No products in the cart.
Regulon, 21 pcs.
€20.25 €16.88
EAN: 5997001357767
SKU: 117453
Categories: Contraceptive, Gynecology and Obstetrics, Hormonal, Medicine
Description
Pharmaceutical group:
Contraceptive (estrogen+gestagen).
Pharmic action:
Regulon is a monophasic oral contraceptive. Its main contraceptive effect is to inhibit the synthesis of gonadotropins and suppress ovulation. In addition, by increasing the viscosity of cervical mucus, the movement of sperm through the cervical canal is slowed, and changes in the condition of the endometrium prevent the implantation of a fertilized egg.
Ethinylestradiol is a synthetic analog of endogenous estradiol.
Desogestrel has pronounced gestagenic and anti-estrogenic effects similar to endogenous progesterone, weak androgenic and anabolic activity.
Regulon has beneficial effects on lipid metabolism: it increases HDL concentration in blood plasma without affecting LDL concentration.
Menstrual blood loss (at initial menorrhagia) decreases significantly when taking the drug; menstrual cycle is normalized; favorable effects on skin, especially in the presence of acne vulgaris are noted.
Pharmacokinetics:
– Desogestrel
Absorption
Desogestrel is rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the GI tract and is immediately metabolized to 3-keto-desogestrel, which is the biologically active metabolite of desogestrel.
Cmax is reached after 1.5 h and is 2 ng/ml. Bioavailability is 62-81%.
Distribution
3-keto-desogestrel binds to plasma proteins, mainly to albumin and to sex hormone binding globulin (hSPH). Vd is 1.5 L/kg. Css is established by the second half of the menstrual cycle. 3-keto-desogestrel levels increase by a factor of 2 to 3.
Metabolism
In addition to 3-keto-desogestrel (which is formed in the liver and intestinal wall) other metabolites are formed: 3α-ON-desogestrel, 3β-ON-desogestrel, 3α-ON-5α-H-desogestrel (first phase metabolites). These metabolites have no pharmacological activity and partially, by conjugation (the second phase of metabolism), are converted to polar metabolites – sulfates and glucuronates. Blood plasma clearance is about 2 ml/min/kg body weight. T1/2 of 3-keto-desogestrel is 30 hours. Metabolites are excreted in the urine and feces (4:6 ratio).
– Ethinylestradiol
Intake
Ethinylestradiol is rapidly and completely absorbed from the GI tract. Cmax is reached 1-2 hours after taking the drug and is 80 pg/ml. The bioavailability of the drug due to presystemic conjugation and “first pass” effect through the liver is about 60%.
Distribution
Ethinylestradiol is completely bound to plasma proteins, mainly to albumin. Vd is 5 l/kg. Css is established by 3-4 days of administration, with serum ethinylestradiol levels 30-40% higher than after a single dose of the drug.
Metabolism
Presystemic conjugation of ethinylestradiol is significant. Passing the intestinal wall (first phase of metabolism) it undergoes conjugation in the liver (second phase of metabolism).
Ethinylestradiol and its conjugates of the first phase of metabolism (sulfates and glucuronides) are excreted in bile and enter enter enterohepatic circulation. Blood plasma clearance is about 5 ml/min/kg body weight.
Elimination
The T1/2 of ethinylestradiol averages about 24 hours. About 40% is excreted with the urine and about 60% with the feces.
Indications
Indications
Oral contraception.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmaceutical group:
contraceptive (estrogen + gestagen).
Pharmaceutical action:
Regulon is a monophasic oral contraceptive. The main contraceptive effect is to inhibit the synthesis of gonadotropins and suppress ovulation. In addition, by increasing the viscosity of cervical mucus, the movement of sperm through the cervical canal slows down, and changes in the condition of the endometrium prevent the implantation of a fertilized egg.
Ethinyl estradiol is a synthetic analogue of endogenous estradiol.
Desogestrel has a pronounced gestagenic and antiestrogenic effect, similar to endogenous progesterone, and weak androgenic and anabolic activity.
