior to the on-demand short-acting beta2-adrenomimetic in terms of improved bronchial asthma control (based on results from the Asthma Control Assessment Questionnaire of 5 items (ACQ5)). Improvement in disease control was less pronounced with Symbicort® on-demand compared to maintenance dose budesonide (1 inhaled 200 mcg/dose twice daily) in combination with a short-acting beta2-adrenomimetic on-demand. The mean difference in the effect of ACQ5 therapy was not clinically significant in either comparison (assessed by a difference of 0.5 or more). These results were observed in a clinical trial setting with significantly higher adherence to budesonide maintenance therapy than in actual practice.
In the SYGMA trials, improvement in pulmonary function relative to baseline (mean prebronchodilator BEP1) was statistically significantly greater in patients receiving Symbicort® for anti-inflammatory seizure/symptoms compared with patients receiving an on-demand beta2-adrenomimetic short-acting. Statistically significantly less improvement in lung function was noted with Symbicort® on-demand compared with budesonide maintenance dose (1 inhaled 200 mcg/dose twice daily) in combination with a short-acting beta2-adrenomimetic on-demand. For both comparisons, the mean differences in therapy effect were small (approximately 30 to 55 mL, corresponding to approximately 2% of the baseline mean).
. In another clinical program involving 12076 patients in 5 studies, an observational study of 4447 patients treated with Symbicort® as maintenance therapy and for seizure/symptom control with anti-inflammatory action (therapy B) for 6 to 12 months There was a statistically and clinically significant reduction in the number of severe exacerbations and increased time to first exacerbation compared to a combination of Symbicort® or budesonide as maintenance therapy and a beta2-adrenoceptor for seizure control. There was also effective control of disease symptoms, pulmonary function, and a reduction in the frequency of prescription of inhalation for seizure control. No development of tolerance to prescribed therapy was detected.
The results of 6 double-blind studies with 14385 patients with bronchial asthma (including 1847 adolescents) demonstrated comparable efficacy and safety of the drug in adolescent and adult patients. The number of adolescent patients taking more than 8 inhalations for at least one day as maintenance therapy and to control attacks/symptoms with anti-inflammatory effects was limited, and use in this regimen was infrequent.
In patients who sought care for an acute asthma attack, Symptom Control (relief of bronchospasm) was as rapid and effective after inhalation of Symbicort® as after prescription of salbutamol and formoterol.
Clinical effectiveness of Simbicort® as maintenance therapy (therapy C)
The addition of formoterol to budesonide reduces asthma symptoms, improves lung function and reduces the rate of exacerbations.
The effect of Simbicort® Turbukhaler® on lung function is consistent with the effect of the combination of budesonide and formoterol monotherapies and greater than that of budesonide alone. In all cases, a short-acting beta2-adrenoceptor was used for seizure control. No decrease of antiasthmatic effect with time was noted. The drug has good tolerability.
Symbicort® Turbukhaler® as maintenance therapy in combination with short-acting beta2-adrenoceptor for seizure control was administered to patients aged 6 to 11 years for 12 weeks (two inhalations of 80/4.5 mcg/dose twice daily). Improvements in pulmonary function and good tolerability of therapy compared to the corresponding dose of budesonide Turbukhaler® were noted.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
In two studies lasting 12 months in patients with moderate to severe COPD (baseline: prebronchodilatation SPH1 < 50% of proper; median postbronchodilatation SPH1 = 42% of proper), there was a significant reduction in the rate of exacerbations of the disease when taking Symbicort® Turbuhaler® compared with patients who received formoterol or placebo alone as therapy (mean exacerbation rate 1.4 compared with 1.8-1.9 in the placebo/formoterol group). No difference was noted between Symbicort® and formoterol administration on first-second forced expiratory volume (FEF1).
