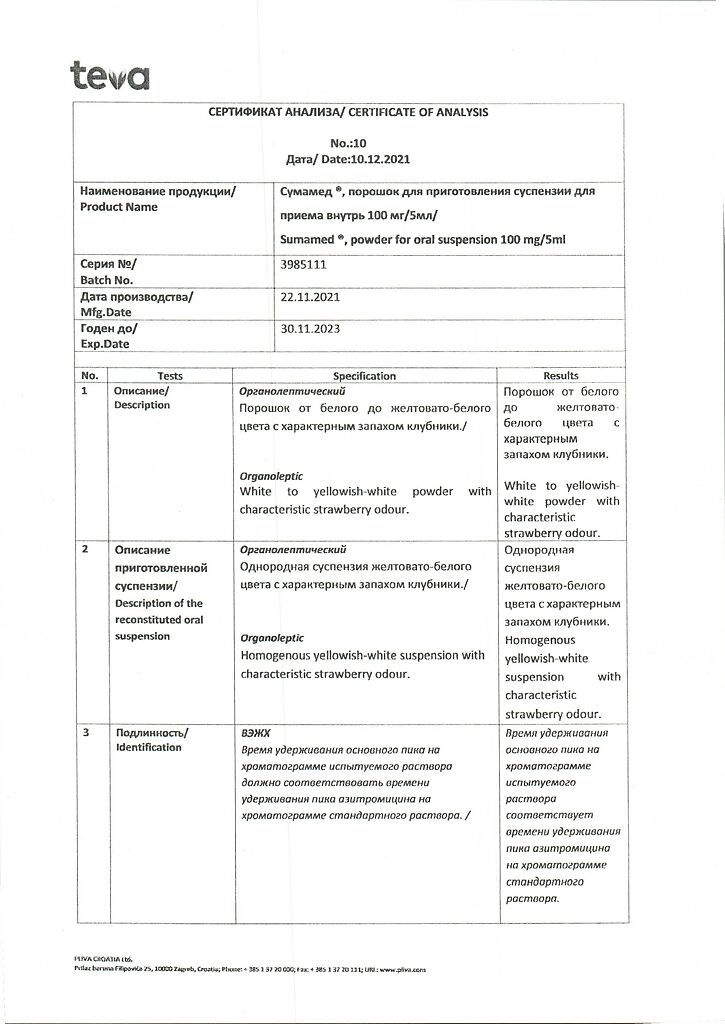
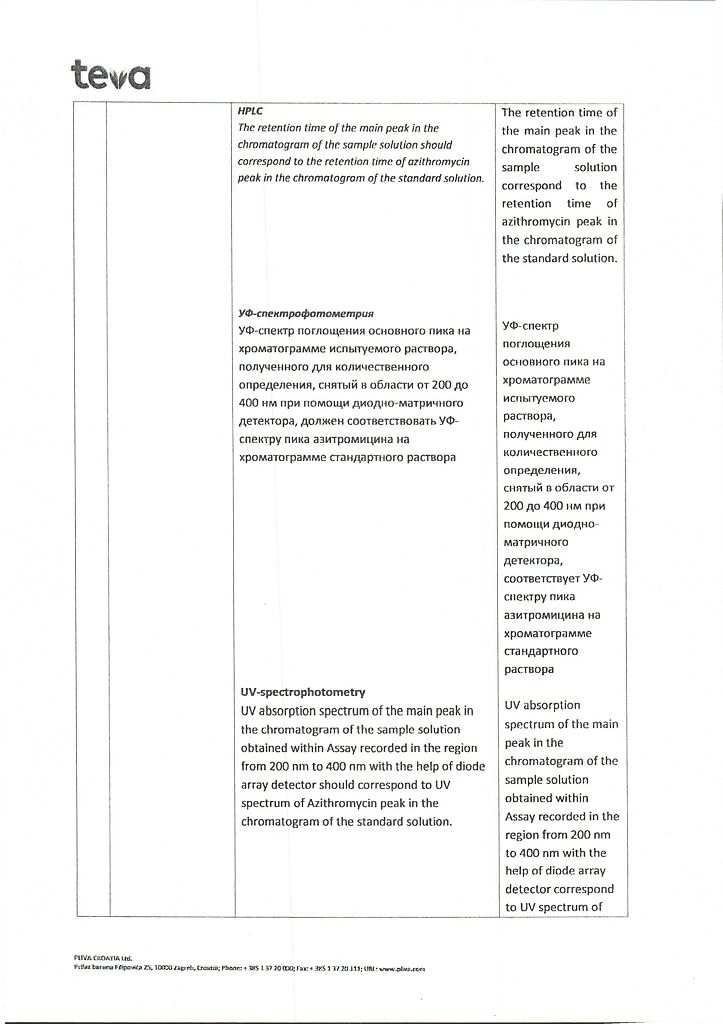
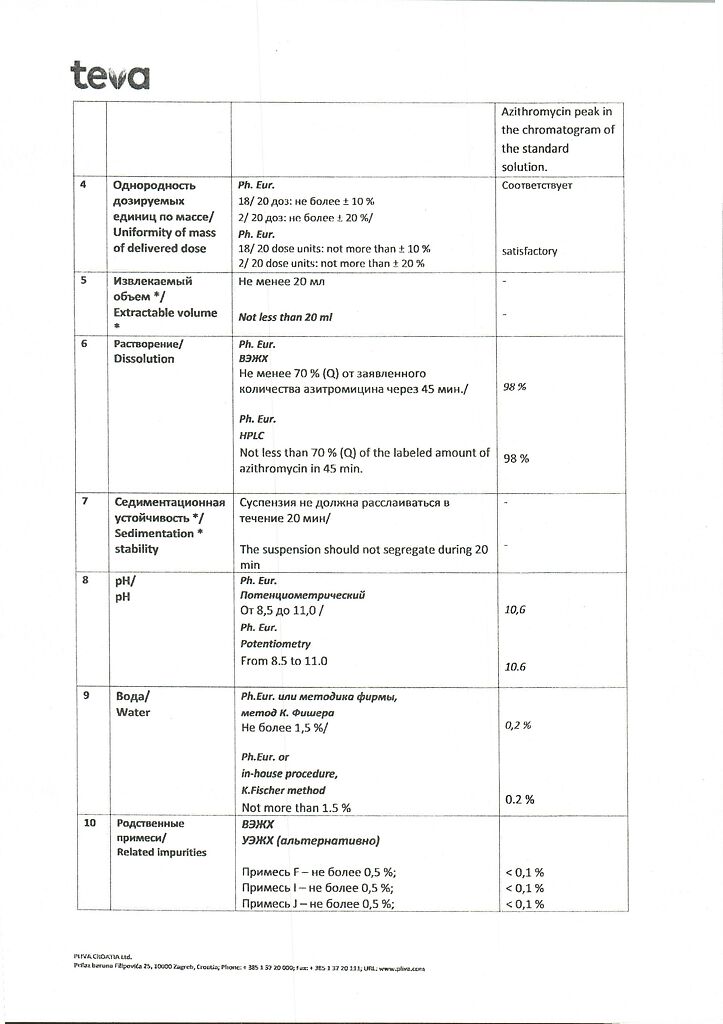
No products in the cart.
Sumamed, 100 mg/5 ml 20.925 g strawberry flavor
€6.28 €5.59
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group: antibiotic-azolid
ATCode: J01FA10
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics.
Azithromycin is a bacteriostatic broad-spectrum antibiotic of the group of macrolide-azalid. It has a broad spectrum of antimicrobial action. Azithromycin mechanism of action is associated with inhibition of microbial cell protein synthesis. Binding to 50S-subunit of ribosome, it inhibits peptide translocase at the translation stage and inhibits protein synthesis, slowing down the growth and reproduction of bacteria. In high concentrations it has a bactericidal effect.
It has activity against a number of Gram-positive, Gram-negative, anaerobic, intracellular and other microorganisms.
Microorganisms can be resistant to the antibiotic from the start or they can become resistant to it.