Regulon has a beneficial effect on lipid metabolism: it increases the concentration of HDL in the blood plasma without affecting the content of LDL.
When taking the drug, the loss of menstrual blood is significantly reduced (in case of initial menorrhagia), the menstrual cycle is normalized, and a beneficial effect on the skin is noted, especially in the presence of acne vulgaris.
Pharmacokinetics:
– Desogestrel
Suction
Desogestrel is quickly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is immediately metabolized into 3-keto-desogestrel, which is a biologically active metabolite of desogestrel.
Cmax is reached after 1.5 hours and is 2 ng/ml. Bioavailability – 62-81%.
Distribution
3-keto-desogestrel binds to plasma proteins, mainly albumin and sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG). Vd is 1.5 l/kg. Css is established by the second half of the menstrual cycle. The level of 3-keto-desogestrel increases 2-3 times.
Metabolism
In addition to 3-keto-desogestrel (which is formed in the liver and in the intestinal wall), other metabolites are formed: 3α-OH-desogestrel, 3β-OH-desogestrel, 3α-OH-5α-H-desogestrel (first phase metabolites). These metabolites do not have pharmacological activity and are partially converted, through conjugation (the second phase of metabolism), into polar metabolites – sulfates and glucuronates. Clearance from blood plasma is about 2 ml/min/kg body weight.
Removal
T1/2 of 3-keto-desogestrel is 30 hours. Metabolites are excreted in urine and feces (in a ratio of 4:6).
– Ethinyl estradiol
Suction
Ethinyl estradiol is quickly and completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Cmax is reached 1-2 hours after taking the drug and is 80 pg/ml. The bioavailability of the drug due to presystemic conjugation and the “first pass” effect through the liver is about 60%.
Distribution
Ethinyl estradiol is completely bound to plasma proteins, mainly albumin. Vd is 5 l/kg. Css is established by the 3-4th day of administration, while the level of ethinyl estradiol in the serum is 30-40% higher than after a single dose of the drug.
Metabolism
Presystemic conjugation of ethinyl estradiol is significant. Bypassing the intestinal wall (first phase of metabolism), it undergoes conjugation in the liver (second phase of metabolism).
Ethinyl estradiol and its conjugates of the first phase of metabolism (sulfates and glucuronides) are excreted into bile and enter the enterohepatic circulation. Clearance from blood plasma is about 5 ml/min/kg body weight.
Removal
T1/2 of ethinyl estradiol averages about 24 hours. About 40% is excreted in the urine and about 60% in feces.
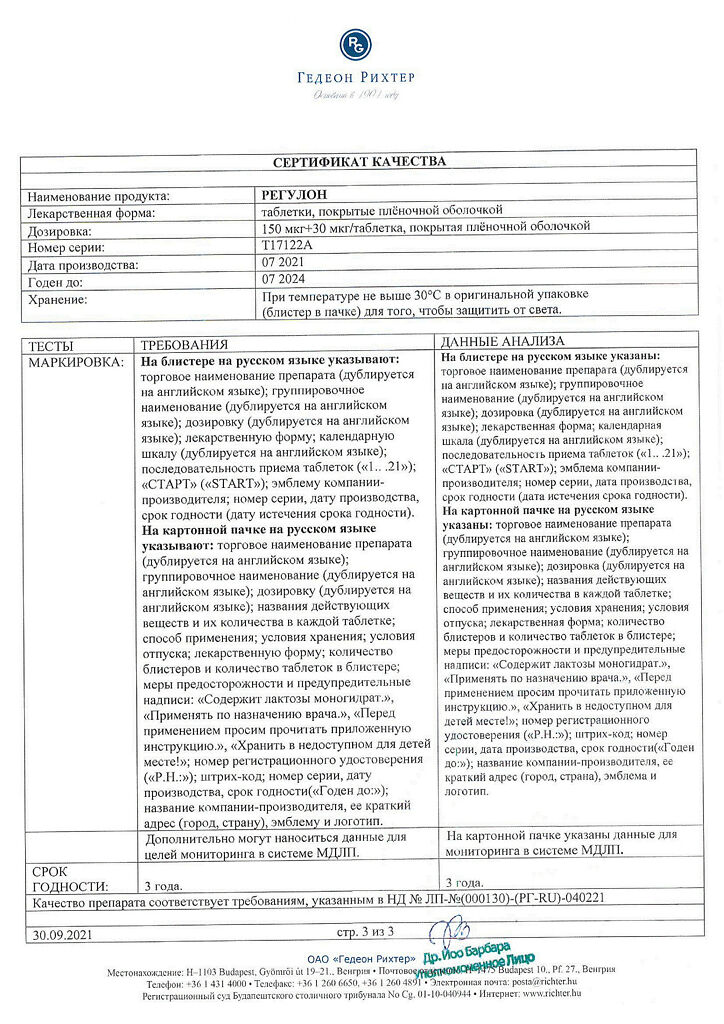
Special instructions
Special instructions