Pharmacokinetics Intake
Symbicort® Turbuhaler® is bioequivalent to the corresponding monotherapies with respect to the systemic effects of budesonide and formoterol. Despite this, a slight increase in cortisol suppression was noted after administration of Symbicort® Turbuhaler® compared to monotherapies. This difference has no effect on clinical safety. There is no evidence of pharmacokinetic interaction between budesonide and formoterol.
The pharmacokinetic parameters for the respective substances are comparable after administration of budesonide and formoterol as monotherapy and as part of Symbicort® Turbukhaler®. For budesonide, when administered as part of the combination drug, the area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) is slightly greater, the drug is absorbed faster and the value of maximum plasma concentration is higher.
For formoterol when given as part of a combination drug, the maximum plasma concentration is the same as for the mono drug.
Inhaled budesonide is rapidly absorbed and reaches maximum plasma concentration 30 minutes after inhalation. The average dose of budesonide delivered to the lungs after inhalation via Turbulhaler® is 32-44% of the delivered dose. Systemic bioavailability is approximately 49% of the delivered dose. In children aged 6 to 16 years, the average dose of budesonide delivered to the lungs after inhalation via Turbulhaler® does not differ from that in adult patients (the final plasma concentration of the drug was not determined).
Inhaled formoterol is rapidly absorbed and reaches maximum plasma concentration 10 minutes after inhalation. The average dose of formoterol delivered to the lungs after inhalation via Turbuhaler® is 28-49% of the delivered dose. Systemic bioavailability is about 61% of the delivered dose.
Distribution and metabolism
Approximately 50% of formoterol and 90% of budesonide bind to plasma proteins. The volume of distribution for formoterol is about 4 l/kg and for budesonide about 3 l/kg. Formoterol is inactivated by conjugation (active O-demethylated metabolites are formed mainly as inactivated conjugates). Budesonide undergoes intensive biotransformation (about 90%) during the first passage through the liver to form metabolites with low glucocorticosteroid activity. Glucocorticosteroid activity of the main metabolites – 6-b-hydroxybudesonide and 16-a-hydroxyprednisolone – does not exceed 1% of similar activity of budesonide. There is no evidence of metabolite interaction or substitution reaction between budesonide and formoterol.
The bulk of the formoterol dose is metabolized in the liver and then excreted by the kidneys: after inhalation, 8-13% of the delivered dose of formoterol is excreted unchanged. Formoterol has a high systemic clearance (approximately 1.4 L/min); the half-life of the drug is on average 17 hours.
Budesonide is metabolized mainly with participation of CYP3A4 isoenzyme. Budesonide metabolites are excreted by the kidneys unchanged or in the form of conjugates.
Only small amounts of unchanged budesonide are detected in the urine. Budesonide has a high systemic clearance (approximately 1.2 L/min).
The pharmacokinetics of formoterol and budesonide in patients with renal impairment have not been studied. Plasma concentrations of budesonide and formoterol may be increased in patients with liver disease.
Indications
Indications
• Bronchial asthma, to achieve overall disease control, including prevention and relief of symptoms, and reducing the risk of exacerbations.
The drug Symbicort Turbuhaler is suitable for the treatment of bronchial asthma of any severity, if it is advisable to use inhaled glucocorticosteroids.
• Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), as symptomatic therapy in patients with COPD with post-bronchodilator FEV1 < 70% predicted and with a history of exacerbations, despite regular bronchodilator therapy.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacodynamic properties
Special instructions
Special instructions
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
The drug Symbicort Turbuhaler does not affect the ability to drive vehicles and machines. May affect the ability to drive vehicles and machinery if side effects develop.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Budesonide, Formoterol
Composition
Composition
Active ingredients: budesonide + formoterol.