In most cases, susceptible microorganisms
1. Gram-positive aerobes
Staphylococcus aureus methicillin-sensitive Streptococcus pneumoniae Streptococcus pyogenes
- Gram-negative aerobes Haemophilus influenzae Haemophilus parainfluenzae Legionella pneumophila Moraxella catarrhalis
Pasteurella multocidaPasteurella multocida Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Anaerobes Clostridium perfringens Fusobacterium spp. Prevotella spp. Porphyriomonas
- Other microorganisms.Chlamydia trachomatis Chlamydia pneumoniae Chlamydia psittaci Mycoplasma pneumoniae Mycoplasma hominis
Borrelia burgdorferi
Microorganisms capable of developing resistance to azithromycin Gram-positive aerobes
Streptococcus pneumoniae penicillin-resistant Initially resistant microorganisms Gram-positive aerobes
Enterococcus faecalis
Staphylococci (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus has a very high frequency of acquired resistance to macrolides)
Gram-positive bacteria that are resistant to erythromycin.
Anaerobes
Bacteroides fragilis
Pharmacokinetics.
Azithromycin is well absorbed and rapidly distributed in the body after oral administration. After a single dose of 500 mg bioavailability is 37% (first pass effect), maximum concentration (0.4 mg/l) in blood is achieved after 2-3 hours, the volume of distribution is 31.1 l/kg, binding to proteins is inversely proportional to the concentration in blood and is 7-50%. It penetrates through cell membranes (effective in infections caused by intracellular pathogens). It is transported by phagocytes to the site of infection, where it is released in the presence of bacteria. Easily passes the histohematic barriers and enters the tissues. Concentration in tissues and cells is 10-50 times higher than in plasma, and in the focus of infection it is 24-34% higher than in healthy tissues.
Asithromycin has a very long half-life of 35-50 h. The tissue elimination half-life is much longer. The therapeutic concentration of azithromycin is maintained up to 5-7 days after the last dose. Azithromycin is mainly excreted unchanged – 50% by the intestine, 6% by the kidneys. In the liver it is demethylated, losing activity.
Indications
Indications
Infectious and inflammatory diseases caused by those sensitive to the drug
microorganisms:
Infections of the upper respiratory tract and ENT organs (pharyngitis/tonsillitis, sinusitis, otitis media);
Lower respiratory tract infections: acute bronchitis, exacerbation of chronic bronchitis, pneumonia, incl. caused by atypical pathogens;
Infections of the skin and soft tissues (erysipelas, impetigo, secondary infected dermatoses);
The initial stage of Lyme disease (borreliosis) is erythema migrans.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group: antibiotic-azalide
ATX code: J01FA10
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics.
Azithromycin is a broad-spectrum bacteriostatic antibiotic from the macrolide-azalide group. Has a wide spectrum of antimicrobial action. The mechanism of action of azithromycin is associated with the suppression of protein synthesis in microbial cells. By binding to the 50S subunit of the ribosome, it inhibits peptide translocase at the translation stage and suppresses protein synthesis, slowing down the growth and reproduction of bacteria. In high concentrations it has a bactericidal effect.
It is active against a number of gram-positive, gram-negative, anaerobic, intracellular and other microorganisms.
Microorganisms may initially be resistant to the action of the antibiotic or may acquire resistance to it.
In most cases, sensitive microorganisms
1. Gram-positive aerobes
Staphylococcus aureus methicillin-sensitive Streptococcus pneumoniae penicillin-sensitive Streptococcus pyogenes
Gram-negative aerobes Haemophilus influenzae Haemophilus parainfluenzae Legionella pneumophila Moraxella catarrhalis
Pasteurella multocida Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Anaerobes Clostridium perfringens Fusobacterium spp. Prevotella spp. Porphyriomonas
Other microorganisms Chlamydia trachomatis Chlamydia pneumoniae Chlamydia psittaci Mycoplasma pneumoniae Mycoplasma hominis
Borrelia burgdorferi
Microorganisms that can develop resistance to azithromycin Gram-positive aerobes
Streptococcus pneumoniae penicillin-resistant Initially resistant microorganisms Gram-positive aerobes
Enterococcus faecalis
Staphylococci (methicillin-resistant staphylococci have a very high frequency of acquired resistance to macrolides)
Gram-positive bacteria resistant to erythromycin.
