No products in the cart.
Nifedipine,10 mg 50 pcs
€2.28 €1.90
Description
Nifedipine is a selective “slow calcium channel blocker” derivative of 1,4-dihydropyridine. It has antianginal and antihypertensive effects. It reduces the flow of extracellular calcium ions inside cardiomyocytes and smooth muscle cells of coronary and peripheral arteries.
Limits spasm and dilates coronary and peripheral (mainly arterial) vessels, reduces blood pressure, total peripheral vascular resistance, reduces post-load and myocardial oxygen demand. Increases coronary blood flow. Negative chrono-, dromo- and inotropic effects are overridden by reflex activation of the sympathoadrenal system in response to peripheral vasodilatation. It enhances renal blood flow, causes moderate natriuresis. Time of onset of clinical effect is 20 min, duration of clinical effect is 4-6 h.
Pharmacokinetics
Nifedipine is rapidly and almost completely (over 90%) absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. After oral administration its bioavailability is 40-60%. Food intake increases the bioavailability. It has a “first pass” effect through the liver.
The maximum concentration in plasma is observed after 1-3 hours and is 65 ng/ml. It penetrates through the blood-brain barrier and the placental barrier, is excreted with breast milk. Binding with blood plasma proteins is 90%. It is completely metabolized in the liver.
It is excreted by kidneys as inactive metabolites (70-80% of the dose taken). The elimination half-life is 2-4 hours. There is no cumulative effect. Chronic renal failure, hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis have no effect on pharmacokinetics. Tolerance to the drug action develops during long-term use (for 2-3 months).
Indications
Indications
Coronary heart disease – exertional and resting angina (including variant); arterial hypertension (as monotherapy or in combination with other antihypertensive drugs).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Nifedipine is a selective blocker of “slow calcium ropes”, a 1,4-dihydropyridine derivative. Has antianginal and antihypertensive effects. Reduces the flow of extracellular calcium ions into cardiomyocytes and smooth muscle cells of the coronary and peripheral arteries.
Reduces spasm and dilates coronary and peripheral (mainly arterial) vessels, reduces blood pressure, total peripheral vascular resistance, reduces afterload and myocardial oxygen demand. Increases coronary blood flow. The negative chrono-, dromo- and inotropic effects are overlapped by reflex activation of the sympathoadrenal system in response to peripheral vasodilation. Increases renal blood flow, causes moderate natriuresis. The onset time of the clinical effect is 20 minutes, the duration of the clinical effect is 4-6 hours.
Pharmacokinetics
Nifedipine is quickly and almost completely (more than 90%) absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. After oral administration, its bioavailability is 40-60%. Eating increases bioavailability. Has a “first pass” effect through the liver.
The maximum concentration in blood plasma is observed after 1-3 hours and is 65 ng/ml. Penetrates the blood-brain and placental barrier and is excreted in breast milk. Communication with blood plasma proteins – 90%. Completely metabolized in the liver.
Excreted by the kidneys in the form of inactive metabolites (70-80% of the dose taken). The half-life is 2-4 hours. There is no cumulative effect. Chronic renal failure, hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis do not affect pharmacokinetics. With long-term use (for 2-3 months), tolerance to the action of the drug develops.
Special instructions
Special instructions
During the treatment period, it is necessary to refrain from engaging in potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions, and from the use of ethanol.
The drug is discontinued gradually (risk of developing withdrawal syndrome).
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Nifedipine
Composition
Composition
Active ingredients:
nifedipine – 10 mg;
Excipients:
magnesium stearate,
microcrystalline cellulose,
lactose monohydrate,
potato starch,
colloidal silicon dioxide (Aerosil),
povidone (low molecular weight medical polyvinylpyrrolidone).
