No products in the cart.
Nemozolol, 400 mg 5 pcs
€27.06 €22.55
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group:
Anthelminthic and antiprotozoal agents.
ATX code: P02CA03
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Albendazole is an anthelmintic drug, the pharmacological properties of which are due to the action of the active substance – albendazole. Albendazole belongs to the group of carbamate benzimidazoles. The mechanism of action of albendazole is its ability to disrupt the activity of microtubular system of cells of the intestinal canal of helminthes, causing damage to tubulin protein. A consequence of this is biochemical disorders in the cell – inhibition of glucose transport and fumaratreductase, which underlies the suppression of cell division at the metaphase stage and which is associated with inhibition of oviposition and development of helminth larvae. Albendazole blocks movement of secretory granules and other organelles in muscle cells of roundworms, causing their death.
Albendazole is effective against most intestinal nematodes and larval (larval stages) of cestodes as well as giardia. Albendazole as an antiparasitic drug has a fairly broad spectrum of action.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption. After oral administration the drug is poorly absorbed in gastrointestinal tract and is not determined in unchanged form in blood plasma. Bioavailability is low when taken orally. Fatty food increases absorption and maximum concentration by 5 times.
Metabolism. Albendazole is rapidly converted in the liver to the primary metabolite – albendazole sulfoxide, which also has anthelmintic activity.
Distribution. Maximum plasma concentration of albendazole sulfoxide is reached 2-5 hours after administration. By 70% metabolite is bound to plasma proteins and completely distributed throughout the body: detected in urine, bile, liver, in the wall and fluid of helminth cysts, cerebrospinal fluid.
Extraction. Albendazole sulfoxide in the liver is converted into albendazole sulfone (secondary metabolite) and other oxidized products. Half-life of albendazole sulfoxide is 8-12 hours. It is excreted through the kidneys in the form of various metabolites. Excretion of albendazole and albendazole sulfoxide through the kidneys is insignificant. Clearance does not change in patients with impaired renal function.
In patients with liver damage – bioavailability is increased, maximum concentration of albendazole sulfoxide in blood plasma is increased by 2 times, and the half-life is prolonged.
Albendazole induces cytochrome SUR1A2 in human liver cells and accelerates metabolism of many drugs.
Indications
Indications
– Nematodes:
ascariasis, causative agent – round helminth Ascaris lumbricoidesl;
trichocephalosis (whipworm), causative agent – round helminth Trichocephalus trichiurus;
enterobiasis (pinworms), causative agent – round helminth Enterobius vermicularis;
hookworm (hookhead), pathogens – Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus;
trichinosis, causative agent—Trichinella spiralis;
toxocariasis, pathogen – Toxocara canis;
Giardiasis, causative agent – Giardia intestinalis;
Strogiloidiasis (intestinal eel), the causative agent is the round helminth Strongiloides strcoralis, as well as mixed infestations.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group:
anthelmintic and antiprotozoal agent.
ATX code: P02CA03
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Albendazole is an anthelmintic drug, the pharmacological properties of which are determined by the action of the active substance – albendazole. Albendazole belongs to the group of carbamate benzimidazoles. The mechanism of action of albendazole is its ability to disrupt the activity of the microtubular system of the cells of the intestinal canal of helminths, thereby causing damage to the tubulin protein. The consequence of this is biochemical disturbances in the cell – inhibition of the transport of glucose and fumarate reductose, which underlies the suppression of cell division at the metaphase stage and with which the inhibition of oviposition and the development of helminth larvae is associated. Albendazole blocks the movement of secretory granules and other organelles in the muscle cells of roundworms, causing their death.
Albendazole is effective against most intestinal nematodes, as well as larval (larval stages) cestodes, as well as Giardia. Albendazole as an antiparasitic drug has a fairly wide spectrum of action.
Pharmacokinetics
Suction. After oral administration, the drug is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is not detected in unchanged form in the blood plasma. Bioavailability when taken orally is low. Eating fatty foods increases absorption and maximum concentration by 5 times.
Metabolism. Albendazole is quickly converted in the liver into the primary metabolite, albendazole sulfoxide, which also has anthelmintic activity.
Distribution. The maximum plasma concentration of albendazole sulfoxide is achieved 2-5 hours after administration. 70% of the metabolite is bound to plasma proteins and is completely distributed throughout the body: found in urine, bile, liver, in the wall and fluid of helminth cysts, and cerebrospinal fluid.
Excretion. Albendazole sulfoxide is converted in the liver to albendazole sulfone (a secondary metabolite) and other oxidized products. The half-life of albendazole sulfoxide is 8-12 hours. It is excreted through the kidneys in the form of various metabolites. Renal excretion of albendazole and albendazole sulfoxide is negligible. In patients with impaired renal function, clearance does not change.
In patients with liver damage, bioavailability increases, the maximum concentration of albendazole sulfoxide in the blood plasma increases by 2 times, and the half-life is extended.
Albendazole induces cytochrome CYP1A2 in human liver cells and accelerates the metabolism of many drugs.