Anaerobes
Bacteroides fragilis
Pharmacokinetics.
After oral administration, azithromycin is well absorbed and quickly distributed in the body. After a single dose of 500 mg, bioavailability is 37% (the “first pass” effect), the maximum concentration (0.4 mg/l) in the blood is created after 2-3 hours, the volume of distribution is 31.1 l/kg, protein binding is inversely proportional to the concentration in the blood and is 7-50%. Penetrates through cell membranes (effective against infections caused by intracellular pathogens). Transported by phagocytes to the site of infection, where it is released in the presence of bacteria. Easily passes histohematic barriers and enters tissues. The concentration in tissues and cells is 10-50 times higher than in plasma, and at the site of infection it is 24-34% higher than in healthy tissues.
Azithromycin has a very long half-life – 35-50 hours. The half-life from tissues is much longer. The therapeutic concentration of azithromycin lasts up to 5-7 days after taking the last dose. Azithromycin is excreted mainly unchanged – 50% by the intestines, 6% by the kidneys. In the liver it is demethylated, losing activity.
Special instructions
Special instructions
When using the drug Sumamed® in patients with diabetes mellitus, as well as on a low-calorie diet, it is necessary to take into account that the suspension contains sucrose (0.32 XE/5 ml).
If you miss one dose of Sumamed®, the missed dose should be taken as soon as possible, and subsequent doses should be taken at intervals of 24 hours.
Sumamed® should be taken at least one hour before or two hours after taking antacids.
The drug Sumamed® should be taken with caution in patients with mild to moderate liver dysfunction due to the possibility of developing fulminant hepatitis and severe liver failure.
If there are symptoms of impaired liver function, such as rapidly increasing asthenia, jaundice, darkening of urine, tendency to bleeding, hepatic encephalopathy, therapy with Sumamed® should be stopped and a study of the functional state of the liver should be performed.
If renal function is impaired: in patients with GFR 10 – 80 ml/min, no dose adjustment is required.
As with the use of other antibacterial drugs, during therapy with Sumamed®, patients should be regularly examined for the presence of non-responsive microorganisms and signs of the development of superinfections, including fungal ones.
The drug Sumamed® should not be used in longer courses than indicated in the instructions, since the pharmacokinetic properties of azithromycin allow us to recommend a short and simple dosage regimen.
There is no data on a possible interaction between azithromycin and ergotamine and dihydroergotamine derivatives, but due to the development of ergotism with the simultaneous use of macrolides with ergotamine and dihydroergotamine derivatives, this combination is not recommended.
With long-term use of the drug Sumamed®, the development of pseudomembranous colitis caused by Clostridium difficile, both in the form of mild diarrhea and severe colitis, is possible. If antibiotic-associated diarrhea develops while taking the drug Sumamed®, as well as 2 months after the end of therapy, clostridial drugs should be excluded
pseudomembranous colitis. Do not use drugs that inhibit intestinal motility.
When treated with macrolides, including azithromycin, prolongation of cardiac repolarization and QT interval was observed, increasing the risk of developing cardiac arrhythmias, including torsade de pointes, which can lead to cardiac arrest.
Caution should be exercised when using the drug Sumamed® in patients with the presence of proarrhythmogenic factors (especially in elderly patients), including congenital or acquired prolongation of the QT interval; in patients taking antiarrhythmic drugs of classes IA (quinidine, procainamide), III (dofetilide, amiodarone and sotalol), cisapride, terfenadine, antipsychotic drugs (pimozide), antidepressants (citalopram), fluoroquinolones (moxifloxacin and levofloxacin), with disturbances of water and electrolyte balance, especially in the case of hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia, clinically significant bradycardia, cardiac arrhythmia, or severe heart failure.
