No products in the cart.
Spasmalgon Effect, 10 pcs.
€6.02 €5.35
Description
Combination drug, has analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic, antipyretic effect.
Paracetamol is a non-narcotic analgesic, has antipyretic and analgesic effect caused by blockade of cyclooxygenase (COX) in the central nervous system (CNS) and effects on the centers of pain and thermoregulation.
Naproxen is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effect due to non-selective inhibition of COX activity which regulates prostaglandin synthesis.
Caffeine causes dilatation of blood vessels in skeletal muscles, heart, kidneys; it increases mental and physical performance, eliminates fatigue and sleepiness; it increases permeability of histohematic barriers and increases bioavailability of nonnarcotic analgesics, thus enhancing therapeutic effect. It has a tonic effect on cerebral vessels.
Drotaverine has myotropic antispasmodic effect caused by inhibition of phosphodiesterase IV, acts on the smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), biliary tract, urogenital system, vessels.
Pheniramine is an H1-histamine receptor blocker. It has antispasmodic and mild sedative effects, reduces the phenomena of exudation, and increases the analgesic effect of paracetamol and naproxen.
Pharmacokinetics:
Paracetamol
Characterized by high and rapid absorption from the GI tract, mainly in the small intestine. The time of reaching maximum plasma concentration (TCmax) is 0.5-1.5 hours after oral administration. Maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) is 5-20 µg/ml. Binding to plasma proteins is insignificant – 15%.
Paracetamol is evenly distributed and penetrates through the blood-brain barrier, as well as into most body tissues. The estimated volume of distribution is 0.95 l/kg. It is metabolized in the liver (90-95%): 80% enters into conjugation reactions with glucuronic acid and sulfates to form inactive metabolites; 17% undergoes hydroxylation to form 8 active metabolites, which conjugate with glutathione to form already inactive metabolites.
In glutathione deficiency these metabolites can block enzyme systems of hepatocytes and cause their necrosis. CYP2E1 isoenzyme is also involved in metabolism of the drug. The elimination half-life (T1/2) is 1.5-2.5 hours. It is excreted by the kidneys as metabolites, mainly conjugates, only 3% unchanged. The drug clearance decreases and T1/2 increases in elderly patients.
Naproxen
The absorption from the gastrointestinal tract of naproxen is fast and complete. Bioavailability is 95%. Food intake has almost no effect on the completeness or rate of absorption. The tCmax is 1-2 hours. Binding to plasma proteins is more than 99%. Equilibrium concentration is reached by 4-5 doses of the drug (2-3 days). Metabolized in the liver to dimethylnaproxen with the participation of CYP2C9 isoenzyme. T1/2 is 12-15 hours. Clearance is 0.13 ml/min/kg. It is excreted by kidneys (98%), 10% of which are unchanged; 0.5-2.5% of the taken dose is excreted in the bile. Cumulation of metabolites is possible in renal insufficiency.
Caffeine
The caffeine contained in the drug is almost completely and quickly absorbed, the maximum concentration in plasma is reached within 1 hour. It quickly passes through the blood-brain and placental barriers, enters the breast milk, and is eliminated (including as metabolites) mainly by the kidneys about 65-80%. The main metabolites are 1-methylxanthine, 1-methylureic acid and acetylated derivatives of uracil, a small amount of caffeine is converted to theophylline and theobromine. T1/2 is 3.5 hours.
Drotaverine
In oral administration, absorption of drotaverine is high and rapid. Bioavailability is 100%. After presystemic metabolism, 65% of the administered dose of drotaverine enters the systemic bloodstream. Time to reach Cmax in blood is 45-60 minutes. Binding to plasma proteins is 95-97%, mainly to albumin, gamma- and beta-globulins, as well as as high-density lipoproteins. It is evenly distributed in tissues, penetrates into smooth muscle cells. It does not penetrate through the blood-brain barrier.
Drotaverine and/or its metabolites may slightly penetrate through the placental barrier. The T1/2 is 8-10 hours. It is almost completely metabolized in the liver by O-desethylation. Metabolites rapidly conjugate with glucuronic acid. The main metabolite is 4′-dezethyldrotaverine, the other metabolites are 6-dezethyldrotaverine and 4′-dezethyldrotaveraldine. T1/2 is 8-10 hours. In 72 hours it is almost completely eliminated from the body. Mostly (more than 50% of drotaverine) is excreted by the kidneys, mainly as metabolites, to a lesser extent (about 30%) in the bile. Unchanged drotaverine is not detected in the urine.