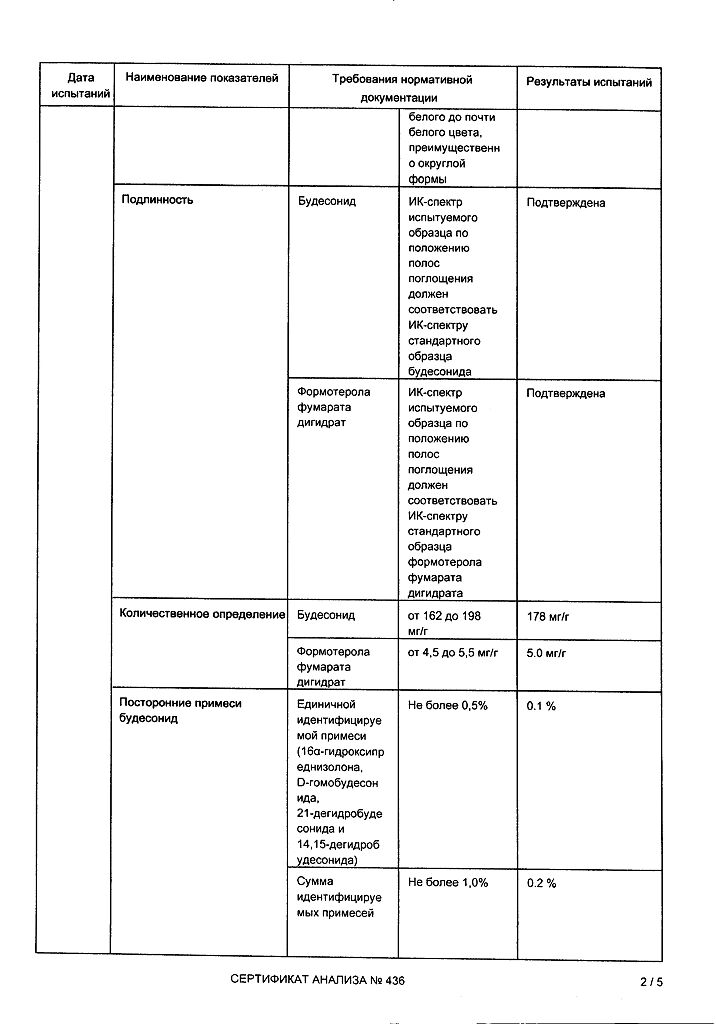
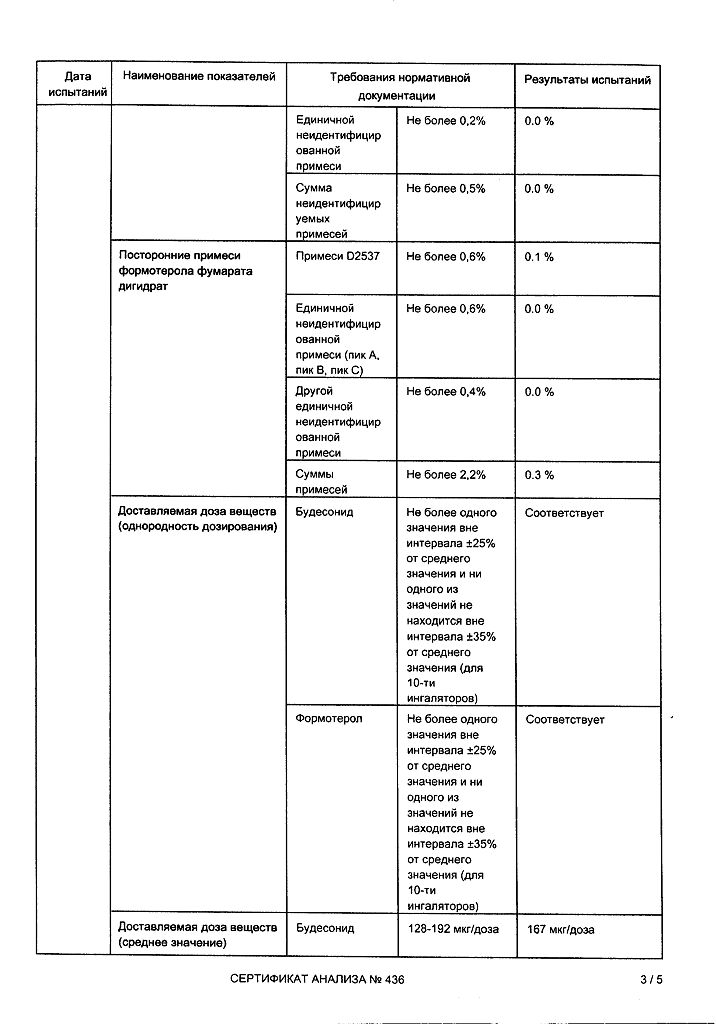
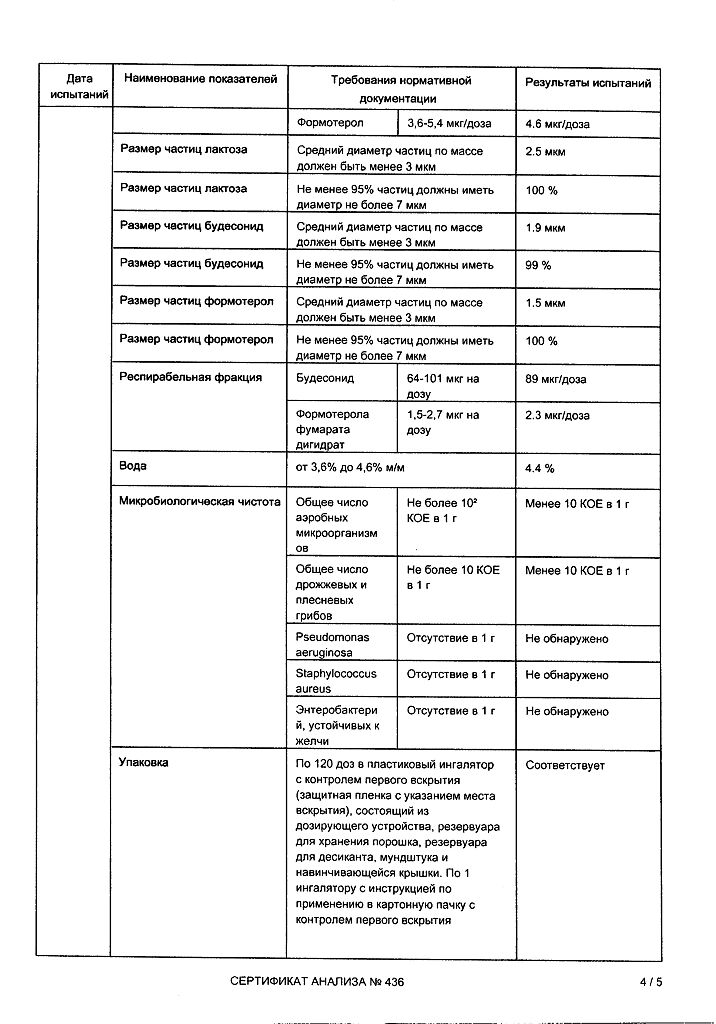
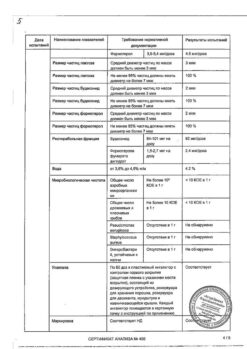
Each delivered dose contains micronized budesonide 160 mcg and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 4.5 mcg.
Excipients, the presence of which must be taken into account in the composition of the medicinal product: lactose monohydrate – 730 mcg/dose (see sections Contraindications and Special instructions and precautions for use).
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
There are no clinical data on the use of Symbicort or the simultaneous use of formoterol and budesonide during pregnancy. The results of an embryofetal toxicity study in rats did not reveal evidence of additional effects when the drugs were used in combination.
