No products in the cart.
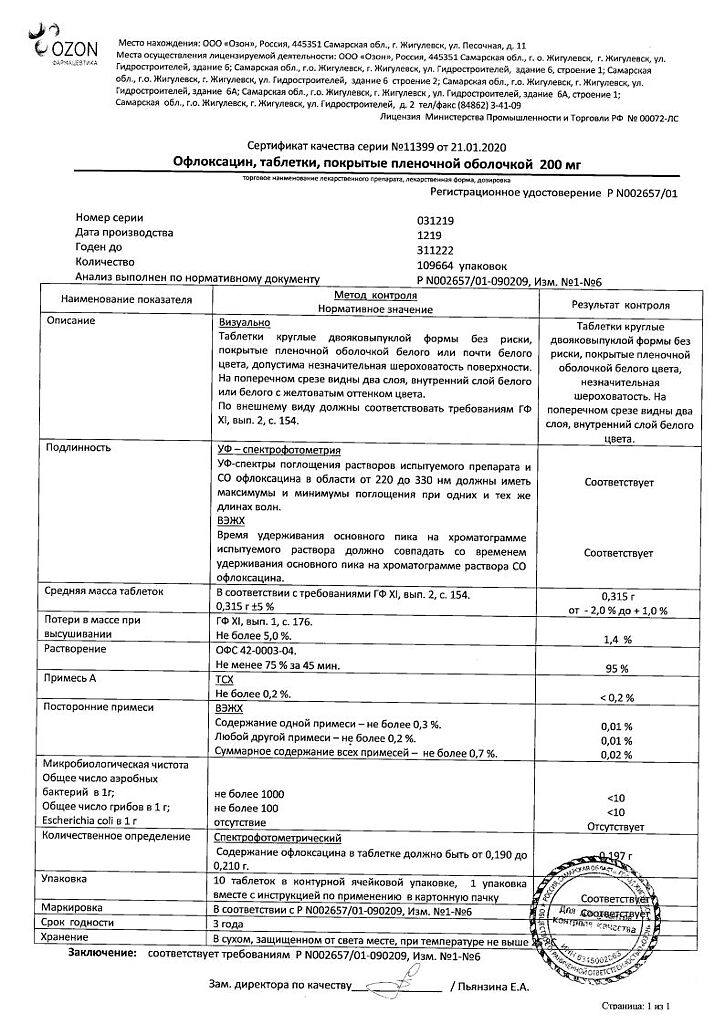
Ofloxacin, 200 mg 10 pcs
€1.92 €1.75
Description
Pharmacological action Pharmacological action – antibacterial, bactericidal.
Blocks DNA-giase and disrupts DNA replication in the microbial cell.
Pharmacodynamics
Active against beta-lactamase-producing microorganisms and fast-growing atypical mycobacteria. Sensitive: Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, Escherichia coli, Citrobacter, Klebsiella spp, (including Klebsiella pneumoniae), Enterobacter spp. (including Enterobacter cloacae), Hafnia, Proteus spp. (including Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris – indole positive and indole negative), Salmonella spp, Shigella spp. (including Shigella sonnei), Yersinia enterocolitica, Campylobacter jejuni, Aeromonas hydrophila, Plesiomonas aeruginosa, Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Haemophilus influenzae, Chlamydia spp, Serratia spp., Providencia spp., Haemophilus ducreyi, Bordetella parapertussis, Bordetella pertussis, Moraxella catarrhalis, Propionibacterium acnes, Staphylococcus spp.
Different sensitivities to the drug are: Enterococcus faecalis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus viridans, Serratia marcescens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter, Mycoplasma hominis, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium fortuitum, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Clostridium perfringens, Corynebacterium spp., Helicobacter pylori, Listeria monocytogenes, Gardnerella vaginalis.
In most cases Nocardia asteroides, anaerobic bacteria (e.g. Bacteroides spp., Peptococcus spp., Peptostreptococcus spp., Eubacterium spp., Fusobacterium spp., Clostridium difficile) are not sensitive. It does not work on Treponema pallidum.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration it is quickly and completely absorbed. Bioavailability is more than 96%, plasma protein binding is 25%. Tmax is 1-2 h, Cmax after doses of 100, 300, 600 mg is 1, 3.4 and 6.9 mg/l. After a single dose of 200 or 400 mg, it is 2.5 mcg/ml and 5 mcg/ml, respectively.
