No products in the cart.
Solantra, cream 1% 30 g
€56.78 €47.32
Description
An antimicrobial and antiprotozoal agent.
Pharmacodynamics
Ivermectin belongs to the group of avermectin. which has an anti-inflammatory effect by inhibiting the production of inflammatory cytokines induced by lipopolysaccharides.
The anti-inflammatory properties of ivermectin for external use have been observed in models of inflammatory skin processes in animals. Ivermectin also causes death of parasites, mainly through selective binding and high affinity for glutamate-regulated chlorine channels found in nerve and muscle cells of invertebrates.
The mechanism of action of Solantra in treating inflammatory skin lesions in rosacea is not known, but may be related both to the anti-inflammatory effects of ivermectin and to the ability of ivermectin to induce Demodex mites, which in turn cause skin inflammation.
Pharmacokinetics
Ivermectin in Solantra was evaluated in a clinical study in adult patients with severe papulopustular rosacea using the maximum tolerated dose of the drug.
At equilibrium (after 2 weeks of treatment), the highest mean (± standard deviation) plasma ivermectin concentrations were observed within 10 ± 8 hours of drug administration (Cmax 2.1 ± 1.0 ng/mL, range: 0.7-4.0 ng/mL), and the highest mean (± standard deviation) AUC0-244 was 36 ± 16 ng/mL, range: 14-75 ng/mL).
The systemic exposure of ivermectin reached a plateau by the end of the second week of equilibrium treatment. For longer treatments in phase 3 studies, the systemic exposure rate of ivermectin remained the same as after two weeks of treatment.
The systemic exposure levels of ivermectin (AUC0-244: 36 ± 16 ng h/mL) were lower under equilibrium concentration conditions than after a single oral dose of 6 mg of ivermectin in healthy volunteers (AUC0-244: 134 ± 66 ng h/mL).
Distribution
In vitro studies have shown that the binding of ivermectin to plasma proteins (predominantly to albumin) is over 99%. Significant binding of ivermectin to erythrocytes was not observed.
Metabolism
In in vitro studies using human liver microsomes and recombinant CYP450 enzymes it was noted that ivermectin is metabolized mainly through CYP3A4 inhibitors.
In vitro studies have shown that ivermectin does not inhibit the CYP450 isoenzymes 1A2, 2A6, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, WA4, 4A11 or 2E1.
Ivermectin does not induce the expression of CYP450 enzymes (1A2, 2B6, 2C9 or WA4) in human hepatocyte culture. The 2 major metabolites of ivermectin (3″-0-demethyl ivermectin and 4a-hydroxy ivermectin) were identified in a clinical pharmacokinetic study of the maximum tolerated dose of the drug and were studied in a phase 2 clinical trial.
Similar to the parent compound, metabolites reached equilibrium by the end of the second week of treatment, with no evidence of accumulation noted for up to 12 weeks. In addition, systemic metabolite exposures (assessed using Cmax and AUC) obtained at equilibrium were much lower than those after oral administration of ivermectin.
Elimination
The final half-life, on average, was 6 days (approximately 145 hours, range: 92-238 hours) in patients who applied the drug to the skin once daily for 28 days in a clinical pharmacokinetic study using the maximum tolerated dose of the drug.
Extraction from the body depends on the degree of absorption after external application of Solantra cream. The pharmacokinetics of ivermectin have not been studied in patients with impaired hepatic or renal function.
Indications
Indications
Treatment of inflammatory skin lesions with rosacea (papulopustular form) in adult patients.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Antimicrobial and antiprotozoal agent.
Pharmacodynamics
Ivermectin belongs to the avermectin group. which exerts anti-inflammatory effects by suppressing the production of inflammatory cytokines induced by lipopolysaccharides.
The anti-inflammatory properties of topical ivermectin have been observed in animal models of skin inflammation. Ivermectin also causes parasite death primarily through selective binding and high affinity to glutamate-regulated chloride channels found in invertebrate nerve and muscle cells.
The mechanism of action of Solantra in the treatment of inflammatory skin lesions in rosacea is not known, but may be related to both the anti-inflammatory effects of ivermectin and the ability of ivermectin to cause the death of Demodex mites, which, in turn, are a factor causing skin inflammation.
Pharmacokinetics
Suction
The absorption of ivermectin contained in Solantra was assessed in a clinical study involving adult patients with severe papulopustular rosacea using the maximum tolerated dose of the drug.
At steady state (after 2 weeks of treatment), the highest mean (± standard deviation) ivermectin plasma concentrations were observed within 10 ± 8 hours after dosing (Cmax 2.1 ± 1.0 ng/ml, range: 0.7-4.0 ng/ml), and the highest mean (± standard deviation) AUC0-244 was 36 ± 16 ng/ml, range: 14-75 ngch/ml).
Systemic exposure to ivermectin reached a plateau by the end of the second week of treatment at steady state. With longer treatment durations in phase 3 studies, systemic exposure to ivermectin remained the same as after two weeks of treatment.
At steady state, systemic exposure levels of ivermectin (AUC0-244: 36 ± 16 ng h/ml) were lower than after a single oral dose of 6 mg ivermectin in healthy volunteers (AUC0-244: 134 ± 66 ng h/ml).
Distribution
An in vitro study showed that the binding of ivermectin to plasma proteins (mainly albumin) is more than 99%. No significant binding of ivermectin to erythrocytes was observed.
Metabolism
In in vitro studies using human liver microsomes and recombinant CYP450 enzymes, ivermectin was observed to be metabolized primarily by CYP3A4 inhibitors.
In vitro studies have shown that ivermectin does not inhibit CYP450 isoenzymes 1A2, 2A6, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 3A4, 4A11 or 2E1.