There is insufficient data on the use of formoterol in pregnant women. In animal studies, adverse events have been observed with very high doses of formoterol.
Data from approximately 2000 pregnancies associated with the use of the drug did not reveal an increased teratogenic risk associated with the use of inhaled budesonide. Glucocorticosteroids have been shown to cause birth defects in animal studies. However, this is probably not significant for patients receiving the drug at recommended doses.
Animal studies have also demonstrated the effects of excess prenatal glucocorticosteroids on increased risks of intrauterine growth restriction, cardiovascular disease in adulthood, and irreversible changes in glucocorticosteroid receptor density, neurotransmitter metabolism, and behavior when exposed to doses below teratogenic levels. During pregnancy, Symbicort should be used only in cases where the benefit of the drug outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. The lowest effective dose of budesonide needed to maintain adequate control of asthma symptoms should be used.
Lactation
Budesonide is excreted in breast milk, however, when used in therapeutic doses, no effect on the child was noted. It is not known whether formoterol passes into women’s breast milk. Formoterol was found in small amounts in the milk of lactating rats. Symbicort can be prescribed to breastfeeding women only if the expected benefit to the mother is greater than any possible risk to the baby.
Fertility
There are no data on the potential effects of budesonide on reproductive function. Animal reproductive studies with formoterol have shown a slight decrease in reproductive function in male rats with high systemic exposure
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to budesonide, formoterol or any of the excipients.
Children’s age up to 12 years.
For children aged 6 to 11 years, it is possible to use the drug Symbicort Turbuhaler 80 mcg + 4.5 mcg/dose.
Lactose intolerance, lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption.
Special instructions and precautions for use
With caution: pulmonary tuberculosis (active or inactive form), fungal, viral or bacterial infections of the respiratory system, thyrotoxicosis, pheochromocytoma, diabetes mellitus, decreased function of the adrenal cortex, uncontrolled hypokalemia, hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy, idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis, severe arterial hypertension, aneurysm of any location or other severe cardiovascular diseases (coronary heart disease, tachyarrhythmia or severe heart failure), prolongation of the QT interval (use of formoterol may cause prolongation of the QTc interval).
Dosage Directions
If the symptoms of bronchial asthma can be controlled, the dose of Symbicort Turbuhaler can be gradually reduced, and it is important to constantly monitor the patient’s condition. The lowest effective dose of Symbicort Turbuhaler should be prescribed.
Patients are advised to carry emergency medications with them at all times: either Symbicort Turbuhaler (for patients with bronchial asthma using Symbicort Turbuhaler to relieve attacks/symptoms with anti-inflammatory effects – therapy A or B), or short-acting beta2-agonists (for all patients using Symbicort Turbuhaler only for maintenance therapy – therapy B).
When using the drug Symbicort as maintenance therapy, the patient’s attention should be drawn to the need for regular use of a maintenance dose of the drug in accordance with the selected therapy, even in cases where there are no symptoms of the disease.
It is recommended to instruct the patient to rinse the mouth with water after inhaling maintenance doses in order to prevent the risk of developing candidiasis of the oral and pharyngeal mucosa. It is also necessary to rinse your mouth with water after inhalation on demand in case of development of candidiasis of the oral mucosa and pharynx.
It is recommended to gradually reduce the maintenance dose of the drug before stopping treatment and it is not recommended to abruptly discontinue treatment. Inhaled glucocorticosteroids should not be completely discontinued, except in cases where temporary withdrawal is necessary to confirm the diagnosis of bronchial asthma.
Increased symptoms of the disease
During therapy with Symbicort Turbuhaler, exacerbations and the development of serious adverse events associated with bronchial asthma may occur. Patients should continue treatment but seek medical attention if asthma symptoms are not controlled or if symptoms worsen after starting therapy.
