No products in the cart.
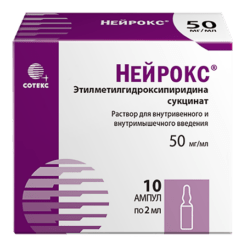
Neurox, 50 mg/ml 5 ml 5 pcs
€10.36 €9.06
Description
Neurox – antihypoxic, nootropic, anxiolytic, anticonvulsant.
Pharmacodynamics
Ethylmethylhydroxypyridine succinate (EMHPS) is an inhibitor of free radical processes, membranoprotector with antihypoxic, stress protective, nootropic, anticonvulsant and anxiolytic action. It belongs to the class of 3-oxypyridines. The mechanism of action is due to the antioxidant and membrane-protective properties. It inhibits lipid peroxidation, increases superoxide dismutase activity, increases lipid-protein ratio, improves the structure and function of cell membrane.
Modulates the activity of membrane-bound enzymes, receptor complexes, which promotes their binding to ligands, preserving the structural and functional organization of biomembranes and transport of neurotransmitters, improving synaptic transmission. Increases the concentration of dopamine in the brain. Increases compensatory activation of aerobic glycolysis and reduces the degree of inhibition of oxidative processes in the Krebs cycle in hypoxia with increased levels of ADP and creatine phosphate, activates the energy-synthesizing function of mitochondria.
It increases resistance to various damaging factors in pathological conditions (shock, hypoxia, ischemia, cerebral circulation disorders, intoxication with ethanol and antipsychotic drugs). It improves metabolism and blood supply of the brain, microcirculation and rheological properties of blood, reduces platelet aggregation. Stabilizes blood cell membranes (erythrocytes and platelets), reducing the likelihood of hemolysis. It has hypolipidemic effect, reduces the content of total cholesterol and LDL.
Normalizes metabolic processes in the ischemic myocardium, reduces the zone of necrosis, restores and/or improves myocardial electrical activity and contractility as well as increases coronary blood flow in the ischemic zone, increases antianginal activity of nitro drugs, reduces the consequences of reperfusion syndrome in acute coronary failure.
The stress-protective effect is manifested by the normalization of post-stress behavior, somatovegetative disorders, restoration of sleep-wake cycles, disturbed learning and memory processes, decrease of dystrophic changes in different structures of the brain.
The EMGPS has a pronounced anti-toxic effect in withdrawal syndrome, eliminates neurological and neurotoxic symptoms of acute alcohol intoxication, corrects behavioral and cognitive disorders. Under the influence of EMGPS the effects of tranquilizers, neuroleptics, antidepressants, hypnotics and anticonvulsants are strengthened, which allows to reduce their doses and side effects.
Pharmacokinetics
When administered by injection, the drug is determined in plasma for 4 hours after administration. Tmax when administered in the m/m is 0.3-0.58 h. Cmax when administered in the m/m dose of 400-500 mg is 2.5-4 µg/mL. EMGPS rapidly passes from the bloodstream to organs and tissues and is rapidly eliminated from the body. Average retention time of the drug in the body when administered by injection is 0.7-1.3 hours. It is metabolized in the liver through glucuronidation.
It is quickly eliminated in the urine, mainly as metabolites (50% within 12 hours) and in a small amount unchanged (0.3% within 12 hours). It is most intensively excreted during the first 4 hours after drug administration. Indicators of urinary excretion of unchanged drug and metabolites have significant individual variability.
Indications
Indications
acute cerebrovascular accidents (as part of complex therapy);
traumatic brain injury, consequences of traumatic brain injury;
dyscirculatory encephalopathy;
syndrome of vegetative (neurocirculatory) dystonia;
mild cognitive disorders of atherosclerotic origin;
anxiety disorders in neurotic and neurosis-like conditions;
acute myocardial infarction (from the first day) as part of complex therapy;
primary open-angle glaucoma of various stages, as part of complex therapy;
relief of withdrawal syndrome in alcoholism with a predominance of neurosis-like and vegetative-vascular disorders;
acute intoxication with antipsychotic drugs.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Neurox – antihypoxic, nootropic, anxiolytic, anticonvulsant.
Pharmacodynamics
Ethylmethylhydroxypyridine succinate (EMHPS) is an inhibitor of free radical processes, a membrane protector with antihypoxic, stress-protective, nootropic, anticonvulsant and anxiolytic effects. Belongs to the class of 3-hydroxypyridines. The mechanism of action is due to antioxidant and membrane protective properties. Suppresses lipid peroxidation, increases superoxide dismutase activity, increases the lipid-protein ratio, improves the structure and function of the cell membrane.