The use of Sumamed® may provoke the development of myasthenic syndrome or cause an exacerbation of myasthenia.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery
If undesirable effects on the nervous system and organ of vision develop, caution should be exercised when performing actions that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Azithromycin
Composition
Composition
1 g of powder for oral suspension contains:
active ingredient:
azithromycin dihydrate* – 25.047 mg, equivalent to azithromycin 23.895 mg;
excipients:
sucrose* 929.753 mg,
sodium phosphate 20.00 mg,
hyprolose 1.60 mg,
xanthan gum 1.60 mg,
strawberry flavor 10,000 mg,
titanium dioxide 5,000 mg,
colloidal silicon dioxide 7,000 mg.
* values are based on the theoretical activity of the substance 95.4%;
the amount of sucrose may vary depending on the actual activity of azithromycin.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
During pregnancy and breastfeeding, it is used only if the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus and child. If it is necessary to use the drug during breastfeeding, it is recommended to stop breastfeeding.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to azithromycin, erythromycin, other macrolides or ketolides, or other components of the drug; severe liver dysfunction; sucrase/isomaltase deficiency, fructose intolerance, glucose-galactose malabsorption; children up to 6 months; simultaneous use of ergotamine and dihydroergotamine.
With caution
Myasthenia; mild to moderate liver dysfunction; end-stage renal failure with GFR (glomerular filtration rate) less than 10 ml/min; in patients with the presence of proarrhythmogenic factors (especially in elderly patients): with congenital or acquired prolongation of the QT interval, in patients receiving therapy with antiarrhythmic drugs of classes IA (quinidine, procainamide), III (dofetilide, amiodarone and sotalol), cisapride, terfenadine, antipsychotic drugs (pimozide), antidepressants (citalopram), fluoroquinolones (moxifloxacin and levofloxacin), with disturbances in water and electrolyte balance, especially in the case of hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia, clinically significant bradycardia, cardiac arrhythmia, or severe heart failure; simultaneous use of digoxin, warfarin, cyclosporine, diabetes mellitus.
Side Effects
Side Effects
The frequency of side effects is classified in accordance with the recommendations of the World Health Organization: very often – at least 10%; often – at least 1%, but less than 10%; infrequently – not less than 0.1%, but less than 1%; rarely – not less than 0.01%, but less than 0.1%; very rarely – less than 0.01%; unknown frequency – cannot be estimated based on available data.
Infectious diseases: uncommon – candidiasis, including oral mucosa, vaginal infection, pneumonia, fungal infection, bacterial infection, pharyngitis, gastroenteritis, respiratory diseases, rhinitis; unknown frequency – pseudomembranous colitis.
From the blood and lymphatic system: infrequently – leukopenia, neutropenia, eosinophilia; very rarely – thrombocytopenia, hemolytic anemia.
From the side of metabolism and nutrition: infrequently – anorexia.
Allergic reactions: uncommon – angioedema, hypersensitivity reaction; unknown frequency – anaphylactic reaction.
From the nervous system: often – headache; infrequently – dizziness, disturbance of taste, paresthesia, drowsiness, insomnia, nervousness; rarely
– agitation; unknown frequency – hypoesthesia, anxiety, aggression, fainting, convulsions, psychomotor hyperactivity, loss of smell, perverted sense of smell, loss of taste, myasthenia gravis, delirium, hallucinations.
From the side of the organ of vision: infrequently – visual impairment.
From the organ of hearing and labyrinthine disorders: infrequently – hearing loss, vertigo; unknown frequency – hearing impairment, including deafness and/or tinnitus.
From the cardiovascular system: infrequently – palpitations,
“flushes” of blood to the face; unknown frequency – decreased blood pressure, increased QT interval on the electrocardiogram, pirouette-type arrhythmia, ventricular tachycardia.
From the respiratory system: infrequently – shortness of breath, nosebleeds.
From the gastrointestinal tract: very often – diarrhea; often – nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain; uncommon – flatulence, dyspepsia, constipation, gastritis, dysphagia, bloating, dry oral mucosa, belching, ulcers of the oral mucosa, increased secretion of the salivary glands; very rarely – change in tongue color, pancreatitis.
From the liver and biliary tract: infrequently – hepatitis; rarely – impaired liver function, cholestatic jaundice; unknown frequency – liver failure (in rare cases – fatal, mainly due to severe liver dysfunction); liver necrosis, fulminant hepatitis.
