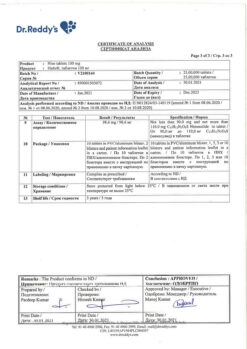
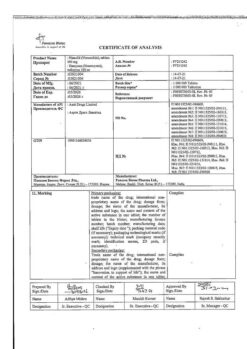
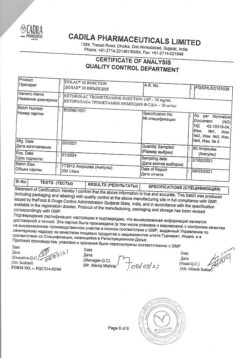
No products in the cart.
Naiz, 100 mg 2 g 9 pcs.
€9.67 €8.06
Description
Acute pain (pain in the back, lower back;
Indications
Indications
Acute pain (pain in the back, lower back;
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacodynamics
Special instructions
Special instructions
Undesirable side effects can be minimized by using the drug in the minimum effective dose with the minimum duration of use necessary to relieve pain.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Nimesulide
Composition
Composition
1 package contains:
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Like other drugs from the class of NSAIDs that inhibit the synthesis of prostaglandins, nimesulide can adversely affect the course of pregnancy and/or the development of the embryo and can lead to premature closure of the ductus arteriosus, hypertension in the fetal pulmonary artery system, impaired renal function, which can progress to renal failure with oliguria in the fetus, an increased risk of bleeding, decreased contractility of the uterus, and the occurrence of peripheral edema in the mother.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to nimesulide or other components of the drug.
History of hyperergic reactions (bronchospasm, rhinitis, urticaria),
associated with the use of acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs, including nimesulide.
Complete or incomplete combination of bronchial asthma, recurrent nasal polyposis or paranasal sinuses with intolerance to acetylsalicylic acid and other NSAIDs (including a history);
History of hepatotoxic reactions to nimesulide.
Concomitant use with other drugs with potential hepatotoxicity (for example, other NSAIDs).
Chronic inflammatory bowel diseases (Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis) in the acute phase.
The period after coronary artery bypass surgery.
Feverish syndrome with colds and acute respiratory viral infections.
Suspicion of acute surgical pathology.
Peptic ulcer of the stomach or duodenum in the acute phase; erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract; history of perforation or gastrointestinal bleeding.
A history of cerebrovascular bleeding or other diseases accompanied by increased bleeding.
Severe blood clotting disorders.
Severe heart failure.
Severe renal failure (creatinine clearance <30 ml/min), confirmed hyperkalemia.
Liver failure or any active liver disease.
Alcoholism, drug addiction.
Hereditary fructose intolerance, sucrase-isomaltase deficiency and glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding period.
Children's age up to 12 years.
With caution:
Arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, compensated heart failure, coronary heart disease,
cerebrovascular diseases, dyslipidemia/hyperlipidemia, peripheral arterial diseases,
hemorrhagic diathesis, smoking, creatinine clearance 30-60 ml/min.
History of ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract; history of infection caused by Helicobacter pylori; old age;
long-term previous use of NSAIDs; severe somatic diseases.
Concomitant use with the following drugs: anticoagulants (for example, warfarin),
antiplatelet agents (eg, acetylsalicylic acid, clopidogrel), oral glucocorticosteroids (eg, prednisolone),
selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (eg, citalopram, fluoxetine, paroxetine, sertraline).
Side Effects
Side Effects
The incidence of adverse reactions is determined in accordance with the recommendations of the World Health Organization:
very common (≥ 1/10), common (≥ 1/100 – < 1/10), uncommon (≥ 1/1,000 – < 1/100), rare (≥ 1/10,000 – < 1/1,000), very rare (< 10,000),
including individual messages.
