No products in the cart.
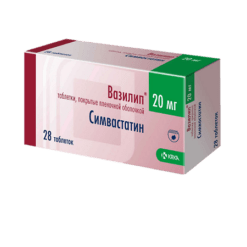
Simvastatin, 20 mg 30 pcs
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
The hyiolipidemic agent is obtained synthetically from the fermentation product of Aspergillus terreus and is an inactive lactone which undergoes hydrolysis in the body to form a hydroxyacid derivative. The active metabolite inhibits Z-hydroxy-Z-methyl-glutaryl-CoA reductase (HMG-CoA reductase), the enzyme that catalyzes the initial reaction of mevalonate formation from HMG-CoA. Since the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate is an early stage of cholesterol (cholesterol) synthesis, simvastatin does not cause accumulation of potentially toxic sterols in the body. HMG-CoA is easily metabolized to acetyl-CoA, which is involved in many synthesis processes in the body.
Induces decrease in plasma concentration of triglycerides (TG), low density lipoproteins (LDL), very low density lipoproteins (VLDL) and total cholesterol (TC) (in cases of heterozygous familial and non-familial forms of hypercholesterolemia in mixed hyperlipidemia when elevated cholesterol concentration is a risk factor). Increases the concentration of high density lipoproteins (HDL) and reduces the ratio of LDL/HDL and LDL/HDL in plasma.
The onset of the effect is 2 weeks after the start of use, the maximum therapeutic effect is achieved after 4-6 weeks. The effect is maintained with continuation of treatment when discontinuation of therapy plasma cholesterol concentration gradually returns to baseline levels.
Pharmacokinetics:
Absorption of simvastatin is high (about 85 %) intake of poor diet (against standard hypocholesterol diet) immediately after taking the preparation does not influence pharmacokinetic profile of simvastatin. After oral administration maximal plasma concentration is reached approximately in 13-24 hours and decreases by 90% in 12 hours. The blood plasma protein binding is about 95%.
Metabolized in liver has the effect of “primary passage” through liver (hydrolyzed with the formation of active derivative: beta-hydroxy acids and other active and inactive metabolites are found). Half-life of active metabolites is 19 hours.
It is eliminated mainly through the intestine (60%) as metabolites. About 10-15% is excreted by the kidneys in the inactive form.
Indications
Indications
nonfatal myocardial infarction;
coronary death;
stroke;
revascularization procedures;
reducing the risk of the need for peripheral blood flow repair surgery and other noncoronary revascularizations;
reducing the risk of hospitalization for angina attacks.
Use v children and adolescents 10-17 years of age with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia:
The use of Simvastatin concomitantly with diet is indicated to reduce elevated concentrations of CHC LDL TG alo B in young males 10-17 years and in girls 10-17 years at least 1 year after menarche (first menstrual bleeding) with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient:
simvasgatin – 20.00 mg;
excipients:
lactose monohydrate – 138.46 mg,
corn starch – 14.00 mg,
microcrystalline cellulose – 10.00 mg,
ascorbic acid – 5.00 mg,
winrolose (hydroxypropyl cellulose) – 4.00 mg,
croscarmellose sodium – 4.00 mg,
citric acid monohydrate – 2.50 mg,
butyl hydroxyanisole – 0.04 mg,
calcium stearate – 2.00 mg;
film coating: [hypromellose – 4.0000 mg, ginrolose (hydroxypropylcellulose) – 1.5520 mg, talc – 1.5408 mg, titanium dioxide – 0.0880 mg, iron oxide black (iron oxide) – 0.3232 mg, iron oxide red (iron oxide) – 0.3120 mg, iron oxide yellow (iron oxide) – 0.1840 mg] or [dry film coating mixture containing hypromellose (50%), hyprolose (hydroxypropylcellulose) (19.4%), talc (19.26%), titanium dioxide (1.1%), iron oxide black (iron oxide) (4.04%), iron oxide red (iron oxide) (3.9%), iron oxide yellow (iron oxide) (2.3%)] – 8.0000 mg.