Contraindications
Contraindications
hypersensitivity to nifedipine and other dihydropyridine derivatives;
acute stage of myocardial infarction (first 4 weeks);
cardiogenic shock, collapse;
arterial hypotension (systolic blood pressure below 90 mmHg);
sick sinus syndrome;
heart failure (in the stage of decompensation);
severe aortic stenosis;
severe mitral stenosis;
tachycardia;
idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis;
pregnancy, lactation period;
age under 18 years (efficacy and safety have not been established).
Use with caution in patients:
with chronic heart failure, severe liver and/or kidney dysfunction; severe cerebrovascular accidents, diabetes mellitus, malignant arterial hypertension, patients on hemodialysis (due to the risk of arterial hypotension).
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the cardiovascular system: facial hyperemia, feeling of heat, tachycardia, peripheral edema (ankles, feet, legs), excessive decrease in blood pressure (BP), syncope, heart failure; in some patients, especially at the beginning of treatment, angina attacks may occur, which requires discontinuation of the drug.
From the nervous system: headache, dizziness, increased fatigue, drowsiness. With prolonged oral administration in high doses – paresthesia of the limbs, tremor.
From the gastrointestinal tract, liver: dyspeptic disorders (nausea, diarrhea or constipation), with long-term use – liver dysfunction (intrahepatic cholestasis, increased activity of “liver” transaminases).
From the musculoskeletal system: arthritis, myalgia.
Allergic reactions: skin itching, urticaria, exanthema, autoimmune hepatitis.
From the hematopoietic organs: anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, thrombocytopenic purpura.
From the urinary system: increased daily diuresis, deterioration of renal function (in patients with renal failure).
Other: “flushes” of blood to the skin of the face, changes in visual perception, gynecomastia (in elderly patients, completely disappearing after withdrawal), hyperglycemia, gum hyperplasia.
Interaction
Interaction
The severity of the decrease in blood pressure increases with the simultaneous administration of nifedigestion with other antihypertensive drugs, cimetidine, ranitidine, diuretics and tricyclic antidepressants.
In combination with nitrates, tachycardia and the hypotensive effect of nifedish are enhanced.
The simultaneous administration of beta-blockers must be carried out under conditions of careful medical supervision, since this may cause an excessive decrease in blood pressure, and in some cases, aggravation of symptoms of heart failure.
Nifedipine reduces the concentration of quinidine in blood plasma. Increases the concentration of digoxin and theophylpine in the blood plasma, and therefore the clinical effect and/or the content of digoxin and theophylline in the blood plasma should be monitored.
Rifampicin weakens the effect of nifedipine (accelerates the metabolism of the latter due to the induction of liver enzyme activity).
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: headache, flushing of the facial skin, decreased blood pressure, depression of the sinus node, bradycardia, arrhythmia.
Treatment: gastric lavage with the administration of activated charcoal, symptomatic therapy aimed at stabilizing the activity of the cardiovascular system. The antidote is calcium; slow intravenous administration of 10% calcium chloride or calcium gluconate is indicated, followed by switching to a long-term infusion.
With a pronounced decrease in blood pressure, intravenous administration of dopamine or dobutamine. In case of conduction disturbances, the administration of atropine, isoprenaline or the installation of an artificial pacemaker is indicated.
For the development of heart failure, intravenous administration of strophanthin. Catecholamines should be used only in case of life-threatening circulatory failure (due to their reduced effectiveness, a high dosage is required, which increases the risk of increasing the tendency to arrhythmia due to intoxication). It is recommended to control blood glucose and electrolytes (potassium and calcium ions), as insulin release is impaired.
Hemodialysis is ineffective.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a place protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 20 °C.
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Ozone/Ozone Pharm, Russia
Additional information
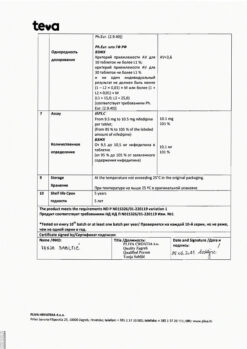
| Shelf life | 3 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a place protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 20 °C. |
| Manufacturer | Ozon, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Ozon |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Nifedipine,10 mg 50 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.