No products in the cart.
Sodium chloride-SOLOPHarm Domus, 0.9% 400 ml
€2.48 €2.25
EAN: 4680013240158
SKU: 280043
Categories: Anesthesia and resuscitation, Anesthesia solutions, Medicine
Description Pharmacotherapeutic group: Rehydrating agent Pharmacodynamics: Pharmacokinetics:
ATC:
B.05.C.B.01 Sodium chloride
B.05.X.A.03 Sodium chloride
The plasma substitute. It has a detoxifying and rehydrating effect. It replenishes the sodium deficiency in various pathological states of the body.
The 0.9% solution of sodium chloride isotonic to human plasma, so it is quickly eliminated from the vascular bed, only temporarily increasing the volume of circulating blood (effectiveness in case of blood loss and shock is insufficient).
Sodium ion concentration is 142 mmol/L (plasma) and 145 mmol/L (interstitial fluid), chloride concentration is 101 mmol/L (interstitial fluid). Excreted by the kidneys.
.
Indications
Indications
Plasma-isotonic fluid replacement, hypochloremic alkalosis, hyponatremia with dehydration, intoxication, dissolution and dilution of parenterally administered drugs (as a base solution).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Rehydrating agent
ATX:
B.05.C.B.01 Sodium chloride
B.05.X.A.03 Sodium chloride
Pharmacodynamics:
Plasma replacement agent. Has a detoxifying and rehydrating effect. Replenishes sodium deficiency in various pathological conditions of the body.
A 0.9% sodium chloride solution is isotonic to human plasma, therefore it is quickly removed from the vascular bed, only temporarily increasing the volume of circulating blood (effectiveness for blood loss and shock is insufficient).
Pharmacokinetics:
The concentration of sodium ions is 142 mmol/l (plasma) and 145 mmol/l (interstitial fluid), the concentration of chloride is 101 mmol/l (interstitial fluid). Excreted by the kidneys.
Special instructions
Special instructions
When carrying out any infusion, it is necessary to monitor the patient’s condition, clinical biological indicators, it is especially important to evaluate blood plasma electrolytes.
In children, sodium excretion may slow down due to immature kidney function. Therefore, in such patients, repeated infusions should be carried out only after determining the concentration of sodium in the blood plasma.
If hypersensitivity reactions or infusion reactions occur, the infusion should be stopped immediately and the necessary therapeutic measures taken as indicated.
Depending on the volume and rate of infusion, intravenous administration of the drug may pose a risk of hypervolemia and/or solute overload and electrolyte imbalance.
In patients with renal failure, the drug should be used with extreme caution or not used at all. Use of the drug in such patients may lead to sodium retention.
Use only a clear solution, without visible inclusions and if the packaging is not damaged. Administer immediately after connecting to the infusion system. The solution should be administered using sterile equipment in compliance with the rules of asepsis and antisepsis. To prevent air from entering the infusion system, fill it with solution, releasing any remaining air from the container completely.
As with all parenteral solutions, the compatibility of added substances with the solution must be determined before reconstitution. Drugs known to be incompatible with it should not be used with 0.9% sodium chloride solution.
A doctor should determine the compatibility of added medicinal substances with a 0.9% sodium chloride solution by checking for possible changes in color and/or the appearance of sediment, insoluble complexes or crystals. Before addition, it is necessary to determine whether the substance being added is soluble and stable in water at the pH level of a 0.9% sodium chloride solution. When adding a drug, it is necessary to determine the isotonicity of the resulting solution before administration.
Before adding drugs to the solution, they must be thoroughly mixed in compliance with aseptic rules. The prepared solution should be administered immediately after preparation, do not store! Any unused dose should be discarded.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Sodium chloride
Composition
Composition
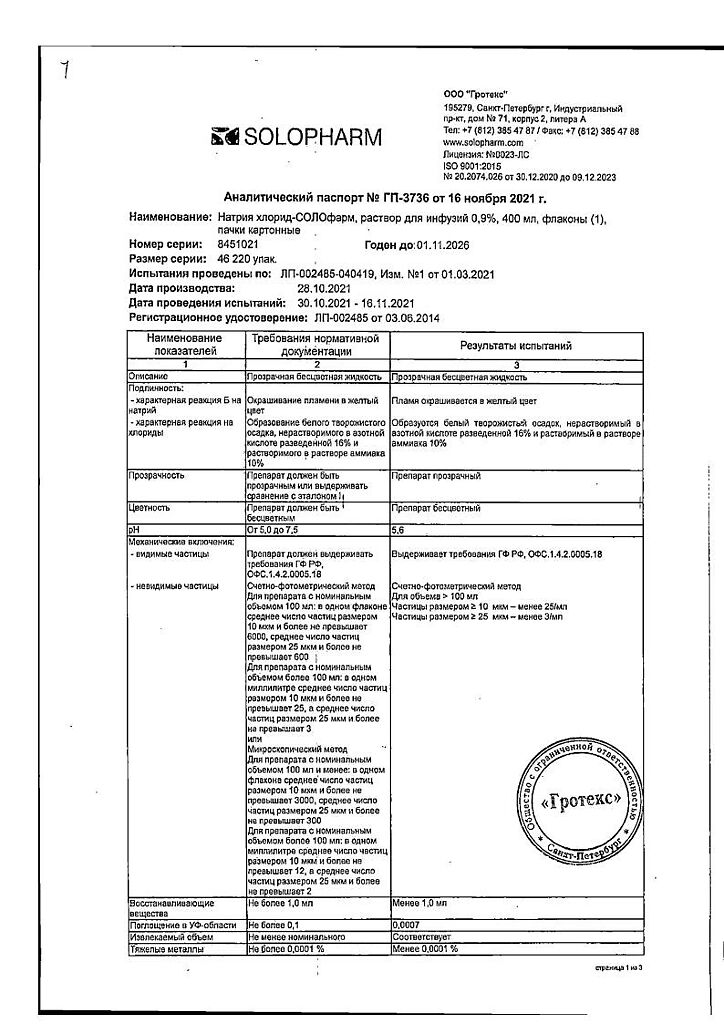
1 liter of solution contains:
active ingredient:
sodium chloride – 9.0 g;
excipient:
water for injection – up to 1.0 l.
