No products in the cart.
Description
Nivolumab is a human monoclonal antibody that blocks the interaction between the programmed death receptor (PD-1) and its ligands (PD-L1 and PD-L2). Nivolumab is a G4 immunoglobulin (IgG4) with an approximate molecular weight of 146 kDa.
PD-I receptor is a negative regulator of T-cell activity. Binding of PD-1 to PD-L1 and PD-L2 ligands, which can be expressed by tumor cells or other cells in the tumor microenvironment, leads to inhibition of T-cell proliferation and cytokine secretion. Nivolumab potentiates the immune response through blockade of PD-1 binding to PD-L1 and PD-L2 ligands. In studies on murine models, blocking PD-1 activity led to a reduction in tumor growth.
Indications
Indications
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
The drug should be administered under the guidance of a physician experienced in the treatment of cancer.
The recommended dose of Opdivo® in adults is 3 mg/kg body weight in the form of a 60-minute intravenous infusion given every 2 weeks. Treatment should be continued if there is a clinical effect or until signs of intolerable toxicity appear.
Increasing or decreasing the dose of the drug is not recommended. Delayed administration of the next dose or withdrawal may be due to individual safety or tolerability of the drug. Recommendations for permanently cancelling or skipping the administration of Opdivo® are shown in Table 1. Detailed recommendations for elimination of immune-mediated adverse reactions are given in section “Special Indications”.
Table 1. Canceling or skipping a dose of Opdivo®
Note: The degree of toxicity corresponds to the general terminology of the National Cancer Institute Criteria for Adverse Events, Version 4.0 (NCI-CTCAE v4)
Renal impairment
No dose adjustment is required for mild to moderate renal impairment.
Hepatic impairment
In mild hepatic impairment a dose adjustment is not required.
Elderly patients
No adjustment of the drug dose is required in patients aged 65 and older.
Interaction
Interaction
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
Opdivo® may cause severe, including fatal, adverse reactions due to effects on the immune system and its specific mechanism of action. Patients should be monitored continuously (at least 5 months after the last dose), since adverse reactions due to the effects of Opdivo® may develop at any time during use or after discontinuation of therapy. If an immune-mediated adverse reaction is suspected, an adequate evaluation should be performed to confirm or rule out another etiology. Based on the severity of the adverse reaction, the use of Opdivo® should be discontinued with or without resumption with administration of glucocorticosteroids.
In the case of immunosuppressive therapy with glucocorticosteroids intended to eliminate adverse reactions, once the condition improves, the dose of glucocorticosteroids is reduced slowly, over at least 1 month. Rapid dose reduction may worsen the severity or recurrence of adverse reactions. Immunosuppressive therapy with drugs other than glucocorticosteroids is prescribed in case of worsening or no improvement with glucocorticosteroids.
The use of Opdivo® should be discontinued while the patient is receiving an immunosuppressive dose of glucocorticosteroids or immunosuppressive therapy.
Opdivo® should be discontinued for any moderate to severe recurrent immune-mediated adverse reactions and discontinued without resumption for severe immune-mediated pneumonitis and immune-mediated hepatitis and life-threatening immune-mediated adverse reactions.
Use of Opdivo® in patients with rapidly progressing melanoma
Physicians should discuss the delayed effect of Opdivo® prior to treatment in patients with rapidly progressing disease.
Immune-mediated pneumonitis
Cases of severe pneumonitis or interstitial lung disease, including fatalities, have been reported during therapy with Opdivo®. Patients should be monitored for signs and symptoms of pneumonitis, such as radiographic changes (e.g., frosted glass-like darkening, foci of inflammation), dyspnea, and hypoxia. Infections and disease-related symptoms should be ruled out.
At grade 3 or 4 pneumonitis severity, Opdivo® should be discontinued without resumption and glucocorticosteroids should be started at a dose equivalent to 2-4 mg/kg/day of methylprednisolone.