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Before starting simvastatin treatment, the patient should be prescribed a standard hypocholesterolemic diet, which should be followed during the entire course of treatment.
Simvastatin should be taken orally once a day in the evening with plenty of water.
The time of taking the drug should not be associated with food intake. The duration of use of the drug is determined by the physician on an individual basis.
Hypercholesterolemia
The recommended dosage of the drug Simvastatin for treatment of hypercholesterolemia is 5 to 80 mg once daily in the evening.
If the drug is ineffective in the dose of 40 mg, it is recommended to switch to another type of hypolipidemic therapy. Using the drug in a dose greater than 40 mg increases the significant risk of myopathy.
The dose of Simvastatin 80 mg should be used only in patients who have not achieved the target LDL concentration with the dose of 40 mg.
The recommended starting dose of the drug for patients with hypercholesterolemia is 10 mg. The dose should be changed (adjusted) at 4-week intervals. In most patients the optimal effect is achieved by taking the drug in doses of up to 20 mg per day.
In patients with homozygous hereditary hypercholesterolemia the recommended daily dose of Simvastatin is 40 mg (2 tablets of 20 mg once daily in the evening or 80 mg in 3 doses (20 mg in the morning, 20 mg during the day and 40 mg in the evening). In such patients, it is recommended to use Simvastatin in combination with other hypolipidemic therapy (e.g., LDL apheresis).
Ischemic Heart Disease
In the treatment of patients with coronary heart disease (CHD) or high risk of CHD, with or without hyperlipidemia, the effective doses of Simvastatin are 20, 40 mg daily. Therefore, the recommended starting dose in such patients is 20 mg per day. Changing (selection) of the dose should be carried out at intervals of 4 weeks, if necessary, the dose can be increased to 40 mg per day (2 tablets of 20 mg of Simvastatin). If LDL is less than 75 mg/dL (1.94 mmol/L), total cholesterol less than 140 mg/dL (3.6 mmol/L), the drug dose should be reduced.
Companion therapy
In patients treated with cyclosporine, danazol, gemfibrozil, other fibrates (except fenofibrate) or nicotinic acid in lipid-lowering doses (more than 1 g/day), the recommended maximum daily dose of Simvastatin should not exceed 10 mg. Further increase of the dose in such situations is not recommended.
In patients concomitantly taking amiodarone or verapamil, the daily dose of Simvastatin should not exceed 20 mg.
In patients concomitantly taking diltiazem, the daily dose of Simvastatin should not exceed 40 mg.
In elderly patients and in patients with mild to moderately severe renal impairment, no adjustment of the drug dose is required.
In patients with significant renal impairment (CKD less than 30 ml/min) the recommended dose of Simvastatin should not exceed 10 mg per day. If it is necessary to increase the dose, such patients should be closely monitored.
Interaction
Interaction
Pharmacodynamic interactions
Concomitant use of simvastatin with fibrates, nicotinic acid in lipid-lowering doses (more than 1 g/day) increases the risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis (when used simultaneously with fenofibrate there is no evidence of increased risk of myopathy compared to monotherapy with each drug separately)./p>
Concomitant use of amlodipine with the drug Simvastatin at a dose of 80 mg has a slightly increased risk of myopathy.
Pharmacokinetic interactions
Inhibitors of cytochrome CYP3A4 isoenzyme (itraconazole, ketoconazole, erythromycin, clarithromycin, telithromycin HIV protease inhibitors and nefazodone) involved in metabolic conversion of simvastatin in liver increase risk of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis during simvastatin therapy. Simultaneous use with these drugs is contraindicated. Caution should be used concomitantly with less potent CYP3A4 isoenzyme inhibitors: cyclosporine, verapamil and diltiazem.
The daily dose of Simvastatin should not exceed 10 mg when used concomitantly with cyclosporine.
The daily dose of simvastatin during concomitant use of amiodarone or verapamil should not exceed 20 mg, and 40 mg during concomitant use of diltiazem, unless the expected benefit clearly exceeds the potential risk of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis.