From the skin and subcutaneous tissues: infrequently – skin rash, itching, urticaria, dermatitis, dry skin, sweating; rarely – photosensitivity reaction; unknown frequency – Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, erythema multiforme, drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic manifestations (DRESS syndrome).
From the musculoskeletal system: uncommon – osteoarthritis, myalgia, back pain, neck pain; unknown frequency – arthralgia.
From the kidneys and urinary tract: infrequently – dysuria, pain in the kidney area; unknown frequency – interstitial nephritis, acute renal failure.
From the genital organs and mammary gland: infrequently – metrorrhagia, dysfunction of the testicles.
Other: infrequently – edema, asthenia, malaise, feeling of fatigue, facial swelling, chest pain, fever, peripheral edema.
Laboratory data: often – a decrease in the number of lymphocytes, an increase in the number of eosinophils, an increase in the number of basophils, an increase in the number of monocytes, an increase in the number of neutrophils, a decrease in the concentration of bicarbonates in the blood plasma; infrequently – increased activity of aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, increased concentration of bilirubin in the blood plasma, increased concentration of urea in the blood plasma, increased concentration of creatinine in the blood plasma, change in the potassium content in the blood plasma, increased activity of alkaline phosphatase in the blood plasma, increased chloride content in the blood plasma, increased concentration of glucose in the blood, increased platelet count, decreased hematocrit, increased concentration of bicarbonates in plasma blood, changes in sodium content in blood plasma.
Interaction
Interaction
Antacids
Antacids do not affect the bioavailability of azithromycin, but reduce the maximum blood concentration by 30%, so the drug should be taken at least one hour before or two hours after taking these drugs.
drugs and food.
Cetirizine
Concomitant use of azithromycin with cetirizine (20 mg) for 5 days in healthy volunteers did not lead to pharmacokinetic interaction or a significant change in the QT interval.
Didanosine (dideoxyinosine)
The simultaneous use of azithromycin (1200 mg/day) and didanosine (400 mg/day) in 6 HIV-infected patients did not reveal changes in the pharmacokinetic indications of didanosine compared to the placebo group.
Digoxin (P-glycoprotein substrates)
Concomitant use of macrolide antibiotics, including azithromycin, with P-glycoprotein substrates, such as digoxin, leads to increased concentrations of P-glycoprotein substrate in the blood serum. Thus, with the simultaneous use of azithromycin and digoxin, it is necessary to take into account the possibility of increasing the concentration of digoxin in the blood serum.
Zidovudine
Concomitant use of azithromycin (single dose of 1000 mg and multiple doses of 1200 mg or 600 mg) has a minor effect on the pharmacokinetics, including renal excretion of zidovudine or its glucuronide metabolite. However, the use of azithromycin caused an increase in the concentration of phosphorylated zidovudine, a clinically active metabolite in peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
The clinical significance of this fact is unclear.
Azithromycin interacts weakly with isoenzymes of the cytochrome P450 system.
Azithromycin has not been shown to participate in pharmacokinetic interactions similar to erythromycin and other macrolides. Azithromycin is not an inhibitor or inducer of cytochrome P450 isoenzymes.
Ergot alkaloids
Given the theoretical possibility of ergotism, the simultaneous use of azithromycin with ergot alkaloid derivatives is not recommended.
Pharmacokinetic studies were conducted on the simultaneous use of azithromycin and drugs whose metabolism occurs with the participation of isoenzymes of the cytochrome P450 system.
Atorvastatin
Concomitant use of atorvastatin (10 mg daily) and azithromycin (500 mg daily) did not cause changes in atorvastatin plasma concentrations (based on an HMC-CoA reductase inhibition assay). However, in the post-marketing period, isolated case reports of rhabdomyolysis have been received in patients receiving concomitant azithromycin and statins.
Carbamazepine
Pharmacokinetic studies involving healthy volunteers did not reveal a significant effect on the plasma concentrations of carbamazepine and its active metabolite in patients receiving concomitant azithromycin.
Cimetidine
In pharmacokinetic studies of the effect of a single dose of cimetidine on the pharmacokinetics of azithromycin, no changes in the pharmacokinetics of azithromycin were detected when cimetidine was used 2 hours before azithromycin.