In grade 2 severe (symptomatic) pneumonitis the use of Opdivo® should be suspended and glucocorticosteroids should be started at a dose equivalent to 1-2 mg/kg/day of methylprednisolone. If improvement occurs, the use of Opdivo® may be continued after a slow decrease in the dose of glucocorticosteroids. If worsening or no improvement occurs and continues despite glucocorticosteroid administration, the glucocorticosteroid dose should be increased to the equivalent of 2-4 mg/kg/day of methylprednisolone and nivolumab should be discontinued without resumption.
Immune-mediated colitis
Cases of severe diarrhea or colitis have been reported during therapy with Opdivo®. Patients should be monitored for signs of diarrhea and additional symptoms of colitis, such as abdominal pain, mucus, or blood in the stool. Infections and disease-related symptoms should be ruled out.
At grade 4 severity of diarrhea or colitis, use of Opdivo® should be discontinued permanently and glucocorticosteroids should be started at a dose equivalent to 1-2 mg/kg/day of methylprednisolone.
In grade 3 diarrhea or colitis, nivolumab should be stopped and glucocorticosteroids should be started at a dose equivalent to 1-2 mg/kg/day of methylprednisolone. If improvement occurs, the use of Opdivo® may be continued after a slow decrease in the dose of glucocorticosteroids. In case of worsening or no improvement that continues despite glucocorticosteroid therapy, nivolumab should be discontinued without resuming.
In cases of grade 2 diarrhea or colitis, the use of Opdivo® should be suspended. Persistent diarrhea or colitis should be managed with glucocorticosteroid administration at a dose equivalent to 0.5-1 mg/kg/day of methylprednisolone. If improvement occurs, nivolumab may be continued after a slow decrease in the dose of glucocorticosteroids. If deterioration or no improvement occurs and continues despite glucocorticosteroid administration, the glucocorticosteroid dose should be increased to the equivalent of 1 -2 mg/kg/day of methylprednisolone and nivolumab should be discontinued without resumption.
Immune-mediated hepatitis
Cases of severe hepatitis have been reported with therapy with Opdivo®. Patients should be monitored for signs and symptoms of hepatitis, such as increased levels of transaminases and total bilirubin. Infections and disease-related symptoms should be ruled out.
In grade 3 or 4 severe increases in transaminases and total bilirubin, the use of Opdivo® should be discontinued without resumption and glucocorticosteroids at a dose equivalent to 1 to 2 mg/kg/day of methylprednisolone should be started.
In 2nd degree severity of transaminase and total bilirubin elevations, the use of Opdivo® should be suspended. Persistent elevation of these laboratory values should be eliminated by administration of glucocorticosteroids at a dose equivalent to 1 – 2 mg/kg/day of methylprednisolone. If improvement occurs, nivolumab may be continued after slowly reducing the dose of glucocorticosteroids. If deterioration or lack of improvement occurs and continues despite glucocorticosteroid administration, the glucocorticosteroid dose should be increased to the equivalent of 1 to 2 mg/kg/day of methylprednisolone and nivolumab should be discontinued without resumption.
Immune-mediated nephritis and renal dysfunction
Cases of severe nephritis or renal dysfunction have been reported during therapy with Opdivo®, so patients should be monitored for signs and symptoms. Asymptomatic elevation of serum creatinine has been noted in most patients. An etiology associated with the disease must be ruled out.
In grade 4 severe serum creatinine elevation, the use of Opdivo® should be discontinued permanently and glucocorticosteroids should be started at a dose equivalent to I to 2 mg/kg/day of methylprednisolone.
In 2nd or 3rd degree severity of serum creatinine increase, the use of Opdivo® should be suspended and glucocorticosteroids should be started at a dose equivalent to 0.5 – 1 mg/kg/day of methylprednisolone. If improvement occurs, nivolumab may be continued after slowly reducing the dose of glucocorticosteroids. If deterioration or lack of improvement occurs and continues despite glucocorticosteroid administration, the glucocorticosteroid dose should be increased to the equivalent of I to 2 mg/kg/day of methylprednisolone and nivolumab should be discontinued without resumption.