If therapy is insufficiently effective or the maximum recommended doses of Symbicort are exceeded, it is necessary to reconsider treatment tactics. Sudden and progressive deterioration in control of symptoms of asthma or COPD is a potentially life-threatening condition and requires urgent medical attention. In this situation, you should consider increasing the dose of glucocorticosteroids, for example, prescribing a course of oral glucocorticosteroids, or treatment with antibiotics in case of infection. In case of severe exacerbation, monotherapy with a combination of an inhaled glucocorticosteroid and a long-acting beta2-adrenergic agonist is not enough.
Transfer from oral therapy
If there is reason to believe that adrenal function has been impaired due to previous systemic glucocorticosteroid therapy, precautions should be taken when transferring patients to treatment with Symbicort.
The benefits of inhaled budesonide therapy generally minimize the need for oral corticosteroids, but patients who discontinue oral corticosteroid therapy may experience long-term adrenal insufficiency. Patients who have previously required acute high-dose corticosteroids or have received long-term treatment with high-dose inhaled corticosteroids may also be at risk. It is necessary to provide additional administration of glucocorticosteroids during periods of stress or surgery.
Excipients
Symbicort Turbuhaler contains lactose (< 1 mg/inhalation). Typically this amount does not cause problems in patients with lactose intolerance.
Interaction with other drugs
Concomitant use with itraconazole, ritonavir or other potent inhibitors of the cytochrome CYP3A4 isoenzyme should be avoided. If this is not possible, the time interval between the use of interacting drugs should be as long as possible. In patients taking strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, it is not recommended to use Symbicort Turbuhaler as maintenance therapy or for symptom relief.
Precautions for specific diseases
Precautions should be taken when treating patients with a prolonged QTc interval. The use of formoterol may cause prolongation of the QTc interval.
When beta2-agonists are used together with drugs that can cause or enhance the hypokalemic effect, for example, xanthine derivatives, steroids or diuretics, the hypokalemic effect of beta2-agonists may be enhanced. Special precautions should be taken in patients with unstable bronchial asthma who use short-acting bronchodilators to relieve attacks during exacerbation of severe bronchial asthma, since the risk of developing hypokalemia increases against the background of hypoxia and in other conditions when the likelihood of developing a hypokalemic effect increases. In such cases, it is recommended to monitor serum potassium levels.
During treatment, blood glucose concentrations should be monitored in patients with diabetes mellitus.
The need for the use and dose of inhaled glucocorticosteroids should be reconsidered in patients with active or inactive forms of pulmonary tuberculosis, fungal, viral or bacterial infections of the respiratory system.
Systemic action
Systemic effects may occur when using any inhaled glucocorticosteroids, especially when using high doses of drugs over a long period of time. Systemic effects are less likely to occur with inhalation therapy than with oral corticosteroids. Possible systemic effects include adrenal suppression, growth retardation in children and adolescents, decreased bone mineral density, cataracts, and glaucoma.
Due to the potential effect of inhaled glucocorticosteroids on bone mineral density, special attention should be paid to patients using high doses of the drug for a long period with risk factors for osteoporosis. Studies of long-term use of inhaled budesonide in children at an average daily dose of 400 mcg (metered dose) or adults at a daily dose of 800 mcg (metered dose) did not show a significant effect on bone mineral density. There is no data regarding the effect of high doses of Symbicort Turbuhaler on bone mineral density.
Adrenal dysfunction
Treatment with systemic corticosteroids or inhaled budesonide should not be abruptly discontinued.
Long-term treatment with high doses of inhaled corticosteroids, especially those exceeding recommended doses, can also lead to clinically significant adrenal suppression. Therefore, additional systemic use of glucocorticosteroids should be considered during periods of stressful situations, such as severe infectious diseases or planned operations. A sharp reduction in the dose of glucocorticosteroids can cause an acute adrenal crisis. Symptoms and signs that may be observed in acute adrenal crisis can be quite vague, but may include anorexia, abdominal pain, weight loss, fatigue, headache, nausea, vomiting, decreased level of consciousness, seizures, hypotension and hypoglycemia.
