No products in the cart.
Prednisolone, tablets 5 mg 100 pcs
€6.38 €5.67
Description
Prednisolone is a synthetic glucocorticoid drug. It has anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, immunosuppressive, antiexsudative and antipruritic effects.
The immunosuppressive effect is associated with inhibition of cytokine release from lymphocytes and macrophages. Other effects are caused by stabilization of cell membranes, decrease of capillaries permeability and improvement of microcirculation.
Prednisolone has a catabolic effect, increases blood glucose levels, causes redistribution of adipose tissue. The drug inhibits synthesis and secretion of ACTH and, secondarily, corticosteroids by adrenal glands.
When used topically and topically prednisolone has therapeutic activity due to its anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic and anti-exudative (due to its vasoconstrictor effect) action.
Indications
Indications
For oral and intramuscular use: rheumatism;
rheumatoid arthritis;
dermatomyositis;
periarteritis nodosa;
scleroderma;
Bekhterev’s disease;
bronchial asthma, status asthmaticus;
acute and chronic allergic diseases;
Addison’s disease, acute adrenal insufficiency, adrenogenital syndrome;
hepatitis, hepatic coma, hypoglycemic conditions, lipoid nephrosis;
agranulocytosis, various forms of leukemia, lymphogranulomatosis, thrombocytopenic purpura, hemolytic anemia;
chorea;
pemphigus, eczema, itching, exfoliative dermatitis, psoriasis, prurigo, seborrheic dermatitis, lupus erythematosus, erythroderma, alopecia.
For use in ophthalmology: allergic, chronic and atypical conjunctivitis and blepharitis;
inflammation of the cornea with intact mucosa;
acute and chronic inflammation of the anterior segment of the choroid, sclera and episclera;
sympathetic inflammation of the eyeball;
after injuries and operations with prolonged irritation of the eyeballs.
For intra-articular administration: chronic polyarthritis, post-traumatic arthritis, osteoarthritis of large joints, rheumatic lesions of individual joints, arthrosis.
For infiltration administration into tissues: epicondylitis, tendovaginitis, bursitis, humeroscapular periarthritis, keloids, sciatica, Dupuytren’s contracture, rheumatic and similar lesions of joints and various tissues.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Prednisolone is a synthetic glucocorticoid drug. It has anti-inflammatory, antiallergic, immunosuppressive, antiexudative and antipruritic effects.
The immunosuppressive effect is associated with inhibition of the release of cytokines from lymphocytes and macrophages. Other effects are caused by stabilization of cell membranes, reduction of capillary permeability, and improvement of microcirculation.
Prednisolone has a catabolic effect, increases blood glucose levels, and causes redistribution of adipose tissue. The drug inhibits the synthesis and secretion of ACTH and, secondarily, corticosteroids by the adrenal glands.
When applied externally and locally, the therapeutic activity of prednisolone is due to its anti-inflammatory, antiallergic and antiexudative (due to the vasoconstrictor effect) effect.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Prednisolone is contraindicated in patients with systemic fungal infections due to the risk of worsening the infection. The drug may in some cases be used for fungal infections treated with amphotericin B to reduce its side effects, but in these cases it can cause circulatory failure and hypertrophy of the left ventricular myocardium, as well as severe hypokalemia. Taking the drug with food can reduce gastrointestinal side effects.
Antacids have not been shown to be effective in preventing ulcers, gastrointestinal bleeding, or intestinal perforation. With long-term treatment, it may be necessary to limit sodium and increase potassium content, as well as increase protein content in food.
In the event of the development of steroid myopathy, if prednisolone therapy cannot be discontinued, replacing it with another GCS can alleviate the symptoms.
The risk of osteoporosis associated with long-term use of corticosteroids can be reduced by taking calcium and vitamin D or, if the patient’s condition allows, by performing appropriate physical exercise.
If psychosis or depression occurs, the dose should be reduced or discontinued if possible. If necessary, phenothiazines or lithium compounds can be used.
In order to alleviate some of the symptoms of GCS withdrawal syndrome (without suppressing the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis), acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs can be prescribed.
