No products in the cart.
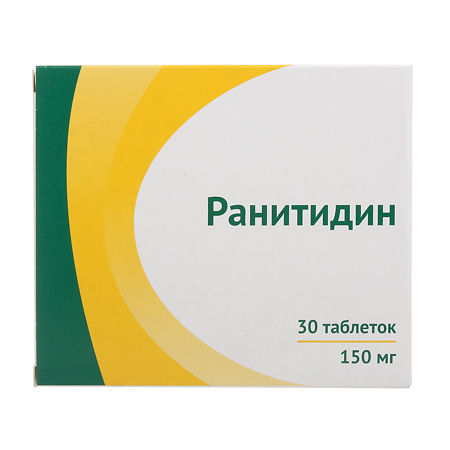
Ranitidine, tablets 150 mg, 30 pcs.
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
EAN: 4607027766290
SKU: 235754
Categories: Medicine, Stomach, intestines, liver, Ulcer and gastritis
Description
Ranitidine blocks histamine H2-receptors of parietal cells of gastric mucosa, reduces basal and stimulated secretion of hydrochloric acid caused by irritation of baroreceptors, food load, action of hormones and biogenic stimulators (gastrin, histamine, pentagastrin). Ranitidine reduces the volume of gastric juice and the content of hydrochloric acid in it, increases pH of the stomach contents, which leads to decrease in pepsin activity. After oral administration in therapeutic doses does not affect the level of prolactin. Inhibits microsomal enzymes.
The duration of action after a single dose is up to 12 hours.
Pharmacokinetics
It is rapidly absorbed, eating does not affect the degree of absorption. With oral administration the bioavailability of ranitidine is about 50%. Cmax in plasma is reached 2-3 hours after intake.
The binding to plasma proteins does not exceed 15%. It is slightly metabolized in the liver with the formation of desmethylranitidine and S-oxide ranitidine.
It has the effect of first passage through the liver. The rate and extent of elimination are little dependent on the state of the liver.
T1/2 after oral administration is 2.5 hours, at CKR 20-30 ml/min – 8-9 hours. It is excreted mainly with urine (60-70%, 35% unchanged), a small amount is excreted with feces. It penetrates poorly through the blood-brain barrier. It penetrates through the placenta. It is excreted with breast milk (concentration in breast milk in women during lactation is higher than in plasma).
Indications
Indications
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
1 tablet contains:
The active ingredient:
Ranitidine (as hydrochloride)150 mg;
Associates:
MCC;
Corn starch;
Collidone VA-64;
Colloidal silicon dioxide;
Magnesium stearate;
Hypromellose;
ethylcellulose;
Polyethylene glycol 6000;
propylene glycol;
sodium lauryl sulfate;
Titanium dioxide;
Sunset Yellow dye.
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Orally, regardless of meals, without chewing, with a small amount of liquid.
Adults and children over 12 years
Peptic ulcer disease of the stomach and duodenum. For treatment of exacerbations it is prescribed in dose – 150 mg 2 times a day (in the morning and in the evening) or 300 mg at night. If necessary, 300 mg 2 times a day. The course of treatment shall be 4-8 weeks. For prevention of exacerbations, it is prescribed 150 mg at night, for smoking patients – 300 mg at night.
Evening ulcers associated with taking NSAIDs. It is prescribed in 150 mg 2 times a day or 300 mg at night for 8-12 weeks.
Prophylaxis of ulcers when taking NSAIDs – 150 mg 2 times a day.
Postoperative and stress ulcers. It is prescribed in 150 mg 2 times a day for 4-8 weeks.
Erosive reflux esophagitis. It is prescribed 150 mg 2 times a day or 300 mg at night. If necessary, the dose can be increased to 150 mg 4 times a day. The course of treatment is 8-12 weeks. Prolonged prophylactic therapy is 150 mg 2 times a day.
The Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. The initial dose is 150 mg 3 times a day, if necessary the dose can be increased.
Prevention of recurrent bleeding. 150 mg 2 times a day.
Prevention of development of Mendelsohn syndrome. It is administered in a dose of 150 mg 2 hours before anesthesia, and preferably 150 mg the night before. In the presence of concomitant hepatic dysfunction, a dose reduction may be required.