Special instructions
Special instructions
It is recommended to treat all family members simultaneously.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Albendazole
Composition
Composition
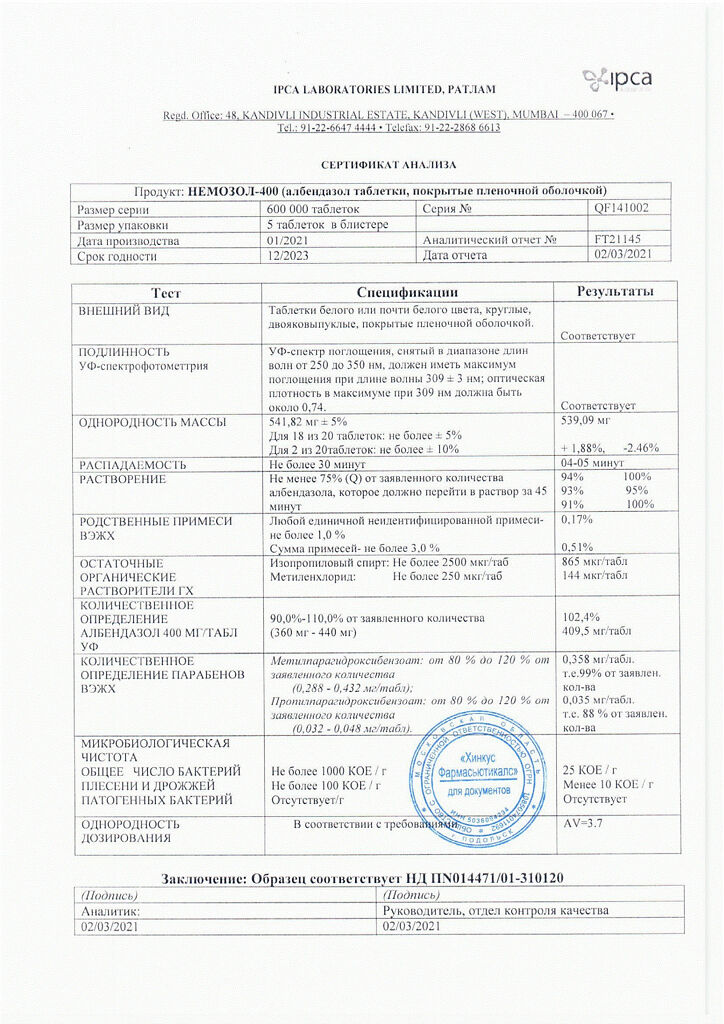
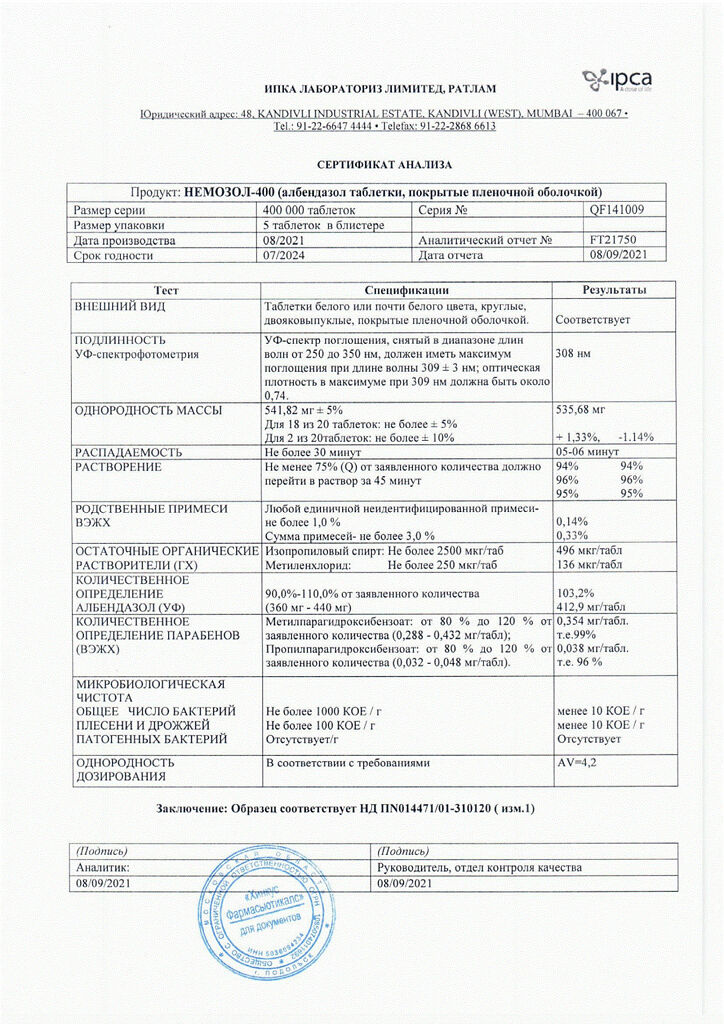
Each film-coated tablet contains:
Active substance:
Contraindications
Contraindications
– Hypersensitivity to albendazole, other components of the drug and other benzimidazole derivatives;
– pathology of the retina;
– children under 3 years of age (for this dosage form);
– pregnancy and breastfeeding period
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the digestive system: impaired liver function with changes in liver function tests (weak or moderate increase in the activity of “liver” transaminases), hepatitis, acute liver failure, epigastric pain, anorexia, constipation, diarrhea and dry mouth. nausea, vomiting.
From the hematopoietic system: inhibition of bone marrow hematopoiesis (leukopenia, granulocytopenia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, aplastic anemia, suppression of bone marrow activity, neutropenia).
Interaction
Interaction
Concomitant use of albendazole with iraziquantel, dexamethasone and cimetidine may increase the concentration of albendazole sulfoxide in the blood.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: increased dose-dependent side effects.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
Store in a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature below 25° C.
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Ipka Laboratories Limited, India
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store in a dry, light-protected place at a temperature below 25° C. |
| Manufacturer | Ipka Laboratories Limited, India |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Ipka Laboratories Limited |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Nemozolol, 400 mg 5 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.