Theoretical osmolarity 308 mOsm/l.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypernatremia, hyperchloremia, hypokalemia; extracellular hyperhydration; intracellular dehydration; circulatory disorders associated with the risk of developing cerebral and pulmonary edema; cerebral edema; pulmonary edema; decompensated heart failure; chronic renal failure; conditions that can cause sodium retention, hypervolemia and edema (central and peripheral), such as: primary aldosteronism and secondary aldosteronism due to, for example, arterial hypertension, congestive heart failure, liver disease (including cirrhosis), kidney disease (including renal artery stenosis and nephrosclerosis), preeclampsia; concomitant administration of glucocorticosteroids in large doses; contraindications to drugs added to the solution.
With caution:
Chronic heart failure, chronic renal failure (oligo-, anuria), acidosis, arterial hypertension, peripheral edema, toxicosis of pregnancy.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Acidosis, overhydration, hypokalemia.
When used correctly, unwanted effects are unlikely.
When using sodium chloride solution 0.9% as a base solution (solvent) for other drugs, the likelihood of side effects is determined by the properties of these drugs.
In this case, if adverse reactions occur, the administration of the solution should be suspended, the patient’s condition assessed, adequate measures taken, and the remaining solution retained for analysis, if necessary.
If any of the side effects indicated in the instructions get worse, or you notice any other side effects not listed in the instructions, tell your doctor.
Interaction
Interaction
Compatible with colloid hemodynamic blood substitutes (mutually enhancing effect).
When mixing with other drugs, it is necessary to visually monitor compatibility.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, cramping abdominal pain, thirst, decreased salivation and lacrimation, increased sweating, fever, tachycardia, increased blood pressure, renal failure, peripheral edema, pulmonary edema, respiratory arrest, headache, dizziness, anxiety, irritability, weakness, muscle cramps and rigidity, generalized convulsions, coma and death.
Excessive administration of sodium chloride solution 0.9% can cause hypernatremia.
Excessive intake of chloride into the body can lead to hyperchloremic acidosis.
If a solution of sodium chloride 0.9% is used as a base solution for the dilution and transport of other drugs, symptoms and complaints with excessive administration are most often associated with the properties of the drugs added to the solution.
In case of unintentional over-administration of the solution, treatment should be stopped and the patient’s condition assessed.
Treatment: symptomatic.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 30 °C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
5 years.
Do not use after the expiration date.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Grotex LLC, Russia
Additional information
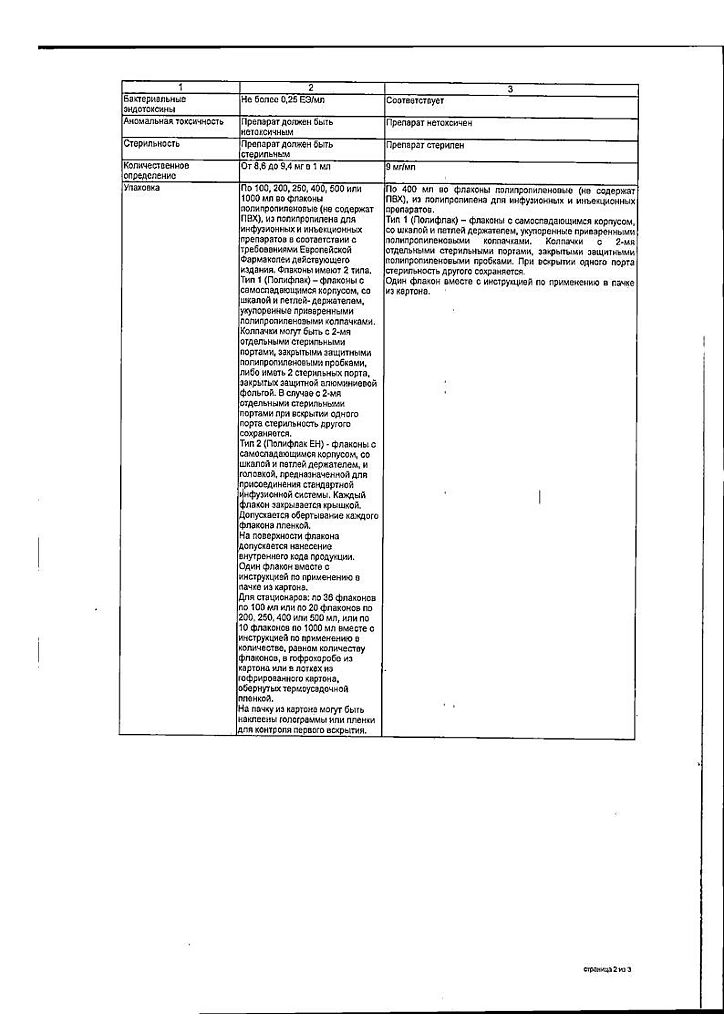
| Shelf life | 5 years. Do not use after the expiration date. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store at a temperature not exceeding 30 ° C. Store out of the reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Grotex Ltd, Russia |
| Medication form | solution for infusion |
| Brand | Grotex Ltd |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Sodium chloride-SOLOPHarm Domus, 0.9% 400 ml with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.