Pheniramine
The maximum concentration of pheniramine in blood plasma is reached after about 1-2.5 hours. T1/2 is 16-19 hours. 70-83% of the dose taken is excreted from the body through the kidneys as metabolites or unchanged.
Indications
Indications
– Pain syndrome of various origins, including pain in joints and muscles; for radiculitis, algodismenorrhea (menstrual pain), neuralgia, toothache, headache (including headaches caused by cerebral vasospasm);
– pain syndrome associated with spasm of smooth muscles, including chronic cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, postcholecystectomy syndrome, renal colic;
– post-traumatic and postoperative pain syndrome, including those accompanied by inflammation;
– colds accompanied by febrile syndrome (as symptomatic therapy).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
The combined drug has analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic, antipyretic effects.
Paracetamol is a non-narcotic analgesic that has an antipyretic and analgesic effect due to the blockade of cyclooxygenase (COX) in the central nervous system (CNS) and its effect on the centers of pain and thermoregulation.
Naproxen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that has anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effects associated with non-selective suppression of COX activity, which regulates prostaglandin synthesis.
Caffeine – causes dilation of blood vessels in skeletal muscles, heart, kidneys; increases mental and physical performance, helps eliminate fatigue and drowsiness; increases the permeability of histohematic barriers and increases the bioavailability of non-narcotic analgesics, thereby enhancing the therapeutic effect. It has a tonic effect on the blood vessels of the brain.
Drotaverine – has a myotropic antispasmodic effect due to inhibition of phosphodiesterase IV, acts on the smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), biliary tract, genitourinary system, blood vessels.
Pheniramine is an H1-histamine receptor blocker. It has an antispasmodic and mild sedative effect, reduces exudation, and also enhances the analgesic effect of paracetamol and naproxen.
Pharmacokinetics:
Paracetamol
It is characterized by high and rapid absorption from the gastrointestinal tract, mainly in the small intestine. The time to reach maximum concentration in blood plasma (TCmax) is 0.5-1.5 hours after oral administration. The maximum concentration in blood plasma (Cmax) is 5-20 mcg/ml. The connection with plasma proteins is insignificant – 15%.
Paracetamol is evenly distributed and penetrates the blood-brain barrier, as well as into most body tissues. The estimated volume of distribution is 0.95 l/kg. Metabolized in the liver (90-95%): 80% enters into conjugation reactions with glucuronic acid and sulfates to form inactive metabolites; 17% undergoes hydroxylation to form 8 active metabolites, which conjugate with glutathione to form inactive metabolites.
With a lack of glutathione, these metabolites can block the enzyme systems of hepatocytes and cause their necrosis. The CYP2E1 isoenzyme is also involved in the metabolism of the drug. The half-life (T1/2) is 1.5-2.5 hours. Excreted by the kidneys in the form of metabolites, mainly conjugates, only 3% unchanged. In elderly patients, drug clearance decreases and T1/2 increases.
Naproxen
Absorption from the gastrointestinal tract of naproxen is rapid and complete. Bioavailability – 95%. Food intake has virtually no effect on either the completeness or the rate of absorption. TCmax – 1-2 hours. Plasma protein binding is more than 99%. Equilibrium concentration is achieved after taking 4-5 doses of the drug (2-3 days). Metabolized in the liver to dimethylnaproxen with the participation of the CYP2C9 isoenzyme. T1/2 – 12-15 hours. Clearance – 0.13 ml/min/kg. Excreted by the kidneys (98%), 10% of which is unchanged; 0.5-2.5% of the dose taken is excreted in bile. In case of renal failure, accumulation of metabolites is possible.
Caffeine
Caffeine, which is part of the drug, is almost completely and quickly absorbed, the maximum concentration in the blood plasma is reached after 1 hour. Quickly passes through the blood-brain and placental barriers, enters breast milk, and is excreted (including in the form of metabolites) mainly by the kidneys, about 65-80%. The main metabolites are 1-methylxanthine, 1-methyluric acid and acetylated uracil derivatives; a small amount of caffeine is converted to theophylline and theobromine. T1/2 – 3.5 hours.