Ivermectin does not induce the expression of CYP450 enzymes (1A2, 2B6, 2C9 or ZA4) in cultured human hepatocytes. The 2 main metabolites of ivermectin (3”-0-demethyl ivermectin and 4a-hydroxy ivermectin) were identified during a clinical pharmacokinetic study using the maximum permissible dose of the drug and were studied during phase 2 clinical trials.
Like the parent compound, the metabolites reached equilibrium by the end of the second week of treatment, with no signs of accumulation observed up to 12 weeks. In addition, systemic exposures of metabolites (assessed using Cmax and AUC) obtained at steady state were much lower than those after oral ivermectin.
Removal
The terminal half-life averaged 6 days (approximately 145 hours, range: 92-238 hours) in patients who applied the drug to the skin once daily for 28 days in a clinical pharmacokinetic study at the maximum tolerated dose of the drug.
Removal from the body depends on the degree of absorption after external application of Solantra cream. The pharmacokinetics of ivermectin have not been studied in patients with hepatic or renal impairment.
Special instructions
Special instructions
The medicinal product contains:
– cetyl alcohol and stearyl alcohol, which can cause local skin reactions (for example, contact dermatitis),
– methyl parahydroxybenzoate (E218) and propyl parahydroxybenzoate (E216), which can cause allergic reactions (including delayed ones),
– propylene glycol, which may cause skin irritation.
After applying the medicine, you must wash your hands.
After the drug has dried, cosmetics can be applied.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Ivermectin
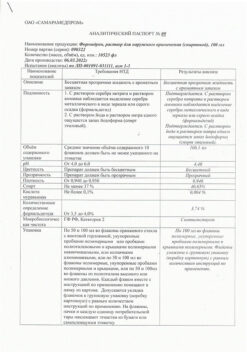
Composition
Composition
1 g of cream contains:
Active ingredient:
Ivermectin 10.0 mg.
Excipients:
Glycerol 40.0 mg,
Isopropyl palmitate 40.0 mg,
Carbomer copolymer type B 2.0 mg,
Dimethicone 20 Cst 5.0 mg,
Disodium edetate 0.5 mg,
Citric acid monohydrate 0.5 mg,
Cetyl alcohol 35.0 mg,
Stearic alcohol 25.0 mg,
Macrogol cetostealyl ester 30.0 mg,
Sorbitan stearate 20.0 mg,
Methyl parahydroxybenzoate 2.0 mg,
Propyl parahydroxybenzoate 1.0 mg,
Phenoxyethanol 10.0 mg,
Propylene glycol 20.0 mg,
Oleyl alcohol 20.0 mg,
Sodium hydroxide solution 10% to pH 6.3±0.3,
purified water up to 1000 mg.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
There are limited or no data on the use of ivermectin in pregnant women. Reproductive toxicity studies following oral administration of ivermectin have shown that the drug has teratogenic potential in rats and rabbits, but due to low systemic exposure when applied topically at the recommended dosage, the drug has a low risk of fetotoxicity in humans.
The use of Solantra during pregnancy is not recommended.
Breastfeeding period
Following oral administration, low concentrations of ivermectin are excreted into breast milk. When the drug is used externally, the release of ivermectin into breast milk has not been studied.
Pharmacokinetic and toxicological data obtained from animal studies also indicate the release of ivermectin into breast milk. A risk to the nursing infant cannot be excluded. If it is necessary to use the drug, you should consult your doctor to decide whether to stop breastfeeding.
Contraindications
Contraindications
– Hypersensitivity to the active substance or any other component of the drug;
– pregnancy;
– breastfeeding period;
– children under 18 years of age (the safety and effectiveness of the drug for this age category have not been studied).
With caution:
Liver dysfunction.
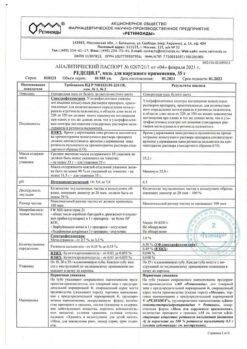
Side Effects
Side Effects
The most common adverse reactions, such as burning sensation, skin irritation, itching and dry skin, were noted in less than 1% of patients treated with the drug during clinical trials.
As a rule, these reactions are mild or moderate in nature and usually subside with continued therapy.
There were no significant differences in the safety profile between patients aged 18 to 65 years and patients over 65 years of age.
Interaction
Interaction
No studies have been conducted to study the interactions of the drug with other drugs.
The simultaneous use of Solantra cream with other drugs for external and systemic use for the treatment of rosacea has not been studied.
Caution should be exercised when ivermectin is used concomitantly with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, as plasma concentrations of the drug may increase significantly.
Overdose
Overdose
There have been no reports of cases of overdose with Solantra.
In case of accidental or significant human exposure to unknown quantities of veterinary dosage forms of ivermectin (ingestion, inhalation, parenteral administration or body surface exposure), the most commonly reported symptoms were skin rash, facial swelling, eyelid swelling, headache, dizziness, asthenia, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea.
Other reported adverse reactions include: seizures, ataxia, dyspnea, abdominal pain, paresthesia, urticaria and contact dermatitis.
In case of accidental ingestion of the drug, symptomatic therapy is carried out, including parenteral administration of fluids and electrolytes, respiratory support (providing oxygen supply and, if necessary, artificial ventilation) and vasopressors (if there is a significant decrease in blood pressure).
To prevent absorption of the ingested drug, inducing vomiting and/or urgent gastric lavage may be indicated, followed by the use of laxatives and other measures to eliminate intoxication.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Galderma Laboratories, France
Additional information
| Manufacturer | Galderm Laboratories, France |
|---|---|
| Medication form | exterior cream |
| Brand | Galderm Laboratories |
Related products
Buy Solantra, cream 1% 30 g with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.