Before starting to use the drug, it is necessary to conduct a general medical examination (detailed family and personal history, blood pressure measurement, laboratory tests) and gynecological examination (including examination of the mammary glands, pelvic organs, cytological analysis of a cervical smear). A similar study during the period of taking the drug is carried out regularly, every 6 months.
The effectiveness of Regulon is reduced if pills are missed, with vomiting and diarrhea, as well as when taken simultaneously with other medications.
The effectiveness of Regulon may decrease if intermenstrual bleeding appears after several months of its use. If menstrual-like bleeding does not appear during the break, taking the pills can be continued only after pregnancy has been ruled out.
The risk of arterial or venous thromboembolic diseases increases with age, with smoking, with a family history of thromboembolic diseases, with obesity (body mass index above 30 kg/m2), with dyslipoproteinemia, with arterial hypertension, with heart valve diseases, with atrial fibrillation, with diabetes mellitus, with prolonged immobilization (after major surgery, after surgery on the lower limbs after severe trauma).
In the presence of congenital or acquired biochemical defects (resistance to activated protein C, hyperchromocysteinemia, deficiency of proteins C, S, deficiency of antithrombin III, the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies), the risk of developing thromboembolic diseases also increases. Targeted treatment of the above conditions reduces the risk of blood clots.
Pregnancy poses a greater risk of blood clots than taking hormonal contraceptives.
Regulon should be stopped immediately in the following cases:
– New onset of severe headaches or worsening of regular migraines.
– Acute deterioration of visual acuity.
– Suspicion of myocardial infarction or thrombosis.
– Sharp increase in blood pressure.
– The appearance of jaundice or hepatitis without jaundice, intense generalized itching.
– The emergence of epilepsy or increased frequency of epileptic seizures.
– 4 weeks before the planned surgical intervention and in case of prolonged immobilization (Regulon can be resumed after 2 weeks from the moment of remobilization).
– Development of pregnancy.
– Use for liver dysfunction: Contraindicated in liver failure.
– Use for impaired renal function: With caution and only after a thorough assessment of the benefits and risks of use, the drug should be prescribed for renal failure (including a history).
– Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery: Studies have not been conducted to study the effect of the drug Regulon on the abilities necessary to drive a car and operate machinery.