The apparent volume of distribution is 100 l. It penetrates into tissues, organs and media of the body: cells (leukocytes, alveolar macrophages), skin, soft tissues, bones, abdominal and pelvic organs, respiratory system, urine, saliva, bile, prostate secretion, passes well through the BBB, placental barrier, secreted with the mother’s milk. It penetrates into the cerebrospinal fluid with inflamed and uninflamed cerebral membranes (14-60%).
It is metabolized in the liver (about 5%) with the formation of N-oxide ofloxacin and dimethylofloxacin. T1/2 is independent of the dose and is 4.5-7 hours. Excreted by the kidneys 75-90% (unchanged), about 4% – in the bile. Extra renal clearance is less than 20%.
After a single dose of 200 mg, it is detectable in the urine within 20-24 hours. With renal/hepatic insufficiency, excretion may be delayed. It does not cumulate.
Indications
Indications
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient: ofloxacin 200 mg;
Excipients:
Corn or potato starch;
MCC;
Talc;
polyvinylpyrrolidone low molecular weight;
magnesium or calcium stearate;
aerosil;
The shell composition: oxypropyl methylcellulose; talc; titanium dioxide; propylene glycol; polyethylene oxide 4000 or opider IIOfloxacin – 400 mg.
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Orally, before or during meals, whole, with water. Doses are selected individually depending on the localization and severity of the infection as well as the sensitivity of microorganisms, the general condition of the patient and liver and kidney function.
Adults: 200-800 mg per day, the course of treatment – 7-10 days, 2 times a day. Dose up to 400 mg in 1 dose, preferably in the morning. In gonorrhea it is 400 mg once.
In patients with impaired renal function (in creatinine Cl 50-20 ml/min), a single dose should be taken once daily or 50% of the average dose twice daily. In creatinine Cl less than 20 ml/min a single dose of 200 mg, then 100 mg per day every other day.
In hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis, 100 mg every 24 hours. Maximum daily dose in hepatic failure is 400 mg.
The duration of treatment course is determined by the sensitivity of the causative agent and clinical picture; the treatment should be continued for at least 3 days after relief of symptoms and complete normalization of temperature. For treatment of salmonellosis the course of treatment shall be 7-8 days, in case of uncomplicated lower urinary tract infections – 3-5 days.
In children – only for vital indications, if it is impossible to substitute other drugs. The average daily dose is 7.5 mg/kg and the maximum dose is 15 mg/kg.
Interaction
Interaction
Probenecid, cimetidine, furosemide, methotrexate increase the plasma concentration. Increases the plasma concentration of glibenclamide. Antacids and iron-containing drugs decrease the efficacy (should be taken 2 hours before or after taking the drug). When concomitant use with vitamin K antagonists, coagulation should be monitored.
.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
It is not the drug of choice for the treatment of pneumonia caused by pneumococci, it is not indicated for the treatment of acute tonsillitis.
At the time of treatment it is necessary to refrain from driving vehicles and engaging in potentially dangerous activities that require increased concentration and quick psychomotor reactions. Alcohol must not be consumed.
Tampax tampons should not be used during treatment with the drug, because of the increased risk of thrush.
Treatment may cause worsening of myasthenia gravis, and increased incidence of porphyria in susceptible patients.
Possible false-negative results in bacteriological diagnosis of tuberculosis (prevents isolation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis).
Contraindications
Contraindications
Side effects
Side effects
Nervous system and sensory organs: headache, dizziness, insomnia, drowsiness, anxiety, extrapyramidal disorders, hallucinations (including visual and auditory), visual, olfactory and gustatory disorders.
Cardiovascular system and blood (hematopoiesis, hemostasis): leuko-, neutro-, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis, eosinophilia, hemolytic anemia, pancytopenia.
Gastrointestinal disorders: anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, pseudomembranous colitis.
Urogenital system disorders: impaired renal function, increased creatinine levels, interstitial nephritis.
Sensory system disorders: rarely – disorders of vision, taste, smell.
Skin disorders: skin rash, redness, vascular purpura.
Allergic reactions: angioedema, bronchospasm, weakness, anaphylactic shock, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, photosensitization.
Others: arthralgia, myalgia, tendon inflammation, hypoglycemia (in the background of diabetes), hyperthermia, sweating.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: dizziness, confusion, lethargy, disorientation, drowsiness, vomiting.
Treatment: gastric lavage, symptomatic therapy.
Pregnancy use
Pregnancy use
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
| Weight | 0.010 kg |
|---|---|
| Shelf life | 2 years |
| Conditions of storage | In a light-protected place at 15-25 °C. Freezing is not allowed. |
| Manufacturer | Ozon, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Ozon |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Ofloxacin, 200 mg 10 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.