Modulates the activity of membrane-bound enzymes and receptor complexes, which promotes their binding to ligands, preservation of the structural and functional organization of biomembranes and transport of neurotransmitters, and improvement of synaptic transmission. Increases the concentration of dopamine in the brain. It enhances the compensatory activation of aerobic glycolysis and reduces the degree of inhibition of oxidative processes in the Krebs cycle under hypoxic conditions with an increase in the level of ADP and creatine phosphate, and activates the energy-synthesizing function of mitochondria.
Increases the body’s resistance to the effects of various damaging factors in pathological conditions (shock, hypoxia and ischemia, cerebrovascular accident, intoxication with ethanol and antipsychotic drugs). Improves metabolism and blood supply to the brain, microcirculation and rheological properties of blood, reduces platelet aggregation. Stabilizes the membranes of blood cells (erythrocytes and platelets), reducing the likelihood of hemolysis. It has a hypolipidemic effect, reduces the content of total cholesterol and LDL.
Normalizes metabolic processes in the ischemic myocardium, reduces the necrosis zone, restores and/or improves the electrical activity and contractility of the myocardium, and also increases coronary blood flow in the ischemic zone, increases the antianginal activity of nitro drugs, reduces the consequences of reperfusion syndrome in acute coronary insufficiency.
The stress-protective effect is manifested in the normalization of post-stress behavior, somatovegetative disorders, restoration of sleep-wake cycles, impaired learning and memory processes, and a reduction in dystrophic changes in various brain structures.
EMGPS has a pronounced antitoxic effect during withdrawal syndrome, eliminates neurological and neurotoxic manifestations of acute alcohol intoxication, and corrects behavioral and cognitive disorders. Under the influence of EMGPS, the effect of tranquilizing, neuroleptic, antidepressant, hypnotics and anticonvulsants is enhanced, which makes it possible to reduce their doses and reduce side effects.
Pharmacokinetics
When administered intramuscularly, the drug is detected in the blood plasma for 4 hours after administration. Tmax with IM administration is 0.3–0.58 hours. Cmax with IM administration at a dose of 400–500 mg is 2.5–4 mcg/ml. EMHPS quickly passes from the bloodstream into organs and tissues and is quickly eliminated from the body. The average retention time of the drug in the body with intramuscular administration is 0.7–1.3 hours. Metabolized in the liver by glucuronidation.
It is rapidly excreted in the urine, mainly in the form of metabolites (50% in 12 hours) and in small quantities unchanged (0.3% in 12 hours). The most intensive elimination occurs during the first 4 hours after taking the drug. Urinary excretion rates of unchanged drug and metabolites have significant individual variability.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Ethylmethylhydroxypyridine succinate
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient:
ethylmethylhydroxypyridine succinate 50 mg;
Excipients:
sodium disulfite – 1 mg;
water for injection – up to 1 ml;
Contraindications
Contraindications
increased individual sensitivity to the drug;
acute renal failure;
acute liver failure;
pregnancy;
breast-feeding;
childhood.
With caution: history of allergic diseases and reactions, incl. hypersensitivity to sulfites.
Side Effects
Side Effects
With parenteral administration (especially intravenous injection): dryness, metallic taste in the mouth, a feeling of spreading warmth throughout the body, sore throat and discomfort in the chest, a feeling of lack of air (usually associated with an excessively high rate of administration and are short-term in nature).
With long-term use – nausea, flatulence, sleep disturbance (drowsiness or difficulty falling asleep).
Allergic reactions.
Interaction
Interaction
Enhances the effect of benzodiazepine anxiolytics, antiepileptic (carbamazepine), antiparkinsonian (levodopa) drugs, nitrates. Reduces the toxic effects of ethanol.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: sleep disturbance (insomnia, in some cases drowsiness); with intravenous administration – a slight and short-term (up to 1.5–2 hours) increase in blood pressure.
Treatment: as a rule, not required – symptoms disappear on their own within 24 hours. In severe cases of insomnia – nitrazepam 10 mg, oxazepam 10 mg or diazepam 5 mg. If blood pressure is excessively increased, use antihypertensive drugs under blood pressure control.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
PharmFirma Sotex, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C |
| Manufacturer | PharmFirm Sotex, Russia |
| Medication form | solution for injections and infusions |
| Brand | PharmFirm Sotex |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Neurox, 50 mg/ml 5 ml 5 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.