No products in the cart.
Normodipine, tablets 5 mg 30 pcs
€6.12 €5.44
Description
Normodipine has antianginal, hypotensive effect.
A slow calcium channel blocker, a dihydropyridine derivative, has antianginal and hypotensive effects. Binding to segments S6 of III and IV domains of alpha1-subunit of L-type calcium channel, it blocks calcium channels, decreases transmembrane transition of calcium ions into cell (more in vascular smooth muscle cells than in cardiomyocytes).
The antianginal action is caused by the dilation of coronary and peripheral arteries and arterioles: in angina pectoris it reduces myocardial ischemia; by dilation of peripheral arterioles it reduces myocardial perfusion, decreases cardiac preload, reduces myocardial oxygen demand.
Dilates coronary arteries and arterioles in unchanged and ischemic areas of the myocardium, increases oxygen supply to the myocardium (especially in vasospastic angina); prevents development of coronary artery spasm (including that caused by smoking). In patients with stable angina a single daily dose increases exercise tolerance, slows down the development of angina and “coronary” ST-segment depression, reduces the frequency of angina attacks and the use of nitroglycerin and other nitrates.
It has a long-term dose-dependent hypotensive effect. The hypotensive effect is due to a direct vasodilatory effect on the vascular smooth muscles. In arterial hypertension a single dose provides clinically significant reduction of BP during 24 hours (in “lying” and “standing” position of the patient).
Orthostatic hypotension when prescribing amlodipine is quite rare. It does not cause a decrease in exercise tolerance, left ventricular ejection fraction. It reduces the degree of left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy.
It does not influence myocardial contractility and conduction, does not cause reflex elevation of HR, inhibits platelet aggregation, increases glomerular filtration rate, has a weak natriuretic effect. It does not increase the severity of microalbuminuria in diabetic nephropathy.
It has no adverse effect on metabolism and concentration of plasma lipids and can be used for treatment of patients with bronchial asthma, diabetes mellitus and gout.
The time of onset of effect is 2-4 hours, the duration of effect is 24 hours.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
When taken orally it is slowly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Food intake has no effect on absorption. Cmax in plasma is reached after 6-9 h in both elderly and young patients. Average absolute bioavailability is 64%.
Distribution
The Css of amlodipine in plasma is reached after continuous use for 7-8 days.
The Vd is approximately 21 L/kg, indicating prevailing tissue distribution. It penetrates through the HEB and into the breast milk.
The binding to plasma proteins is 97%.
Metabolism
About 90% of amlodipine is biotransformed in the liver to form inactive metabolites.
Amlodipine is excreted from the body with urine (10% of dose – unchanged and 60% – as inactive metabolites) and in the feces (20-25% as metabolites). Excretion is biphasic, T1/2 averages 31-48 hours.
The total clearance of amlodiline is 7 ml/min/kg. Amlodipine is not eliminated by hemodialysis.
Pharmacokinetics in special clinical cases
The excretion of amlodipine is slower (T1/2 – 65 h) in elderly patients (older than 65 years) compared to younger patients, but these differences are not clinically relevant.
The prolonged T1/2 in patients with hepatic impairment suggests that long-term administration will result in higher cumulation of the drug in the body (T1/2 is up to 60 h).
The presence of renal impairment in a patient has no significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of amlodipine.
Indications
Indications
arterial hypertension (as monotherapy or in combination with other antihypertensive drugs);
stable angina pectoris (as monotherapy or in combination with other antianginal drugs);
vasospastic angina (Prinzmetal’s angina) (as monotherapy or in combination with other antianginal drugs).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Normodipine has an antianginal and hypotensive effect.
A slow calcium channel blocker, a dihydropyridine derivative, has antianginal and hypotensive effects. By binding to the S6 segments of the III and IV domains of the alpha1 subunit of the L-type calcium channel, it blocks calcium channels, reduces the transmembrane transition of calcium ions into the cell (more into vascular smooth muscle cells than into cardiomyocytes).