Immune-mediated endocrinopathy
Cases of severe endocrinopathy, including hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, insufficient adrenal cortex, hypophysitis, diabetes and diabetic ketoacidosis have been reported during therapy with Opdivo®.
Patients should be monitored for signs and symptoms of endocrinopathies and changes in thyroid function (at the start of treatment, periodically during treatment and based on clinical evaluation). Patients may present with fatigue, headache, altered mental status, abdominal pain, unusual bowel rhythm, and hypotension or nonspecific symptoms that may have similarities to other conditions such as brain metastases or comorbidities. If no other etiology is identified, signs and symptoms of endocrinopathies should be considered immune-mediated.
In symptomatic hypothyroidism, the use of Opdivo® should be suspended and, if necessary, thyroid hormone replacement therapy should be carried out. In symptomatic hyperthyroidism, the use of Opdivo® should be suspended, and if necessary, therapy with antithyroid drugs should be carried out. In case of acute thyroiditis, glucocorticosteroids at a dose equivalent to 1 – 2 mg/kg/day of methylprednisolone should be administered. If improvement occurs, the use of Opdivo® may be continued after a slow reduction in the dose of glucocorticosteroids. Thyroid function should continue to be monitored to monitor the adequacy of the ongoing thyroid hormone replacement therapy.
In symptomatic grade 2 adrenal cortical insufficiency, the use of nivolumab should be suspended and, if necessary, physiological glucocorticosteroid replacement should be performed. In symptomatic grade 3-4 adrenal cortical insufficiency, nivolumab should be discontinued permanently and, if necessary, physiological glucocorticosteroid replacement should be performed.
Adrenal function and hormone levels should continue to be monitored to monitor the adequacy of ongoing glucocorticosteroid replacement therapy.
In symptomatic hypophysitis of 2-3 degrees the use of Opdivo® should be suspended and, if necessary, hormone replacement therapy should be carried out. In case of acute hypophysitis glucocorticosteroids in dose equivalent to 1 – 2 mg/kg/day of methylprednisolone are administered. If improvement occurs, the use of Opdivo® may be continued after slow reduction of the dose of glucocorticosteroids. In symptomatic grade 4 hypophysitis, nivolumab therapy should be discontinued permanently. Pituitary function and hormone levels should continue to be monitored to monitor the adequacy of the ongoing hormone replacement therapy.
In symptomatic diabetes the use of nivolumab should be suspended and insulin replacement therapy, if necessary. Blood sugar levels should be monitored to monitor the adequacy of insulin replacement therapy.
Immune-mediated rash
Cases of severe rash (including rare cases of fatal toxic epidermal necrolysis) that may be immune-mediated have been reported during therapy with the drug Opdivo®. Nivolumab should be discontinued for a grade 3 rash and discontinued without recovery for a grade 4 rash. In severe rash, treatment with glucocorticosteroids at a dose equivalent to 1 to 2 mg/kg/day of methylprednisolone is indicated.
Opdivo® should be administered with caution in patients who have previously experienced severe or life-threatening adverse skin reactions during treatment with other immunostimulant antineoplastic agents.
Other immune-mediated adverse reactions
The following immune-mediated adverse reactions have been reported in less than 1% of patients treated with Opdivo® during clinical trials at any dosage and tumor type: pancreatitis, uveitis, demyelination, autoimmune neuropathy (including facial and abductor nerve paresis), Guillain-Barré syndrome, hypopituitarism, myasthenic syndrome and encephalitis.
If immune-mediated adverse reactions are suspected, an adequate evaluation should be performed to confirm their etiology or to rule out other causes. Based on the severity of the adverse reaction, the use of Opdivo® should be discontinued and therapy with glucocorticosteroids should be started. If improvement occurs, nivolumab may be continued after a slow decrease in the dose of glucocorticosteroids. Opdivo® should be discontinued without resumption if any recurrent severe immune-mediated adverse reactions and any life-threatening immune-mediated adverse reactions occur.
Infusion reactions
Cases of severe infusion reactions have been reported during clinical trials. In case of severe infusion reactions, the administration of Opdivo® should be discontinued with the administration of appropriate drug therapy. Patients with mild to moderate infusion reactions may continue therapy with Opdivo® under continuous observation and premedication in accordance with the current standards of prevention of infusion reactions.