Drotaverine
When taken orally, absorption of drotaverine is high and rapid. Bioavailability – 100%. After first-pass metabolism, 65% of the administered dose of drotaverine enters the systemic circulation. The time to reach Cmax in the blood is 45-60 minutes. Plasma protein binding is 95-97%, mainly with albumin, gamma and beta globulins, as well as high-density lipoproteins. Evenly distributed in tissues, penetrates smooth muscle cells. Does not penetrate the blood-brain barrier.
Drotaverine and/or its metabolites may slightly penetrate the placental barrier. T1/2 – 8-10 hours. Almost completely metabolized in the liver by O-desethylation. Metabolites quickly conjugate with glucuronic acid. The main metabolite is 4′-desethyldrotaverine, other metabolites are 6-desethyldrotaverine and 4′-desethyldrotaveraldine. T1/2 – 8-10 hours. Within 72 hours it is almost completely eliminated from the body. Basically (more than 50% of drotaverine) is excreted by the kidneys, mainly in the form of metabolites, to a lesser extent (about 30%) – with bile. Unchanged drotaverine is not detected in urine.
Pheniramine
The maximum concentration of pheniramine in blood plasma is achieved after approximately 1-2.5 hours. T1/2 – 16-19 hours. 70-83% of the dose taken is excreted from the body through the kidneys in the form of metabolites or unchanged.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Avoid simultaneous use of SPAZMALGON® EFFECT with other products containing paracetamol and/or other NSAIDs, including products to relieve symptoms of colds, flu and nasal congestion.
When using the drug SPAZMALGON® EFFECT for more than 5-7 days, peripheral blood parameters and the functional state of the liver should be monitored. Paracetamol distorts the results of laboratory tests of glucose and uric acid in blood plasma.
If it is necessary to determine 17-ketosteroids, SPAZMALGON® EFFECT should be discontinued 48 hours before the study.
Please note that naproxen increases bleeding time.
The effect of caffeine on the central nervous system depends on the type of nervous system and can manifest itself as both excitation and inhibition of higher nervous activity.
During the treatment period, the patient should avoid drinking alcohol.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles. Wed and fur.:
In some cases, a decrease in concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions is possible, therefore, during the treatment period, the patient should be careful when driving vehicles and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Paracetamol, Naproxen, Caffeine, Drotaverine, Pheniramine
Composition
Composition
1 film-coated tablet contains:
active ingredients: paracetamol 325.0 mg, naproxen 100.0 mg, caffeine 50.0 mg, drotaverine hydrochloride 40.0 mg, pheniramine maleate 10.0 mg;
excipients: microcrystalline cellulose 118.6 mg, pregelatinized corn starch 30.0 mg, hyprolose 20.0 mg, croscarmellose sodium 60.0 mg, citric acid 10.0 mg, disodium edetate 0.4 mg, ascorbic acid 20.0 mg, talc 12.0 mg, magnesium stearate 4.0 mg;
film coating: Opadry fx green 65 F210000 30.0 mg (polyvinyl alcohol 14.100 mg, talc 6.588 mg, macrogol 3.990 mg, pearlescent pigment* 3.000 mg, polysorbate 80 0.810 mg, titanium dioxide 0.750 mg, dye-based aluminum varnish indigo carmine 0.507 mg, aluminum varnish based on quinoline yellow dye 0.255 mg).
*Pearlescent pigment consists of mica and contains 69-75% potassium aluminosilicate (E555) and 25-31% titanium dioxide (E171).
Contraindications
Contraindications
– Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
– erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract (in the acute phase);
– gastrointestinal bleeding;
– complete or incomplete combination of bronchial asthma, recurrent polyposis of the nose and paranasal sinuses and intolerance to acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs (including a history);
– severe liver failure;
– severe renal failure;
– inhibition of bone marrow hematopoiesis;
– condition after coronary artery bypass surgery;
– severe organic diseases of the cardiovascular system (including acute myocardial infarction);
– paroxysmal tachycardia;
– frequent ventricular extrasystole;
– severe arterial hypertension;
– hyperkalemia;
– pregnancy and breastfeeding;
– children and adolescents up to 18 years of age.
With caution:
The drug should be used with caution in patients with cerebrovascular diseases, diabetes mellitus, peripheral arterial diseases, a history of ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, mild or moderate renal and hepatic insufficiency, viral hepatitis, alcoholic liver damage, benign hyperbilirubinemia (Gilbert, Dubin-Johnson and Rotor syndromes), epilepsy, a tendency to seizures, deficiency glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, in elderly patients.