The antianginal effect is due to the expansion of the coronary and peripheral arteries and arterioles: in case of angina pectoris, it reduces the severity of myocardial ischemia; by expanding peripheral arterioles, it reduces peripheral vascular resistance, reduces preload on the heart, and reduces myocardial oxygen demand.
Expands coronary arteries and arterioles in unchanged and ischemic areas of the myocardium, increases the supply of oxygen to the myocardium (especially with vasospastic angina); prevents the development of spasm of the coronary arteries (including those caused by smoking). In patients with stable angina, a single daily dose increases exercise tolerance, slows down the development of angina and “ischemic” depression of the ST segment, reduces the frequency of angina attacks and the consumption of nitroglycerin and other nitrates.
It has a long-term dose-dependent hypotensive effect. The hypotensive effect is due to a direct vasodilating effect on vascular smooth muscle. For arterial hypertension, a single dose provides a clinically significant reduction in blood pressure over 24 hours (in the patient’s “lying” and “standing” position).
Orthostatic hypotension when prescribing amlodipine is quite rare. Does not cause a decrease in exercise tolerance or left ventricular ejection fraction. Reduces the degree of left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy.
It has no effect on myocardial contractility and conductivity, does not cause a reflex increase in heart rate, inhibits platelet aggregation, increases the glomerular filtration rate, and has a weak natriuretic effect. In diabetic nephropathy, it does not increase the severity of microalbuminuria.
It does not have any adverse effect on metabolism and plasma lipid concentrations and can be used in the treatment of patients with bronchial asthma, diabetes mellitus and gout.
The onset of the effect is 2-4 hours, the duration of the effect is 24 hours.
Pharmacokinetics
Suction
When taken orally, it is slowly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Eating does not affect absorption. Cmax in blood plasma is reached after 6-9 hours in both elderly and young patients. The average absolute bioavailability is 64%.
Distribution
Css of amlodipine in blood plasma is achieved after continuous use for 7-8 days.
Vd is approximately 21 l/kg, indicating predominant tissue distribution. Penetrates through the blood-brain barrier and into breast milk.
Plasma protein binding – 97%.
Metabolism
About 90% of amlodipine is biotransformed in the liver with the formation of inactive metabolites.
Removal
Amlodipine is excreted from the body in the urine (10% of the dose unchanged and 60% in the form of inactive metabolites) and in feces (20-25% in the form of metabolites). Elimination is biphasic, T1/2 averages 31-48 hours.
The total clearance of amlodiline is 7 ml/min/kg. Hemodialysis does not remove amlodipine.
Pharmacokinetics in special clinical situations
In elderly patients (over 65 years of age), the elimination of amlodipine is slower (T1/2 – 65 hours) compared to young patients, but these differences are not clinically significant.
Prolongation of T1/2 in patients with liver failure suggests that with long-term administration, the accumulation of the drug in the body will be higher (T1/2 – up to 60 hours).
The presence of renal failure in the patient does not significantly affect the pharmacokinetics of amlodipine.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Influence on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Amlodipine
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient:
amlodipine;
Excipients:
magnesium stearate;
sodium carboxymethyl starch;
calcium hydrogen phosphate anhydrous;
MCC
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Contraindicated.
Contraindications
Contraindications
pregnancy; lactation period; age under 18 years (due to lack of clinical experience in use); severe arterial hypotension (systolic blood pressure less than 90 mm Hg); collapse; cardiogenic shock; clinically significant aortic stenosis; unstable angina (with the exception of Prinzmetal’s angina); hypersensitivity to amlodipine and other dihydropyridine derivatives.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Allergic reactions: uncommon – skin itching, rash (including erythematous, maculopapular rash); very rarely – urticaria, angioedema, erythema multiforme.