Paradoxical bronchospasm
As with any other inhalation therapy, paradoxical bronchospasm may occur with an immediate increase in wheezing after dosing. In this regard, you should stop therapy with Symbicort, reconsider treatment tactics and, if necessary, prescribe alternative therapy.
Pediatric patient population
It is recommended to regularly monitor the growth of children receiving long-term glucocorticosteroid therapy in inhaled form. In case of established growth retardation, therapy should be reconsidered in order to reduce the dose of inhaled glucocorticosteroid. It is necessary to carefully evaluate the ratio of the benefits of glucocorticosteroid therapy to the possible risk of growth retardation. When choosing therapy, it is recommended to consult a pediatric pulmonologist.
Based on limited data from studies of long-term corticosteroid use, it can be assumed that most children and adolescents treated with inhaled budesonide will eventually achieve normal adult height. However, minor short-term growth retardation has been reported, mainly in the first year of treatment.
Population of patients with COPD
Data from clinical studies of Symbicort Turbuhaler in patients with COPD with a pre-bronchodilation forced expiratory volume in the first second (FEV1) > 50% predicted and with a post-bronchodilator FEV1 < 70% predicted are not available.
Clinical studies and meta-analyses have shown that the use of inhaled corticosteroids during maintenance treatment of COPD may lead to an increased risk of pneumonia. Clinicians should be aware of the possibility of pneumonia in patients with COPD, since the clinical signs of pneumonia and exacerbation of the disease often overlap.
Side Effects
Side Effects
With the combined use of budesonide and formoterol, there was no increase in the incidence of adverse reactions. The most common adverse reactions associated with the use of the drug are such pharmacologically expected adverse reactions for beta2-adrenergic agonists, such as tremor and palpitations; symptoms are usually of moderate severity and resolve on their own within a few days after starting treatment.
Adverse reactions associated with the use of budesonide or formoterol are listed below by organ system class and incidence. The frequency of reactions is presented in the following gradation: very often (≥1/10), often (≥1/100, but <1/10), infrequently (≥1/1000, but <1/100), rarely (≥1/10000, but <1/1000), very rarely (<1/10000).
Infections and infestations: often – candidiasis of the oral mucosa and pharynx, pneumonia (in patients with COPD)
Immune system disorders: rarely – immediate and delayed hypersensitivity reactions (for example, dermatitis, exanthema, urticaria, pruritus, angioedema, anaphylactic reaction)
Endocrine disorders: very rarely – Cushing’s syndrome, suppression of adrenal function, growth retardation, decreased bone mineral density. Metabolic and nutritional disorders: rarely – hypokalemia; very rarely – hyperglycemia. Mental disorders: infrequently – aggressiveness, psychomotor agitation, anxiety, sleep disturbances; very rarely – depression, behavioral disorders (mainly in children)
Nervous system disorders: often – headache, tremor; infrequently – dizziness; very rarely – taste disturbances
Violations of the organ of vision: infrequently – blurred vision; very rarely – cataract, glaucoma
Cardiac disorders: often – palpitations; infrequently – tachycardia; rarely – arrhythmia (for example, atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia, extrasystole); very rarely – angina pectoris, prolongation of the QTc interval
Vascular disorders: very rarely – fluctuations in blood pressure Disorders of the respiratory system, chest and mediastinal organs: often – cough, hoarseness, mild irritation of the pharyngeal mucosa; rarely – bronchospasm
Gastrointestinal disorders: uncommon – nausea
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: uncommon – bruising
Muscle, skeletal and connective tissue disorders: uncommon – muscle cramps
Systemic effects of inhaled corticosteroids may occur when high doses are used over a long period of time.