If any of the listed diseases/conditions are present, the patient should consult a doctor before using the drug.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Allergic reactions: skin rash, itching, urticaria, angioedema.
From the hematopoietic organs: thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, agranulocytosis, anemia, methemoglobinemia.
From the side of the central nervous system: agitation, anxiety, increased reflexes, tremor, headache, sleep disturbances, dizziness, decreased concentration.
From the cardiovascular system: palpitations, arrhythmias, increased blood pressure (BP).
From the digestive system: erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, nausea, vomiting, epigastric discomfort, abdominal pain, constipation, impaired liver function.
From the urinary system: impaired renal function.
From the senses: hearing loss, tinnitus, increased intraocular pressure in patients with angle-closure glaucoma.
Other: dermatitis, tachypnea (increased breathing).
If any of these side effects get worse, or the patient notices any other side effects not listed in the instructions, he should inform the doctor.
Interaction
Interaction
When taking the drug SPAZMALGON® EFFECT simultaneously with barbiturates, tricyclic antidepressants, rifampicin, and alcohol-containing drinks, the risk of hepatotoxicity increases (these combinations should be avoided).
Paracetamol enhances the effect of indirect anticoagulants and reduces the effectiveness of uricosuric drugs.
Long-term use of barbiturates reduces the effectiveness of paracetamol.
The simultaneous use of paracetamol with ethanol (drinks and medications containing alcohol) increases the risk of acute pancreatitis.
Inhibitors of microsomal oxidation (including cimetidine) reduce the risk of hepatotoxicity of paracetamol.
Diflunisal increases the plasma concentration of paracetamol by 50%, which increases the risk of hepatotoxicity.
Naproxen can cause a decrease in the diuretic effect of furosemide, an increase in the effect of indirect anticoagulants, increases the toxicity of sulfonamides and methotrexate, reduces the excretion of lithium and increases its concentration in the blood plasma.
With the combined use of caffeine and barbiturates, primidone, anticonvulsants (hydantoin derivatives, especially phenytoin), it is possible to increase metabolism and increase the clearance of caffeine; while taking caffeine and cimetidine, oral contraceptives, disulfiram, ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin – a decrease in the metabolism of caffeine in the liver (slowing its excretion and increasing its concentration in the blood).
Concomitant use of caffeinated beverages and other CNS stimulants may result in excessive CNS stimulation.
When used concomitantly, drotaverine may weaken the antiparkinsonian effect of levodopa.
With simultaneous use of pheniramine with tranquilizers, hypnotics, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, alcohol, the depressant effect on the central nervous system may be enhanced.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: pale skin, anorexia (lack of appetite), abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, gastrointestinal bleeding, agitation, restlessness, confusion, tachycardia, arrhythmia, hyperthermia (increased body temperature), frequent urination, headache, tremors or muscle twitching; epileptic seizures, increased activity of “liver” transaminases, hepatonecrosis, increased prothrombin time.
Symptoms of liver dysfunction may appear 12-48 hours after an overdose. In case of severe overdose, liver failure develops with progressive encephalopathy, coma, death; acute renal failure with tubular necrosis; arrhythmia, pancreatitis. If you suspect an overdose, you should immediately seek medical help from a doctor.
Treatment: gastric lavage followed by taking activated charcoal.
The specific antidote for paracetamol poisoning is acetylcysteine. The administration of acetylcysteine is important within 8 hours after taking paracetamol. In case of gastrointestinal bleeding, it is necessary to administer antacids and gastric lavage with an ice-cold 0.9% sodium chloride solution; maintaining pulmonary ventilation and oxygenation; for epileptic seizures – intravenous administration of diazepam; maintaining the balance of fluids and salts in the body.
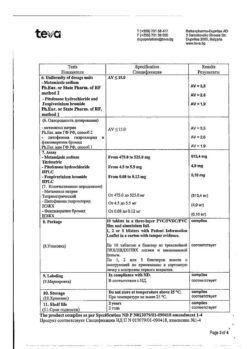
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years.
Do not use after expiration date.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Balkanpharma – Dupnitsa AD, Bulgaria
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years. Do not use after the expiration date. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. Keep out of reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Balkanfarma – Dupnitsa AD, Bulgaria |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Balkanfarma – Dupnitsa AD |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Spasmalgon Effect, 10 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.