Interaction
Interaction
Cimetidine does not affect the pharmacokinetics of amlodipine. In in vitro studies, amlodipine does not affect the binding of digoxin, phenytoin, warfarin and indomethacin to blood proteins.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: tachycardia, marked decrease in blood pressure, excessive peripheral vasodilation (risk of developing severe and persistent arterial hypotension, including with the development of shock and death).
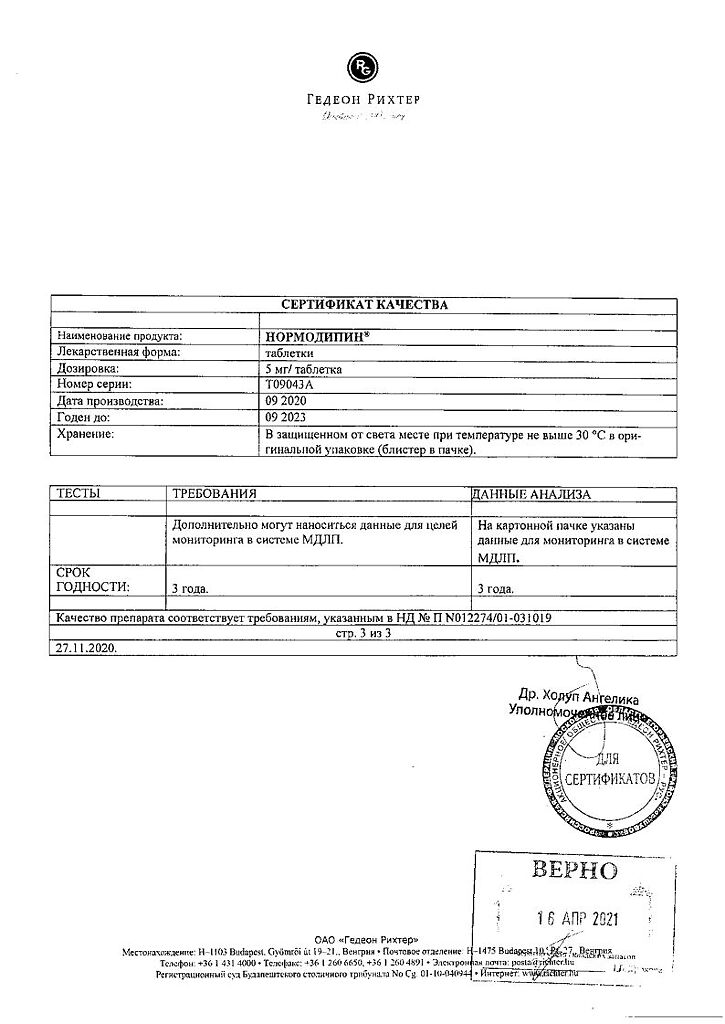
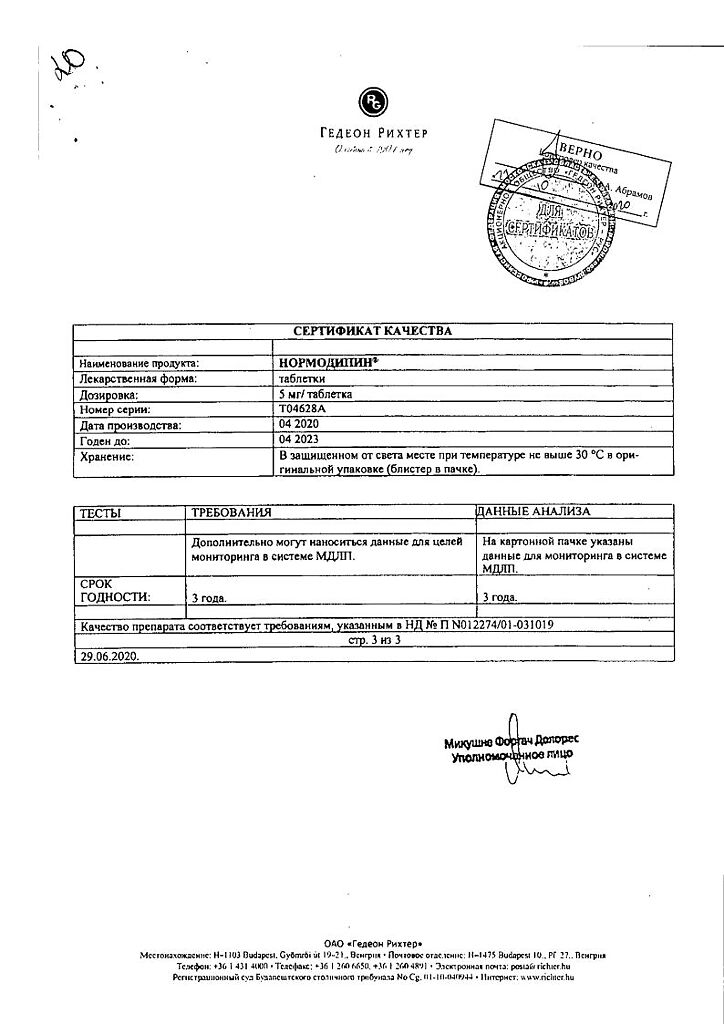