In patients with renal impairment with a creatinine Cl less than 50 mL/min, the recommended dose is 150 mg/day.
Interaction
Interaction
Smoking reduces the efficacy of ranitidine.
Enhances serum concentrations of metoprolol (80% and 50%, respectively), with increased metoprolol elimination half-life from 4.4 to 6.5 hours.
Due to the increase in the pH of the stomach contents, the absorption of itraconazole and ketoconazole may be reduced with concomitant administration.
It inhibits hepatic metabolism of phenazone, aminophenazone, diazepam, hexobarbital, propracolol, diazepam, lidocaine, phenytoin, theophylline, aminophylline, indirect anticoagulants, glipizide, buformin, metronidazole, calcium antagonists.
Drugs that depress bone marrow increase the risk of neutropenia.
In concomitant use with antacids, sucralfate in high doses may slow down absorption of ranitidine, therefore a break of at least 2 hours between taking these drugs.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
Treatment with ranitidine may mask symptoms associated with gastric carcinoma, so ulcerative cancer should be ruled out before starting treatment.
Ranitidine, like all H2-histamine blockers, should not be abruptly withdrawn (ricochet syndrome).
In long-term treatment of debilitated patients under stress, bacterial lesions of the stomach with subsequent spread of infection are possible.
There are reports that ranitidine may cause acute attacks of porphyria.
H2-histamine receptor blockers should be taken 2 hours after taking itraconazole or ketoconazole to avoid significantly reducing their absorption.
May increase glutamate transpeptidase activity.
May cause a false positive reaction to a urine protein test.
H2-histamine receptor blockers may counteract the effects of pentagastrin and histamine on gastric acid-producing function, so the use of H2-histamine receptor blockers is not recommended during the 24 hours preceding the test.
Histamine H2-histamine receptor blockers may inhibit the skin reaction to histamine, and this may cause false-positive results (we recommend that N2-histamine receptor blockers not be used prior to diagnostic skin testing for immediate allergic skin reactions).
When treating, avoid eating foods, drinks, and other medications that may irritate the gastric mucosa.
Pediatric use
The safety and effectiveness of ranitidine in children under 12 years of age has not been established.
Impact on driving and operating machinery
At the time of treatment, it is necessary to refrain from potentially hazardous activities requiring increased concentration and rapid psychomotor reactions.
Contraindications
Contraindications
With caution: renal and/or hepatic insufficiency, cirrhosis with portosystemic encephalopathy in anamnesis, acute porphyria (including anamnesis).
Side effects
Side effects
Digestive system disorders: nausea, dry mouth, constipation, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain; rarely – hepatocellular, cholestatic or mixed hepatitis, acute pancreatitis.
Hematopoietic organs: leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis, pancytopenia, bone marrow hypo- and aplasia, immune hemolytic anemia.
Cardiovascular system: decreased blood pressure, bradycardia, arrhythmia, atrio-ventricular block.
Nervous system disorders: increased fatigue, drowsiness, headache, dizziness; confusion, tinnitus, irritability, hallucinations (mainly in elderly and severe patients), involuntary movements.
Senses: blurred vision, paresis of accommodation.
Musculoskeletal disorders: arthralgia, myalgia.
Endocrine system disorders: hyperprolactinemia, gynecomastia, amenorrhea, decreased libido, impotence.
Allergic reactions: urticaria, skin rash, angioedema, anaphylactic shock, bronchospasm, erythema multiforme.
Others: alopecia, hypercreatininemia.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: convulsions, bradycardia, ventricular arrhythmias.
Treatment: symptomatic. In the development of seizures – diazepam IV, in bradycardia or ventricular arrhythmias – atropine, lidocaine. Hemodialysis is effective.
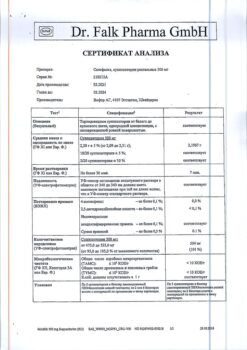
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, light-protected place at 15-30 °C. |
| Manufacturer | Ozon, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Ozon |
Related products
Buy Ranitidine, tablets 150 mg, 30 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.