Simvastatin at a dose of 20-40 mg/day in healthy volunteers and patients with hypercholesterolemia potentiates the effects of indirect coumarin derivative anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin), particularly increases in prothrombin time and international normalized ratio (MHO). Therefore, in patients taking coumarin anticoagulants, prothrombin time and MHO should be determined before starting simvastatin therapy, during the initial treatment period, when changing the dose of simvastatin or when withdrawing the drug. When stable prothrombin time and MHO are achieved, further monitoring should be performed at intervals recommended for patients receiving anticoagulant therapy. Simvastatin therapy does not cause changes in prothrombin time and risk of bleeding in patients not taking anticoagulants.
Colestyramine and colestipol reduce bioavailability (the use of simvastatin is possible 4 hours after the use of these drugs, with an additive effect).
Simvastatin increases the plasma concentration of digoxin.
Grapefruit juice contains one or more components that inhibit the CYP3A4 isoenzyme and may increase the plasma concentration of substances metabolized by CYP3A4 isoenzyme. The increase in HMG-KoA reductase inhibitor activity after consuming 250 ml of juice per day is minimal and of no clinical significance. However, consumption of a large volume of juice (more than 1 liter per day) when using simvastatin significantly increases the inhibitory activity against HMG-CoA reductase in plasma. In this regard, it is necessary to
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
In the beginning of therapy with simvastatin, there may be a transient increase in liver enzymes.
Liver function tests should be performed regularly before initiating therapy and thereafter (monitor liver enzyme activity at 6 weeks for the first 3 months, then at 8 weeks for the remaining first year, and then once every six months), and a liver function test should be performed when doses are increased. If the dose is increased to 80 mg, a liver function test should be performed after 3 months. If there is a persistent increase in transaminase activity (3 times the baseline level), simvastatin should be discontinued.
Simvastatin, like other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, should not be used if there is an increased risk of rhabdomyolysis and renal failure (with severe acute infection, arterial hypotension, trauma, planned major surgery, severe metabolic disorders).
The withdrawal of hypolipidemic agents during pregnancy has no significant effect on the results of long-term treatment of primary hypercholesterolemia.
In patients with reduced thyroid function (hypothyroidism) or in the presence of certain kidney diseases (nephrotic syndrome) when cholesterol levels increase, therapy of the underlying disease should be given first.
Simvastatin should be used with caution in people who abuse alcohol and/or have a history of liver disease.
The patient should be on a hypocholesterolemic diet before and during treatment.
The concomitant administration of grapefruit juice may increase the severity of side effects associated with taking simvastatin, so concomitant administration should be avoided.
Simvastatin is not indicated in cases with hypertriglyceridemia types I, IV and V.
The treatment with simvastatin may cause myopathy leading to rhabdomyolysis and renal failure. The risk of this pathology increases in patients receiving one or more of the following drugs simultaneously with simvastatin: fibrates (gemfibrozil, fenofibrate), cyclosporine, nefazadone, macrolides (erythromycin, clarithromycin), antifungal agents of azole group (ketoconazole, intraconazole) and HIV protease inhibitors (ritonavir). The risk of myopathy is also increased in patients with severe renal insufficiency.
Predisposing factors for myopathy include older age (over 65), being female, uncontrolled hypothyroidism, and renal failure.
All patients starting therapy with Simvastatin, as well as patients who need to increase the dose of the drug, should be warned about the possibility of myopathy and the need to seek immediate medical attention if unexplained pain, muscle soreness, sluggishness or muscle weakness occur, especially if accompanied by malaise or fever. Therapy with the product should be stopped immediately if myopathy is diagnosed or suspected.
In order to diagnose the development of myopathy, regular measurements of CPK are recommended.
The treatment with Simvastatin may increase serum CPK, which should be considered in differential diagnosis of chest pain. The criterion for discontinuation of the product is an increase in serum CPK more than 10 times the upper limit of normal. In patients with myalgia, myasthenia and/or marked increase in CPK activity, treatment with the product should be discontinued.
