No products in the cart.
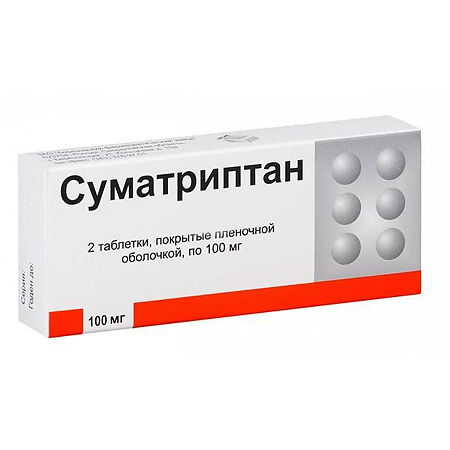
Sumatriptan tablets, 100 mg 2 pcs.
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Sumatriptan is an antimigraine agent.
Pharmacodynamics
Sumatriptan is a specific selective agonist of 5NT1D-serotonin receptors (5-hydroxytryptamine-1-like) located mainly in the blood vessels of the brain. Stimulation of 5HT1D-serotonin receptors leads to vasoconstriction. The drug does not affect other subtypes of 5HT-serotonin receptors (5HT2-5HT7).
In experimental studies it is shown that sumatriptan causes selective narrowing of carotid arteries, which supply blood to extracranial and intracranial tissues, including cerebral membranes (dilation of these vessels and/or ichothecia is the main mechanism of migraine development in humans), while not having a significant effect on cerebral blood flow.
It is also experimentally established that sumatriptan suppresses the activity of receptors of trigeminal afferent fiber endings. It eliminates nausea and photophobia associated with migraine attack.
Pharmacokinetics
Intake. After oral administration, sumatriptan is rapidly absorbed, after 45 min its plasma concentration reaches 70% of the maximum value. After oral intake of sumatriptan in a dose of 100 mg, maximum plasma concentration is reached in 2-2.5 hours and averages 54 ng/ml. Absolute bioavailability when administered orally is on average 14% due to presystemic metabolism and incomplete absorption.
Distribution. Binding with plasma proteins is 14-21%, total volume of distribution averages 170 l (2.4 l/kg).
Metabolism. Sumatriptan is metabolized by oxidation with the participation of monoamine oxidase (MAO) (mainly isoenzyme A) to form metabolites, the main of which is the indole acetic analog of sumatriptan, which has no pharmacological activity against 5HT1- and 5NT2-serotonin receptors, and its glucuronide.
Elimination. The elimination half-life is 2-2.5 hours. On average, plasma clearance is 1160 ml/minute, renal clearance is 260 ml/minute. Extra renal clearance is 40% after oral administration. It is excreted by the kidneys, mainly as metabolites (97% after oral administration) of free acid or glucuronide, the rest is excreted by the intestine.
Indications
Indications
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
1 film-coated tablet contains:
the active ingredient:
sumatriptan (sumatriptan succinate) 100.00 mg (140.00 mg).
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Overly (swallow the tablet whole with water).
The initial single dose is 50 mg; if necessary, the dose can be increased to 100 mg. If migraine symptoms do not disappear and do not decrease after the first dose, a second dose to stop an ongoing attack is not indicated.
To control subsequent attacks (when symptoms decrease or disappear and then resume), a second dose may be taken within the next 24 hours, provided that the interval between doses is at least 2 hours. The maximum daily dose when taken orally is 300 mg.
Interaction
Interaction
Possible prolonged vasospasm when concomitantly administered with ergotamine and ergotamine-containing drugs.
Possible decrease in the intensity of sumatriptan metabolism, increase in its concentration, with interaction between sumatriptan and MAO inhibitors.
In concomitant use of sumatriptan and drugs from the group of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, weakness, hyperreflexia, and impaired coordination of movements may occur.
The interaction of sumatriptan with propranololol, flunirizine, pizotifen and ethanol has not been noted.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
Sumatriptan is not intended to prevent migraine.
Sumatriptan should only be taken if the diagnosis of migraine is certain.
Sumatriptan should be used as soon as possible after a migraine attack, but the drug is equally effective at any stage of an attack.
If the first dose has no effect, the diagnosis should be clarified.
Patients of cardiovascular risk group should not start therapy without prior evaluation (post-menopausal women, men over 40 years of age, people with CHD risk factors). Before administering sumatriptan to patients with newly diagnosed or atypical migraine, other potentially dangerous neurological diseases should be excluded.
Pain and tightness in the chest may occur after taking sumatriptan. The pain may be intense and irradiate into the neck. If these symptoms are suspected to be a manifestation of CHD, an appropriate evaluation should also be performed.
Impact on driving ability and operating machinery
In migraine, as well as during sumatriptan therapy, drowsiness may develop. Therefore, during sumatriptan use, caution should be exercised when driving motor transport and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities requiring increased concentration and rapid psychomotor reactions.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Side effects
Side effects
The incidence of side effects is classified according to the recommendations of the World Health Organization: very frequently – at least 10%; frequently – at least 1%, but less than 10%; infrequently – at least 0.1%, but less than 1%; rarely – at least 0.01%, but less than 0.1%; very rarely – less than 0.01% (including single cases).
Cardiovascular system disorders: very rare – bradycardia, tachycardia, arrhythmia, transient increase of blood pressure (BP) (immediately after treatment start), transient signs of myocardial ischemia on electrocardiogram, coronary spasm, myocardial infarction, Raynaud’s syndrome, decrease of BP, “tides” of blood to the face.
Respiratory system disorders: often – shortness of breath, transient mucous membrane irritation or burning sensation in the nasal cavity or throat.
The digestive system: frequently – nausea, vomiting; slight increase in the activity of “liver” enzymes; very rarely – ischemic colitis, diarrhea, a feeling of discomfort in the abdominal area.
Nervous system disorders: frequently – dizziness, somnolence, sensitivity disorders, including paraesthesia, hypoesthesia; very rarely – seizures (usually with seizures in the anamnesis); unknown frequency – tremor, dystonia, anxiety.
Visually: infrequent – diplopia, flickering of “flickers” before eyes, nystagmus, scotoma, decreased visual acuity; very rare – partial transient loss of vision (it should be noted that visual disturbances may be associated with the attack of migraine).
Musculoskeletal system: often – myalgia; unknown frequency – neck stiffness, arthralgia.
Allergic reactions: very rare – skin rash, urticaria, pruritus, erythema, anaphylaxis.
Others: often – pain, tingling, sensation of heat, feeling of weakness and/or fatigue, nosebleed, feeling of tightness or heaviness (these symptoms are usually transient, but can be intense and occur in any part of the body, including the chest and neck); unknown frequency – increased sweating.
Overdose
Overdose
Sumatriptan did not cause any side effects when administered in a single subcutaneous dose of 12 mg. When administered subcutaneously at a dose greater than 16 mg or when administered orally greater than 400 mg, sumatriptan did not cause any unanticipated side effects other than those listed above.
Treatment: gastric lavage, administration of activated charcoal, patient monitoring for at least 10 hours, symptomatic therapy if necessary.
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C, in a dry place protected from light and out of the reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Berezovsky Pharmaceutical Plant, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Berezovsky Pharmaceutical Plant |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Sumatriptan tablets, 100 mg 2 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.