Indirect anticoagulants (coumarin derivatives)
In pharmacokinetic studies, azithromycin did not affect the anticoagulant effect of a single 15 mg dose of warfarin administered to healthy volunteers. Potentiation of the anticoagulant effect has been reported after simultaneous use of azithromycin and indirect anticoagulants (coumarin derivatives). Although a causal relationship has not been established, the need for frequent monitoring of prothrombin time should be considered when using azithromycin in patients receiving indirect oral anticoagulants (coumarin derivatives).
Cyclosporine
In a pharmacokinetic study involving healthy volunteers who took azithromycin (500 mg/day once) orally for 3 days, followed by cyclosporine (10 mg/kg/day once), a significant increase in the maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) and the area under the concentration-time curve (AUC0-5) of cyclosporine was detected. Caution is advised when using these drugs together. If simultaneous use of these drugs is necessary, it is necessary to monitor the concentration of cyclosporine in the blood plasma and adjust the dose accordingly.
Efavirenz
Concomitant use of azithromycin (600 mg/day once) and efavirenz (400 mg/day) daily for 7 days did not cause any clinically significant pharmacokinetic interaction.
Fluconazole
Concomitant use of azithromycin (1200 mg once) did not change the pharmacokinetics of fluconazole (800 mg once). The total exposure and half-life of azithromycin did not change with simultaneous use of fluconazole, however, a decrease in Cmax of azithromycin was observed (by 18%), which had no clinical significance.
Indinavir
Concomitant use of azithromycin (1200 mg once) did not cause a statistically significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of indinavir (800 mg three times a day for 5 days).
Methylprednisolone
Azithromycin does not have a significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of methylprednisolone.
Nelfinavir
The simultaneous use of azithromycin (1200 mg) and nelfinavir (750 mg 3 times a day) causes an increase in the equilibrium concentrations of azithromycin in the blood serum. No clinically significant side effects were observed and no dose adjustment of azithromycin was required when used concomitantly with nelfinavir.
Rifabutin
The simultaneous use of azithromycin and rifabutin does not affect the concentration of each drug in the blood serum. Neutropenia has sometimes been observed with simultaneous use of azithromycin and rifabutin. Although neutropenia has been associated with the use of rifabutin, a causal relationship between the use of the combination of azithromycin and rifabutin and neutropenia has not been established.
Sildenafil
When used in healthy volunteers, there was no evidence of the effect of azithromycin (500 mg/day daily for 3 days) on the AUC and Cmax of sildenafil or its main circulating metabolite.
Terfenadine
In pharmacokinetic studies, there was no evidence of interaction between azithromycin and terfenadine. There have been isolated cases reported where the possibility of such an interaction could not be completely excluded, but there was no concrete evidence that such an interaction occurred.
It has been found that the simultaneous use of terfenadine and macrolides can cause arrhythmia and prolongation of the QT interval.
Theophylline
No interaction has been detected between azithromycin and theophylline.
Triazolam/midazolam
No significant changes in pharmacokinetic parameters were detected with simultaneous use of azithromycin with triazolam or midazolam in therapeutic doses.
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole
Concomitant use of trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole with azithromycin did not show a significant effect on Cmax, total exposure or renal excretion of trimethoprim or sulfamethoxazole. Azithromycin serum concentrations were consistent with those found in other studies.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: nausea, temporary hearing loss, vomiting, diarrhea.
Treatment: symptomatic therapy.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
Powder for preparing a suspension – 2 years. Prepared suspension – 5 days.
Do not use after expiration date.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Pliva Hrvatska d.o.o., Croatia
Additional information
| Shelf life | Powder for suspension preparation – 2 years. Prepared suspension – 5 days. Do not use after the expiration date. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store at the temperature not more than 25 °С. Keep out of reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Pliva Hrvatska d.o.o., Croatia |
| Medication form | Powder for oral suspension |
| Brand | Pliva Hrvatska d.o.o. |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Sumamed, 100 mg/5 ml 20.925 g strawberry flavor with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.