The drug is effective both as monotherapy and in combination with bile acid sequestrants.
If the current dose is missed, the product should be taken as soon as possible.
If it is time to take the next dose, the dose should not be doubled.
Patients with severe renal insufficiency should have their renal function monitored.
The duration of use of the product is determined by the attending physician on an individual basis.
The use of simvastatin is not recommended in women of childbearing age who do not use reliable methods of contraception.
Impact on driving and operating machinery
Cautious driving and operating machinery must be observed (risk of dizziness).
Synopsis
Synopsis
Contraindications
Contraindications
The use of the drug in the form of granules for oral solution in children under 2 years of age is possible only if there are vital indications and under close medical supervision.
With caution it is used in case of gastric and duodenal ulcer, esophageal varices, hemoptysis, pulmonary hemorrhage, phenylketonuria, bronchial asthma, adrenal diseases, hepatic and/or renal insufficiency, arterial hypertension.
Side effects
Side effects
Digestive system disorders: constipation, abdominal pain, flatulence, dyspepsia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, pancreatitis, hepatitis, cholestatic jaundice, liver function disorders, increased activity of “liver” transaminases, ALP and CPK.
CNS and sense organs: asthenia, headache, paresthesia, dizziness, peripheral neuropathy, insomnia, memory impairment, muscle cramps, blurred vision, impaired sense of taste, myasthenia, weakness.
Musculoskeletal system: myopathy, rhabdomyolysis, myalgia, muscle cramps.
Allergic and immunopathological reactions: developed hypersensitivity syndrome (angioedema, lupus-like syndrome, rheumatic polymyalgia, vasculitis, dermatomyositis, thrombocytopenia, eosinophilia, increased sedimentation, arthritis, arthralgia, urticaria, photosensitization, blood flushing to the skin, shortness of breath).
Dermatological reactions: skin rash, itching, alopecia.
Others: anemia, palpitations, acute renal failure (due to rhabdomyolysis), decreased potency.
Overdose
Overdose
No specific symptoms have been identified in any of the known few cases of overdose (maximum dose of 450 mg taken).
The treatment: symptomatic, it is necessary to carry out general measures: monitoring and maintenance of vital functions, prevention of further absorption of the drug (gastric lavage, administration of activated charcoal or laxatives). Liver and renal functions and serum CPK concentration should be monitored. There is no specific antidote.
In case of myopathy with rhabdomyolysis and acute renal failure (a rare but severe side effect), the product should be stopped immediately and the patient should be given a diuretic and sodium bicarbonate (intravenous infusion).
Rhabdomyolysis can cause hyperkalemia, which can be managed with intravenous calcium chloride or calcium gluconate, glucose and insulin infusion, potassium ion exchangers or, in severe cases, hemodialysis.