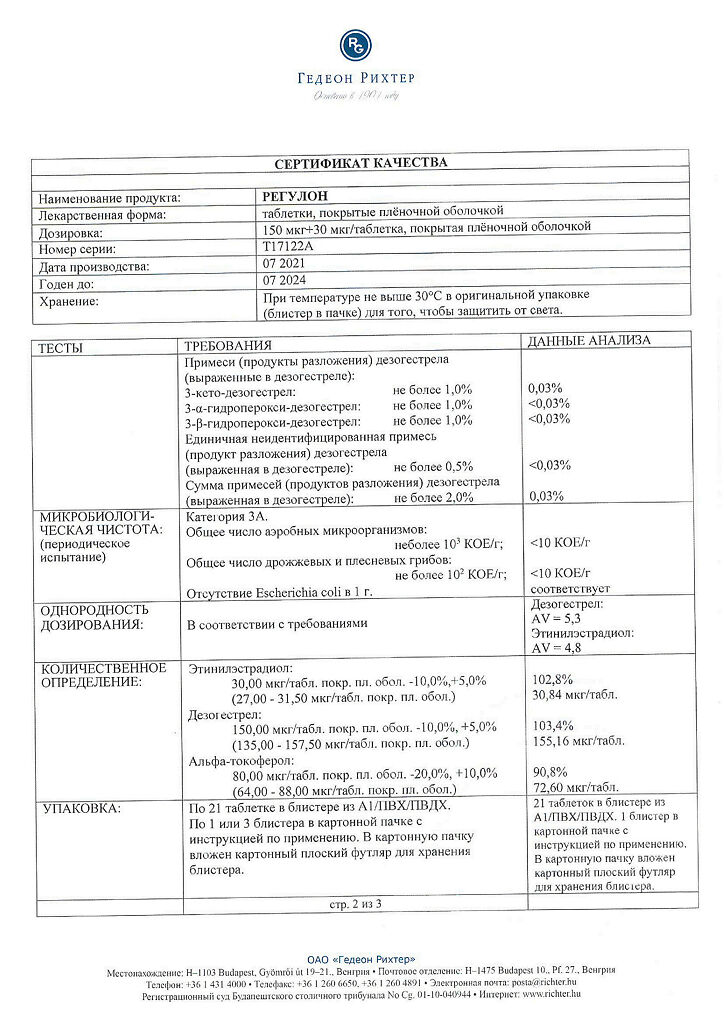
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Desogestrel, Ethinylestradiol
Composition
Composition
1 tablet contains:
active substances:
ethinyl estradiol 0.03 mg,
desogestrel 0.15 mg,
excipients:
α-tocopherol – 0.08 mg;
magnesium stearate – 0.08 mg;
colloidal silicon dioxide – 0.8 mg;
stearic acid – 0.8 mg;
povidone – 2.4 mg;
potato starch – 8 mg;
lactose monohydrate – 67.66 mg,
film shell:
propylene glycol – 0.03 mg;
macrogol 6000 – 0.22 mg;
hypromellose – 0.75 mg
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Regulon is contraindicated for use during pregnancy. Regulon should be stopped 3 months before the planned pregnancy. If pregnancy occurs, the drug should be discontinued.
Epidemiological studies have shown that among children born to women who took hormonal contraceptives before pregnancy, the incidence of malformations does not increase. In cases of taking the drug in the early stages of pregnancy, no teratogenic effect was detected.
The use of Regulon is contraindicated during lactation (breastfeeding), because it reduces the secretion of breast milk and changes its composition. In addition, the active substances are excreted in small quantities in breast milk.
Contraindications
Contraindications
the presence of severe and/or multiple risk factors for venous or arterial thrombosis (including severe or moderate arterial hypertension with blood pressure ≥ 160/100 mm Hg);
presence or indication in history of precursors of thrombosis (including transient ischemic attack, angina pectoris);
migraine with focal neurological symptoms, incl. in the anamnesis;
venous or arterial thrombosis/thromboembolism (including myocardial infarction, stroke, deep vein thrombosis of the leg, pulmonary embolism) currently or in history;
a history of venous thromboembolism;
diabetes mellitus (with angiopathy);
pancreatitis (including a history), accompanied by severe hypertriglyceridemia;
dyslipidemia;
severe liver diseases, cholestatic jaundice (including during pregnancy), hepatitis, incl. history (before normalization of functional and laboratory parameters and within 3 months after their normalization);
jaundice when taking GCS;
gallstone disease currently or in history;
Gilbert’s syndrome, Dubin-Johnson syndrome, Rotor syndrome;
liver tumors (including history);
severe itching, otosclerosis or its progression during a previous pregnancy or taking corticosteroids;
hormone-dependent malignant neoplasms of the genital organs and mammary glands (including if they are suspected);
vaginal bleeding of unknown etiology;
smoking over the age of 35 (more than 15 cigarettes per day);
pregnancy or suspicion of it;
lactation period;
hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
The drug should be prescribed with caution in conditions that increase the risk of developing venous or arterial thrombosis/thromboembolism: age over 35 years, smoking, family history, obesity (body mass index more than 30 kg/m2), dyslipoproteinemia, arterial hypertension, migraine, epilepsy, valvular heart disease, atrial fibrillation, prolonged immobilization, extensive surgery, surgical intervention on lower extremities, severe trauma, varicose veins and superficial thrombophlebitis, the postpartum period, the presence of severe depression (including a history), changes in biochemical parameters (activated protein C resistance, hyperhomocysteinemia, antithrombin III deficiency, protein C or S deficiency, antiphospholipid antibodies, including antibodies to cardiolipin, including lupus anticoagulant), sugar diabetes not complicated by vascular disorders, SLE, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, sickle cell anemia, hypertriglyceridemia (incl. family history), acute and chronic liver diseases.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Side effects requiring discontinuation of the drug
