No products in the cart.
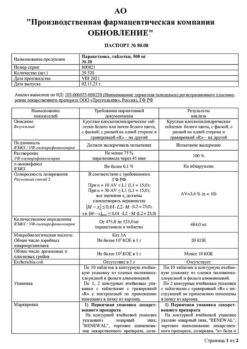
Paracetamol, tablets 500 mg 10 pcs.
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Paracetamol is an analgesic and antipyretic. It blocks the synthesis of prostaglandins in the central nervous system by inhibiting cyclooxygenase 1 and cyclooxygenase 2, affecting the centers of pain and thermoregulation.
Indications
Indications
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Adults, including the elderly and children over 12 years:
By 0.5-1 g, 1-2 hours after meals with plenty of fluid in 4-6 hours, the maximum daily dose up to 4 g per day.
The interval between doses should be at least 4 hours. Do not take more than 8 tablets within 24 hours.
In patients with hepatic or renal dysfunction, with Gilbert’s syndrome, in elderly patients the daily dose should be reduced and the interval between doses should be increased.
In children:
Daily dose from 3 to 6 years of age (from 15 to 22 kg) – 1 g, to 9 years of age (to 30 kg) – 1.5 kg, to 12 years of age (to 40 kg) – 2 g. The frequency of administration – 4 times a day, the interval between each dose – at least 4 hours.
If symptoms persist, consult a physician.
Do not exceed the stated dose. If you have taken a dose exceeding the recommended dose, seek medical attention, even if you feel well. An overdose of paracetamol can cause liver failure.
The drug should not be used for more than five days as a pain reliever and more than three days as an antipyretic without a doctor’s prescription and supervision. Increasing the daily dose of the drug or the duration of treatment is possible only under the supervision of a physician.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
to avoid toxic liver damage, do not take paracetamol with alcoholic drinks, or with people who have a tendency to drink alcohol spirits chronically.
Peripheral blood count and liver function monitoring are necessary during long-term treatment.
Interaction: The drug when taken for a long time increases the effect of indirect anticoagulants (warfarin and other coumarins), which increases the risk of bleeding. Inducers of microsomal oxidation enzymes in the liver (barbiturates, diphenine, carbamazepine, rifampicin, zidovudine, phenytoin, ethanol, flumecinol, phenylbutazone and tricyclic antidepressants) increase the risk of hepatotoxic effects in overdose.
Long-term use of barbiturates reduces the effectiveness of paracetamol.
Ethanol promotes acute pancreatitis.
Microsomal oxidation inhibitors (cimetidine) reduce the risk of hepatotoxic effects. Concomitant use with other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs increases nephrotoxic effect.
The concomitant use of paracetamol in high doses and salicylates increases the risk of kidney and bladder cancer. Diflunisal increases the plasma concentration of paracetamol by 50% – risk of hepatotoxicity.
Myelotoxic drugs increase the manifestation of hematotoxicity of the drug. Metoclopramide and domperidone increase and cholestyramine decreases the absorption rate of paracetamol. The drug may decrease the activity of uricosuric drugs.
Contraindications
Contraindications
With caution:
Use with caution in benign hyperbilirubinemia (including Gilbert syndrome), viral hepatitis, alcoholic liver damage, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, alcoholism, pregnancy, during lactation, the elderly. The drug should not be taken simultaneously with other paracetamol-containing drugs.
Side effects
Side effects
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms:
Pallor of the skin, anorexia, nausea, vomiting; hepatonecrosis (severity of necrosis directly depends on the degree of overdose). If overdose is suspected, seek medical attention immediately. Toxic effects of the drug in adults may be observed after taking over 10-15 g of paracetamol: increased “liver” transaminases activity, increased prothrombin time (12-48 hours after intake); clinical picture of liver damage becomes apparent after 1-6 days. Rarely, liver dysfunction develops fulminantly and may be complicated by renal failure (tubular necrosis).
Treatment:
The victim should be gastric lavage within the first 4 hours of poisoning, take adsorbents (activated charcoal) and consult a physician, administration of SH-group donators and precursors of glutathione synthesis – methionine in 8-9 hours after overdose and N-acetylcysteine – in 12 hours. The need for additional therapeutic measures (further methionine administration, intravenous N-acetylcysteine administration) is determined depending on the concentration of paracetamol in the blood, as well as on the time elapsed after its administration.
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
| Conditions of storage | Store in a dry, protected from light and out of the reach of children, at a temperature not exceeding + 25 ° C. |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Update PFC AO, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Update PFC AO |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Paracetamol, tablets 500 mg 10 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.