Pregnancy use
Pregnancy use
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
| Conditions of storage | Store in a dry place protected from light at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. Keep out of reach of children. |
|---|---|
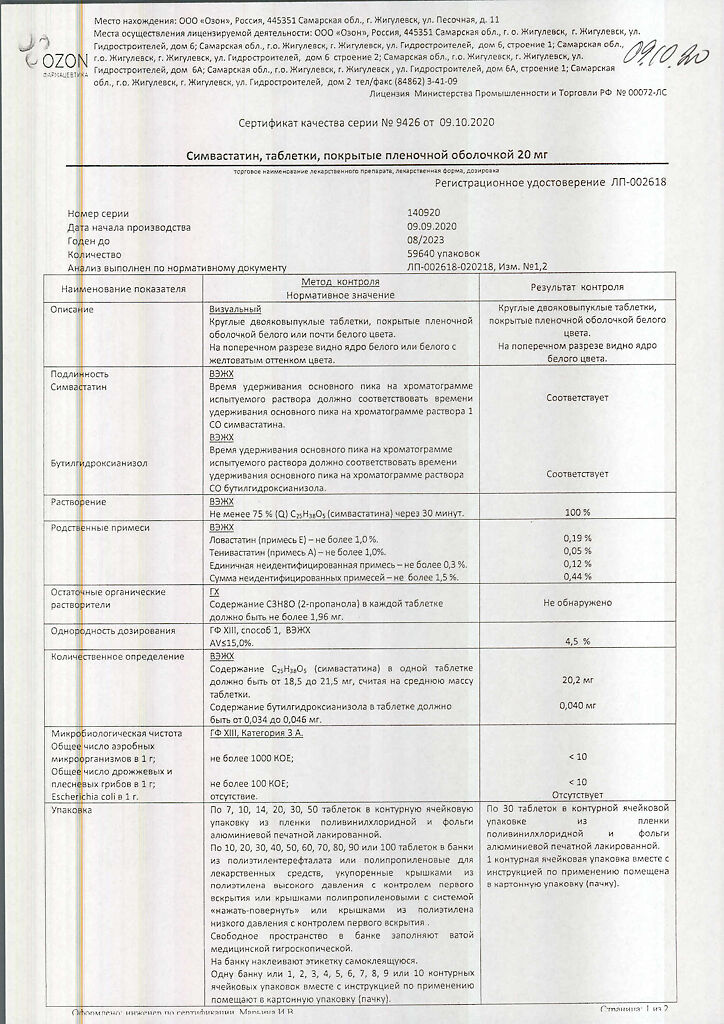
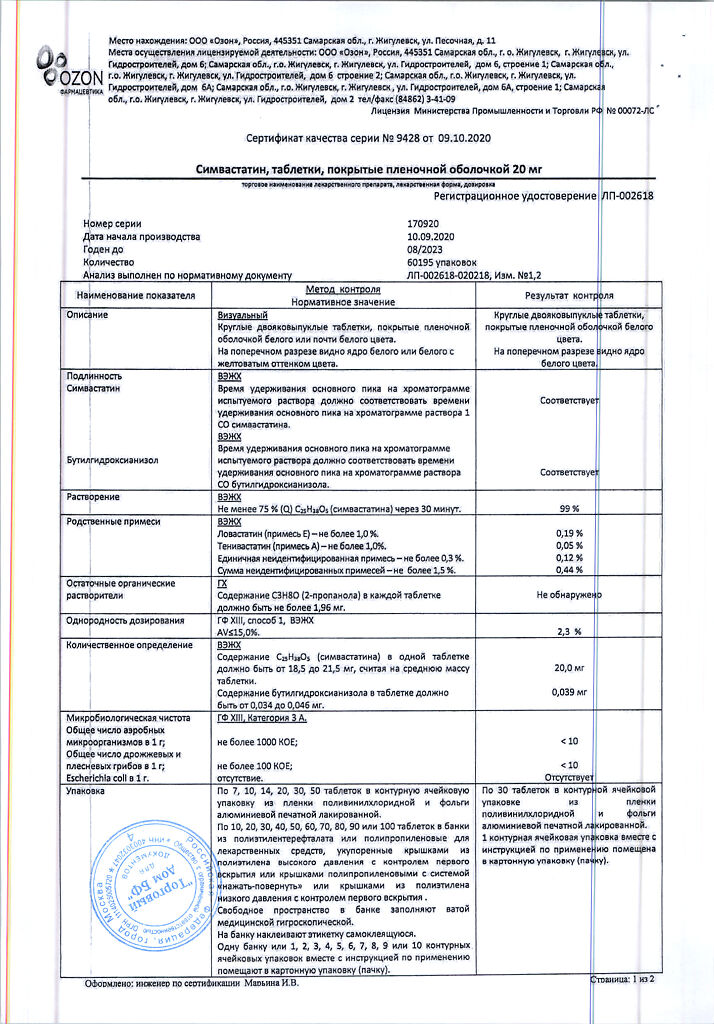
| Manufacturer | Ozon, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Ozon |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Simvastatin, 20 mg 30 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.