The use of beta2-agonists can lead to an increase in the blood levels of insulin, free fatty acids, glycerol and ketone bodies.
Children
It is recommended to regularly monitor the growth of children receiving long-term treatment with inhaled glucocorticosteroids.
Interaction
Interaction
Pharmacokinetic interactions
Potent CYP3A4 inhibitors (eg, ketoconazole, itraconazole, voriconazole, posaconazole, clarithromycin, telithromycin, nefazodone and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) protease inhibitors) are likely to markedly increase budesonide plasma concentrations and concomitant use should be avoided. If this is not possible, the time interval between taking the inhibitor and budesonide should be as long as possible.
In patients taking strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, it is not recommended to use Symbicort Turbuhaler as maintenance therapy or for symptom relief.
The potent CYP3A4 inhibitor ketoconazole, when administered at a dose of 200 mg once daily, increased the plasma concentration of budesonide during concomitant oral administration (single dose of 3 mg) by an average of 6 times. When ketoconazole was prescribed 12 hours after budesonide, the concentration increased on average only 3 times; this suggests that dividing the administration time may reduce the increase in plasma concentrations. Limited data on this interaction for high doses of inhaled budesonide indicate the possibility of a marked increase in plasma drug concentrations (on average 4-fold) when itraconazole 200 mg is used once daily with inhaled budesonide (single dose of 1000 mcg).
Pharmacodynamic interactions
Beta blockers may weaken or inhibit the effect of formoterol. Therefore, Symbicort should not be co-administered with beta-blockers (including eye drops) unless there is a compelling reason to do so.
Concomitant use of quinidine, disopyramide, procainamide, phenothiazines, antihistamines (terfenadine) and tricyclic antidepressants may prolong the QTc interval and increase the risk of ventricular arrhythmia.
In addition, levodopa, levothyroxine, oxytocin and alcohol can reduce the tolerance of the heart muscle to beta2-agonists.
Co-administration of monoamine oxidase inhibitors, as well as drugs with similar properties, such as furazolidone and procarbazine, may cause an increase in blood pressure.
There is an increased risk of developing arrhythmias in patients undergoing general anesthesia with halogenated hydrocarbon preparations.
Concomitant use of other beta-adrenergic or anticholinergic drugs may have potentially additive bronchodilatory effects.
Hypokalemia may increase the susceptibility to the development of arrhythmias in patients taking cardiac glycosides.
Hypokalemia may result from therapy with beta2-agonists and may be exacerbated by concomitant use of xanthine derivatives, glucocorticosteroids and diuretics.
There was no interaction between budesonide and formoterol with other drugs used to treat bronchial asthma.
Children
Drug interaction studies were conducted only in adult patients.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms
Symptoms of formoterol overdose: tremor, headache, rapid heartbeat. In isolated cases, the development of tachycardia, hyperglycemia, hypokalemia, prolongation of the QTc interval, arrhythmia, nausea and vomiting was reported.
The use of formoterol at a dose of 90 mcg for 3 hours in patients with acute bronchial obstruction was safe.
In case of acute overdose of budesonide, even in significant doses, no clinically significant effects are expected. With chronic use of excessive doses, systemic effects of glucocorticosteroids, such as hypercortisolism and suppression of adrenal function, may occur.
If it is necessary to discontinue the drug Symbicort Turbuhaler due to an overdose of formoterol, which is part of the combination drug, the issue of prescribing an appropriate glucocorticosteroid should be considered.
Treatment
Supportive and symptomatic treatment may be prescribed.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At temperatures below 30 C, in places inaccessible to children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years. Do not use after expiration date.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
AstraZeneca AB, Sweden
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years. Do not use after the expiration date. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature below 30 C, out of the reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | AstraZeneca AB, Sweden |
| Medication form | metered inhalation powder |
| Brand | AstraZeneca AB |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Symbicort Turbuhaler, 160+4, 5 mcg/dose 120 doses with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.