No products in the cart.
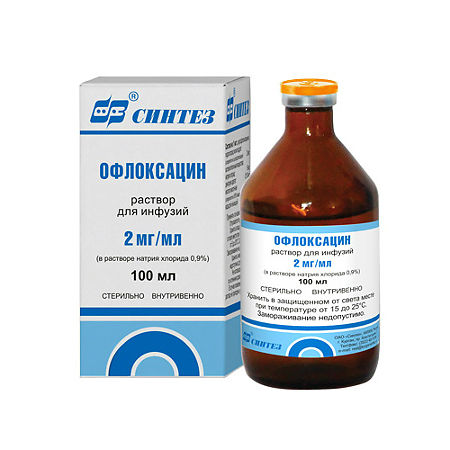
Ofloxacin, 2 mg/ml 100 ml
€1.02 €0.85
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Ofloxacin is bactericidal, antibacterial.
It acts on the bacterial enzyme DNA-hyraza, which provides superspiralization and thus the stability of bacterial DNA (destabilization of DNA chains leads to their death). It has a broad spectrum of action and has a bactericidal effect.
Pharmacodynamics
Active against beta-lactamase-producing microorganisms and fast-growing atypical mycobacteria. Sensitive: Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, Escherichia coli, Citrobacter, Klebsiella spp, (including Klebsiella pneumoniae), Enterobacter spp. (including Enterobacter cloacae), Hafnia, Proteus spp. (including Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris – indole positive and indole negative), Salmonella spp, Shigella spp. (including Shigella sonnei), Yersinia enterocolitica, Campylobacter jejuni, Aeromonas hydrophila, Plesiomonas aeruginosa, Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Haemophilus influenzae, Chlamydia spp, Serratia spp., Providencia spp., Haemophilus ducreyi, Bordetella parapertussis, Bordetella pertussis, Moraxella catarrhalis, Propionibacterium acnes, Staphylococcus spp.
Different sensitivities to the drug are: Enterococcus faecalis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus viridans, Serratia marcescens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter, Mycoplasma hominis, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium fortuitum, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Clostridium perfringens, Corynebacterium spp., Helicobacter pylori, Listeria monocytogenes, Gardnerella vaginalis.
In most cases Nocardia asteroides, anaerobic bacteria (e.g. Bacteroides spp., Peptococcus spp., Peptostreptococcus spp., Eubacterium spp., Fusobacterium spp., Clostridium difficile) are not sensitive. It does not work on Treponema pallidum.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration it is quickly and completely absorbed. Bioavailability is more than 96%, plasma protein binding is 25%. Tmax is 1-2 h, Cmax after doses of 100, 300, 600 mg is 1, 3.4 and 6.9 mg/l. After a single dose of 200 or 400 mg, it is 2.5 mcg/ml and 5 mcg/ml, respectively.
The apparent volume of distribution is 100 l. It penetrates into tissues, organs and media of the body: cells (leukocytes, alveolar macrophages), skin, soft tissues, bones, abdominal and pelvic organs, respiratory system, urine, saliva, bile, prostate secretion, passes well through the BBB, placental barrier, secreted with the mother’s milk. It penetrates into the cerebrospinal fluid with inflamed and uninflamed cerebral membranes (14-60%).
It is metabolized in the liver (about 5%) with the formation of N-oxide ofloxacin and dimethylofloxacin. T1/2 is independent of the dose and is 4.5-7 hours. Excreted by the kidneys 75-90% (unchanged), about 4% – in the bile. Extra renal clearance is less than 20%.
After a single dose of 200 mg, it is detectable in the urine within 20-24 hours. With renal/hepatic insufficiency, excretion may be delayed. It does not cumulate.
Indications
Indications
Infectious and inflammatory diseases caused by microorganisms sensitive to ofloxacin:
– respiratory tract infections (bronchitis, pneumonia);
– ENT organs (sinusitis, otitis media, tracheitis/except pneumococcal infections);
– infections of the skin and soft tissues;
– infections of bones and joints;
– infectious and inflammatory diseases of the abdominal cavity (including biliary tract infections;
– kidney infections (pyelonephritis), urinary tract (cystitis, urethritis);
– infections of the pelvic organs (endometritis, salpingitis, oophoritis, cervicitis, parametritis, prostatitis) and genital organs (colpitis, orchitis, epididymitis);
– gonorrhea;
– chlamydia;
– sepsis;
– prevention of infections in patients with impaired immune status (including neutropenia).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Ofloxacin is bactericidal, antibacterial.