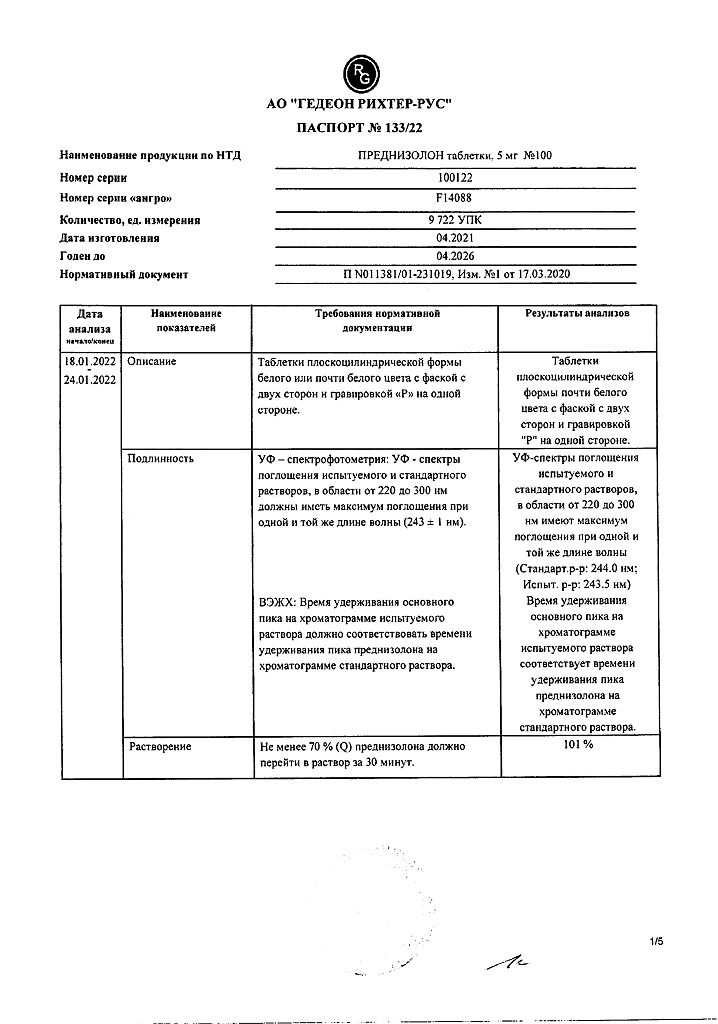
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Prednisolone
Composition
Composition
1 tablet contains:
Active substance:
prednisolone 5 mg;
Excipients:
lactose;
potato starch;
gelatin;
magnesium stearate
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Taking GCS by women of childbearing age and pregnant women is permissible only when its potential benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. Women of childbearing age should be warned of the potential risk to the fetus.
There are not enough controlled observations in humans. In animal studies, corticosteroids have been associated with an increased incidence of cleft palate, miscarriage, placental insufficiency, and fetal growth restriction. Although the teratogenic effect of GCS in humans has not been confirmed, there is evidence indicating an increased risk of placental insufficiency.
sufficiency, malnutrition at birth and fetal death in women who took GCS during pregnancy. They can cause adrenal insufficiency in the fetus and newborn.
Breastfeeding should be stopped during treatment. Prednisolone is excreted in breast milk and can cause undesirable effects in the child, such as growth retardation or inhibition of the production of endogenous adrenal hormones.
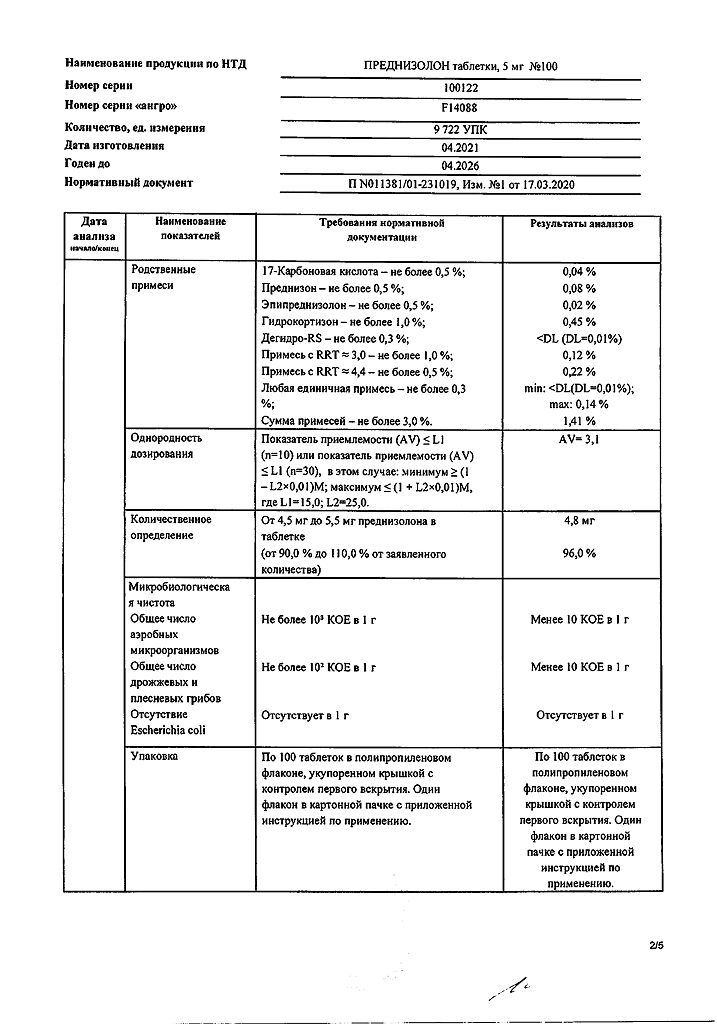
Contraindications
Contraindications
Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, osteoporosis, Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, tendency to thromboembolism, renal failure, severe arterial hypertension, systemic mycoses, viral infections, vaccination period, active form of tuberculosis, glaucoma, productive symptoms in mental illness.