From the cardiovascular system: arterial hypertension; rarely – arterial and venous thromboembolism (including myocardial infarction, stroke, deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities, pulmonary embolism); very rarely – arterial or venous thromboembolism of the hepatic, mesenteric, renal, retinal arteries and veins.
From the senses: hearing loss caused by otosclerosis.
Other: hemolytic-uremic syndrome, porphyria; rarely – exacerbation of reactive systemic lupus erythematosus; very rarely – Sydenham’s chorea (passing after discontinuation of the drug).
Other side effects that are more common but less severe. The advisability of continuing to use the drug is decided individually after consultation with a doctor, based on the benefit/risk ratio.
From the reproductive system: acyclic bleeding/bloody discharge from the vagina, amenorrhea after discontinuation of the drug, changes in the state of vaginal mucus, the development of inflammatory processes in the vagina, candidiasis, tension, pain, enlarged mammary glands, galactorrhea.
From the digestive system: nausea, vomiting, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, the occurrence or exacerbation of jaundice and/or itching associated with cholestasis, cholelithiasis.
Dermatological reactions: erythema nodosum, exudative erythema, rash, chloasma.
From the central nervous system: headache, migraine, mood lability, depression.
On the part of the organ of vision: increased sensitivity of the cornea (when wearing contact lenses).
Metabolism: fluid retention in the body, change (increase) in body weight, decreased tolerance to carbohydrates.
Other: allergic reactions.
Interaction
Interaction
With simultaneous use of Regulon with antispasmodics, phenobarbital derivatives, antibiotics (tetracycline, ampicillin, rifampicin, isoniazid, neomycin, penicillin, chloramphenicol), carbamazepine, phenylbutazone, analgesics, anxiolytics, activated carbon, sulfonamides, nitrofurans, anti-migraine drugs, griseofulvin, laxatives and some medicinal plants (for example, St. John’s wort) may change the nature of menstruation and reduce the contraceptive effect of Regulon.
Regulon, when used simultaneously, reduces the effectiveness of oral anticoagulants, anxiolytics (diazepam), tricyclic antidepressants, guanethidine, theophylline, caffeine, vitamins, clofibrate, glucocorticosteroids, paracetamol.
When Regulon is used simultaneously with oral hypoglycemic drugs or insulin, the control of carbohydrate metabolism may be impaired, because Regulon may reduce carbohydrate tolerance and increase the need for insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents, which may require dose adjustment.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: metrorrhagia. Taking the drug in high doses was not accompanied by the appearance of severe symptoms.
Treatment: in the first 2-3 hours after taking the drug in a high dose, gastric lavage is recommended. There is no specific antidote, treatment is symptomatic.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At 15–30 °C
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Gedeon Richter, Hungary
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At 15-30 °C |
| Manufacturer | Gedeon Richter, Hungary |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Gedeon Richter |
Other forms…
Related products
Gynecology and Obstetrics
Buy Regulon, 21 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.