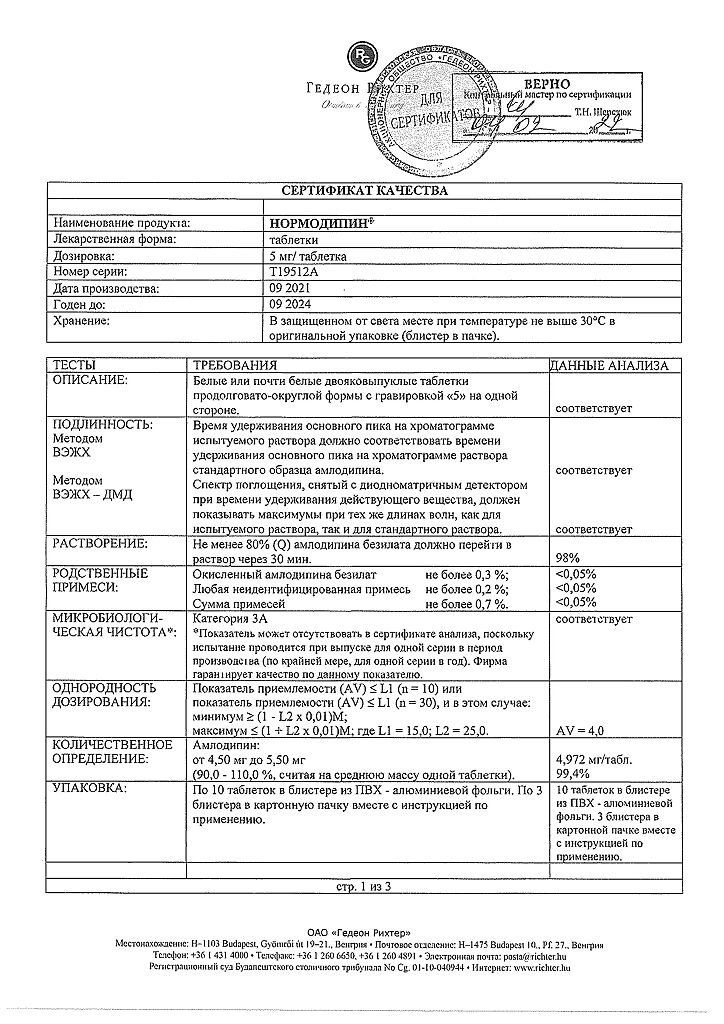
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At a temperature not exceeding 30 °C
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Gedeon Richter, Hungary
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature not exceeding 30 °C |
| Manufacturer | Gedeon Richter, Hungary |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Gedeon Richter |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Normodipine, tablets 5 mg 30 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.