Hypersensitivity to prednisolone.
Infiltration administration into lesions of the skin and tissues – with chickenpox, specific infections, mycoses, with a local reaction to vaccination.
In ophthalmology – viral and bacterial eye diseases, primary glaucoma, diseases of the cornea with damage to the epithelium.
In dermatology – bacterial, viral, fungal skin lesions, tuberculosis, syphilis, skin tumors.
Side Effects
Side Effects
With short-term use of prednisolone, like other corticosteroids, side effects are rarely observed. When using prednisolone for a long time, the following side effects may develop:
Disturbances of water and electrolyte metabolism: sodium and fluid retention in the body, hypokalemia, hypokalemic alkalosis.
From the cardiovascular system: increased blood pressure, circulatory failure.
From the musculoskeletal system: muscle weakness, steroid myopathy, loss of muscle mass, osteoporosis, compression fracture of the spine, aseptic necrosis of the heads of the femur and humerus, pathological fractures of long tubular bones.
From the gastrointestinal tract: steroid ulcer with possible perforation and bleeding, pancreatitis, flatulence, ulcerative esophagitis, indigestion, nausea, increased appetite.
From the skin: atrophic stripes, acne, delayed wound healing, thinning of the skin, petechiae and hematomas, erythema, increased sweating, allergic dermatitis, urticaria, angioedema.
From the nervous system and sensory organs: increased intracranial pressure with optic nerve congestion syndrome (pseudotumor of the brain – more often in children, usually after too rapid dose reduction, symptoms – headache, deterioration of visual acuity or double vision); convulsions, dizziness, headache, sleep disturbance, posterior subcapsular cataract, increased intraocular pressure, glaucoma; exophthalmos.
Endocrine status: secondary adrenal and hypothalamic-pituitary insufficiency (especially during stressful situations such as illness, injury, surgery); Cushing’s syndrome; growth suppression in children; menstrual irregularities; decreased tolerance to carbohydrates; manifestation of latent diabetes mellitus and increased need for insulin or oral antidiabetic drugs in patients with diabetes mellitus, hirsutism.
From the side of metabolism: negative nitrogen balance as a result of protein catabolism, hyperglycemia, glycosuria.
Mental disorders: symptoms simulating schizophrenia, mania or delirium (most often appear during the first two weeks of treatment). Women and patients with lupus erythematosus are most susceptible to mental disorders.
Other: anaphylactic reactions and hypersensitivity reactions, obliterating endarteritis, weight gain, masking the symptoms of infectious diseases, fainting.
Interaction
Interaction
Cardiac glycosides: increased risk of cardiac arrhythmias and glycoside toxicity associated with hypokalemia.
Barbiturates, antiepileptic drugs (phenytoin, carbamazepine), rifampicin, glutethimide accelerate the metabolism of GCS (by inducing microsomal enzymes) and weaken their effect.
Antihistamines weaken the effect of prednisolone.
Amphotericin B, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: hypokalemia, left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy, circulatory failure.
Paracetamol: hypernatremia, peripheral edema, increased calcium excretion, risk of hypocalcemia and osteoporosis. Increased risk of paracetamol hepatotoxicity.
Anabolic steroids, androgens: increased risk of developing peripheral edema, acne; use with caution, especially in cases of liver and heart disease.
Oral contraceptives containing estrogens: an increase in the concentration of globulins that bind glucocorticosteroids in the blood serum, a slowdown in metabolism, an increase in T1/2, an increase in the effect of prednisolone.
Anticholinergic drugs (mainly atropine) – increase intraocular pressure.
Anticoagulants (coumarin derivatives, indanedione, heparin), streptokinase, urokinase: decreased, and in some patients increased, effectiveness; the dose should be determined based on the PT; increased risk of ulcer formation and bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract.