Acts on the bacterial enzyme DNA gyrase, which ensures supercoiling and, thus, stability of bacterial DNA (destabilization of DNA chains leads to their death). It has a wide spectrum of action and has a bactericidal effect.
Pharmacodynamics
Active against microorganisms producing beta-lactamases and fast-growing atypical mycobacteria. Sensitive: Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, Escherichia coli, Citrobacter, Klebsiella spp., (including Klebsiella pneumoniae), Enterobacter spp. (including Enterobacter cloacae), Hafnia, Proteus spp. (including Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris – indole-positive and indole-negative), Salmonella spp., Shigella spp. (including Shigella sonnei), Yersinia enterocolitica, Campylobacter jejuni, Aeromonas hydrophila, Plesiomonas aeruginosa, Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Haemophilus influenzae, Chlamydia spp. (including Chlamydia trachomatis), Legionella spp., Serratia spp., Providencia spp., Haemophilus ducreyi, Bordetella parapertussis, Bordetella pertussis, Moraxella catarrhalis, Propionibacterium acnes, Staphylococcus spp., Brucella spp.
The following have varying sensitivity to the drug: Enterococcus faecalis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus viridans, Serratia marcescens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter, Mycoplasma hominis, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium fortuitum, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Clostridium perfringens, Corynebacterium spp., Helicobacter pylori, Listeria monocytogenes, Gardnerella vaginalis.
Generally insensitive: Nocardia asteroides, anaerobic bacteria (eg Bacteroides spp., Peptococcus spp., Peptostreptococcus spp., Eubacterium spp., Fusobacterium spp., Clostridium difficile). Does not affect Treponema pallidum.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration, it is quickly and completely absorbed. Bioavailability – over 96%, binding to plasma proteins – 25%. Tmax is 1–2 hours, Cmax after administration at a dose of 100, 300, 600 mg is 1, 3.4 and 6.9 mg/l. After a single dose of 200 or 400 mg, it is 2.5 mcg/ml and 5 mcg/ml, respectively.
The apparent volume of distribution is 100 l. Penetrates into tissues, organs and environments of the body: into cells (leukocytes, alveolar macrophages), skin, soft tissues, bones, abdominal and pelvic organs, respiratory system, urine, saliva, bile, prostate secretions, passes well through the BBB, placental barrier, and is excreted in breast milk. Penetrates into the cerebrospinal fluid in inflamed and non-inflamed meninges (14–60%).
Metabolized in the liver (about 5%) to form N-oxide ofloxacin and dimethylofloxacin. T1/2 does not depend on the dose and is 4.5–7 hours. 75–90% is excreted by the kidneys (unchanged), about 4% with bile. Extrarenal clearance is less than 20%.
After a single dose of 200 mg, it is detected in the urine within 20–24 hours. In case of renal/liver failure, excretion may slow down. Does not cumulate.
Special instructions
Special instructions
It is not a drug of choice for the treatment of pneumonia caused by pneumococci, and is not indicated for the treatment of acute tonsillitis.
During the treatment period, it is necessary to refrain from driving vehicles and engaging in potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions. You can’t drink alcohol.
During treatment with the drug, you should not use hygienic tampons like Tampax, due to the increased risk of developing thrush.
During treatment, the course of myasthenia gravis may worsen and attacks of porphyria may increase in predisposed patients.
False-negative results are possible in the bacteriological diagnosis of tuberculosis (prevents the isolation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis).
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Ofloxacin
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient:
ofloxacin 2 g;
Excipients:
sodium chloride;
water for injections – up to 1 l
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, epilepsy (including a history), decreased seizure threshold (including after traumatic brain injury, stroke or inflammatory processes in the central nervous system); age up to 18 years (skeletal growth is not yet completed), pregnancy, lactation period.