Patients on a controlled sodium diet
Each milliliter of Opdivo® drug contains 0.1 mmol (or 2.5 mg) of sodium, which must be considered when treating patients on a controlled sodium diet.
Impact on driving, operating machinery
In view of the possible occurrence of adverse reactions such as fatigue, patients should refrain from driving and engaging in potentially hazardous activities requiring increased concentration and quick psychomotor reactions during treatment with Opdivo® until it is established that these adverse reactions do not occur.
Contraindications
Contraindications
With caution
Opdivok® has limited experience with BRAF mutation-positive melanoma therapy in previously untreated patients.
Patients with concomitant brain metastases, active autoimmune disease or disease requiring therapy with systemic immunosuppressants have been excluded from the main clinical trial of PKC. In the absence of data, nivolumab should be used with caution in these patient groups after careful assessment of the benefit-risk ratio based on individual indices.
Selected Patient Groups
The following patient groups did not participate in clinical trials:
In the absence of data, Opdivo® should be used with caution in these patient groups after a risk-benefit assessment based on individual measures.
Side effects
Side effects
Overdose
Overdose
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store at 2 to 8 ° C in a light-protected place. Do not freeze. Do not shake. Keep out of reach of children. |
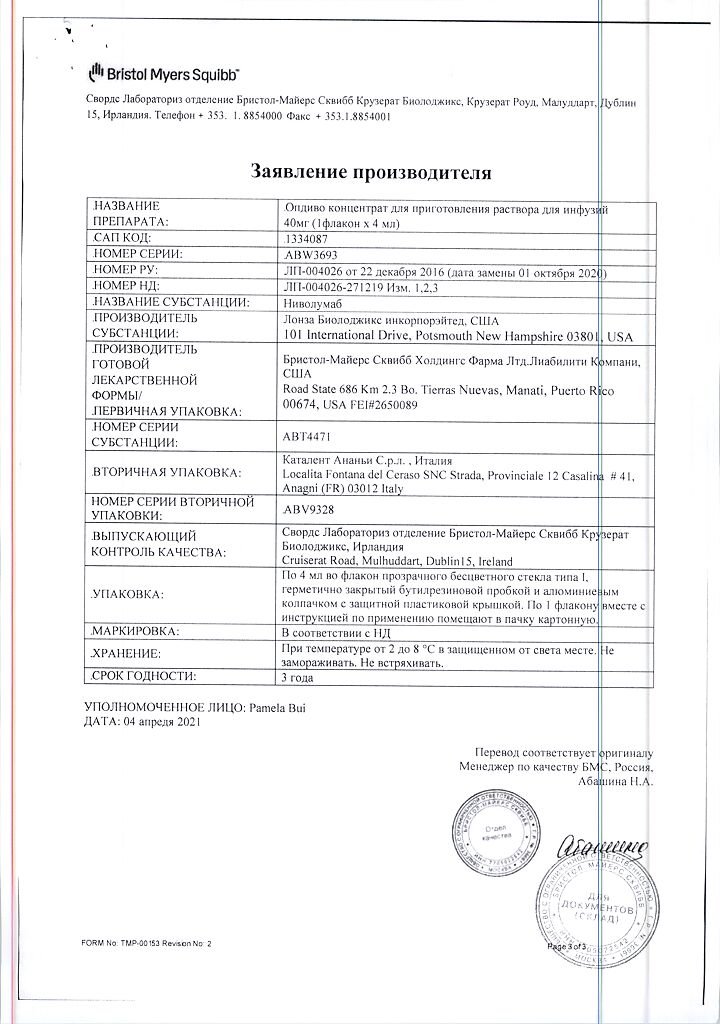
| Manufacturer | Bristol-Myers Squibb, USA |
| Medication form | concentrate for preparation of infusion solution |
| Brand | Bristol-Myers Squibb |
Related products
Buy Opdivo, 10 mg/ml concentrate 4 ml with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.