Tricyclic antidepressants may increase psychiatric disorders associated with prednisolone. They should not be prescribed for the treatment of these disorders.
Oral antidiabetic drugs, insulin: weakening of the hypoglycemic effect, increasing the concentration of glucose in the blood. It is possible to adjust the dose of antidiabetic drugs.
Antithyroid drugs, thyroid hormones – changes in thyroid function (the dose of these drugs may be adjusted or discontinued).
Diuretics: weakening of the effect of diuretics (potassium-sparing), hypokalemia.
Laxatives: decreased effect, hypokalemia.
Ephedrine can accelerate the metabolism of GCS (prednisolone dose adjustment is possible).
Immunosuppressive drugs: increased risk of infection, lymphoma and other lymphoproliferative diseases.
Isoniazid: decrease in the concentration of isoniazid in the blood plasma, mainly in individuals with rapid acetylation (dose changes are possible).
Mexiletine: acceleration of the metabolism of mexiletine and reduction of its concentration in the blood serum.
Drugs that block neuromuscular conduction (depolarizing muscle relaxants): Hypocalcemia associated with the use of prednisolone may increase synaptic blockade, leading to an increase in the duration of neuromuscular blockade.
NSAIDs, acetylsalicylic acid, alcohol: weakened effect, increased risk of developing peptic ulcers and bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract.
Drugs and food containing sodium: peripheral edema, arterial hypertension (it may be necessary to reduce sodium intake from food and medications high in sodium; sometimes the use of GCS requires additional sodium).
Vaccines containing live viruses: during the period of use of immunosuppressive doses of GCS, viral replication and the development of viral diseases are possible; decreased antibody production (simultaneous use is not recommended).
Other vaccines: increased risk of neurological complications and decreased antibody production.
Folic acid: increased need for this drug.
Overdose
Overdose
The risk of overdose increases with long-term use of prednisolone, especially in large doses.
Symptoms: increased blood pressure, peripheral edema, increased undesirable effects described above.
Treatment: You should temporarily stop taking the drug or reduce the dose.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At temperatures below 25 °C.
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Gedeon Richter, Hungary
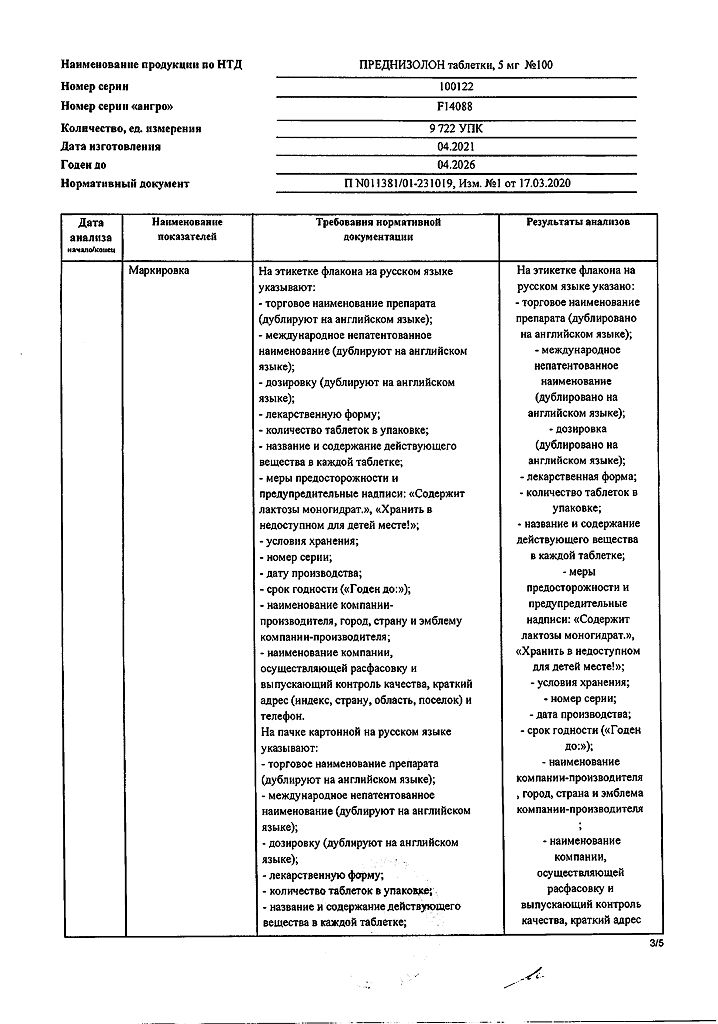
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At temperatures below 25 °C. |
| Manufacturer | Gedeon Richter, Hungary |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Gedeon Richter |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Prednisolone, tablets 5 mg 100 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.