Interaction
Interaction
Glucocorticosteroids: Increase the risk of gastrointestinal ulcers or bleeding.
Antiplatelet agents and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors: increase the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
Anticoagulants: NSAIDs may enhance the effect of anticoagulants such as warfarin.
Due to the increased risk of bleeding, this combination is not recommended and is contraindicated in patients with severe coagulation disorders.
If combination therapy cannot be avoided, careful monitoring of blood clotting parameters is necessary.
Diuretics: NSAIDs may reduce the effect of diuretics. In healthy volunteers, nimesulide temporarily reduces the excretion of sodium under the influence of furosemide, to a lesser extent the excretion of potassium, and reduces the diuretic effect itself.
Co-administration of nimesulide and furosemide leads to a decrease (by approximately 20%) in the area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) and a decrease in the cumulative excretion of furosemide without changing the renal clearance of furosemide.
Co-administration of furosemide and nimesulide requires caution in patients with impaired renal or cardiac function.
ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor antagonists: NSAIDs may reduce the effect of antihypertensive drugs.
In patients with mild to moderate renal failure (creatinine clearance 30-80 ml/min), co-administration of ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists or substances that suppress the cyclooxygenase system (NSAIDs, antiplatelet agents) may further deteriorate renal function and cause acute renal failure, which is usually reversible.
These interactions should be considered in patients taking nimesulide in combination with ACE inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor antagonists. Therefore, coadministration of these drugs should be used with caution, especially in elderly patients.
Patients should be kept adequately hydrated and renal function should be closely monitored after initiating concomitant therapy.
There is evidence that NSAIDs reduce the clearance of lithium, which leads to increased plasma lithium concentrations and its toxicity.
When prescribing nimesulide to patients receiving lithium therapy, plasma lithium concentrations should be regularly monitored.
No clinically significant interactions were observed with glibenclamide, theophylline, digoxin, cimetidine and antacid drugs (for example, a combination of aluminum and magnesium hydroxides).
Nimesulide inhibits the activity of the CYP2C9 isoenzyme. When taken simultaneously with nimesulide drugs,
metabolized with the participation of this isoenzyme, the concentration of these drugs in plasma may increase.
When used simultaneously with antiepileptic drugs (valproic acid), antifungal drugs (ketoconazole), antituberculosis drugs (isoniazid), amiodarone, methotrexate, methyldopa, amoxicillin in combination with clavulanic acid, an additive hepatotoxic effect is possible.
Due to the high degree of binding of nimesulide to plasma proteins, patients concomitantly taking sulfonamides should be under medical supervision, undergoing examinations at short intervals.
When prescribing nimesulide less than 24 hours before or after taking methotrexate, caution must be exercised
since in such cases the concentration of methotrexate in plasma and, accordingly, the toxic effects of this drug may increase.
Due to their effect on renal prostaglandins, inhibitors of prostaglandin synthetase, such as nimesulide, may increase the nephrotoxicity of cyclosporines.
In vitro studies have shown that nimesulide is displaced from the binding sites by tolbutamide and salicylic acid.
Although these interactions were determined in blood plasma, these effects were not observed during clinical use of the drug.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: apathy, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, pain in the epigastric region. Gastrointestinal bleeding may occur.
In rare cases, increased blood pressure, acute renal failure, respiratory depression and coma, and anaphylactoid reactions are possible.
Treatment: Symptomatic. There is no specific antidote. In case the overdose occurred within the last 4 hours,
it is necessary to induce vomiting and/or provide intake of activated carbon (60 to 100 g per adult) and/or osmotic laxative. Forced diuresis and hemodialysis are ineffective due to the high binding of the drug to proteins.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Kanonpharma production CJSC, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At the temperature not more than 25 ° C. Keep out of reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Kanonfarma Production ZAO, Russia |
| Medication form | granules for preparation of oral solution |
| Brand | Kanonfarma Production ZAO |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Naiz, 100 mg 2 g 9 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.