With caution – atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels, cerebrovascular accidents (history), chronic renal failure, organic lesions of the central nervous system.
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the gastrointestinal tract: gastralgia, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, flatulence, abdominal pain, increased activity of liver transaminases, hyperbilirubinemia, cholestatic jaundice, pseudomembranous enterocolitis.
From the nervous system and sensory organs: headache, dizziness, uncertainty of movements, tremors, convulsions, numbness and paresthesia of the extremities, intense dreams, “nightmare” dreams, psychotic reactions, anxiety, state of excitation, phobias, depression, confusion, hallucinations, increased intracranial pressure; impaired color vision, diplopia, impaired taste, smell, hearing and balance. When using the ointment – a burning sensation and discomfort in the eyes, hyperemia, itching and dryness of the conjunctiva, photophobia, lacrimation.
From the musculoskeletal system: tendinitis, myalgia, arthralgia, tenosynovitis, tendon rupture.
From the cardiovascular system and blood (hematopoiesis, hemostasis): tachycardia, decrease in blood pressure (with intravenous administration; with a sharp decrease in blood pressure, the administration is stopped), vasculitis, collapse; leukopenia, agranulocytosis, anemia, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, hemolytic and aplastic anemia.
Allergic reactions: skin rash, itching, urticaria, allergic pneumonitis, allergic nephritis, eosinophilia, fever, Quincke’s edema, bronchospasm, Stevens-Johnson and Lyell syndrome, photosensitivity, erythema multiforme, rarely – anaphylactic shock.
From the skin: pinpoint hemorrhages (petechiae), bullous hemorrhagic dermatitis, papular rash with crust, indicating vascular damage (vasculitis).
From the genitourinary system: acute interstitial nephritis, impaired renal function, hypercreatininemia, increased urea content.
Other: dysbacteriosis, superinfection, hypoglycemia (in patients with diabetes), vaginitis.
Interaction
Interaction
Compatible with the following infusion solutions: isotonic sodium chloride solution, Ringer’s solution, 5% fructose solution, 5% dextrose (glucose) solution.
Do not mix with heparin (risk of precipitation).
Food products, antacids containing Al3+, Ca2+, Mg2+ or iron salts reduce the absorption of ofloxacin, forming insoluble complexes (the interval between doses of these drugs should be at least 2 hours).
Reduces the clearance of theophylline by 25% (with simultaneous use, the dose of theophylline should be reduced).
Cimetidine, furosemide, methotrexate and drugs that block tubular secretion increase the plasma concentration of ofloxacin.
Increases the concentration of glibenclamide in plasma.
When taken simultaneously with vitamin K antagonists, it is necessary to monitor the blood coagulation system.
When prescribed with NSAIDs, nitroimidazole and methylxanthine derivatives, the risk of developing neurotoxic effects increases.
When administered concomitantly with glucocorticoids, the risk of tendon rupture increases, especially in the elderly.
When prescribed with drugs that alkalinize urine (carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, sodium bicarbonate), the risk of crystalluria and nephrotic effects increases.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: dizziness, confusion, lethargy, disorientation, drowsiness, vomiting.
Treatment: gastric lavage, symptomatic therapy.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a place protected from light, at a temperature of 15–25 °C. Freezing is unacceptable.
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
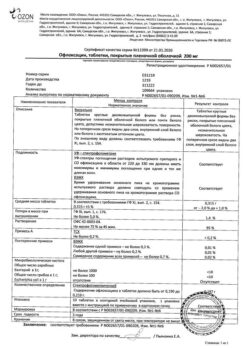
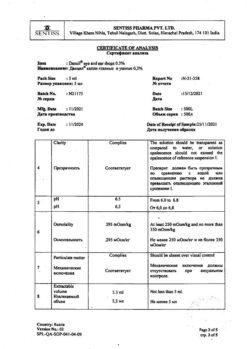
Sintez, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a light-protected place at 15-25 °C. Freezing is not allowed. |
| Manufacturer | Sintez OAO, Russia |
| Medication form | solution for infusion |
| Brand | Sintez OAO |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Ofloxacin, 2 mg/ml 100 ml with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.