No products in the cart.
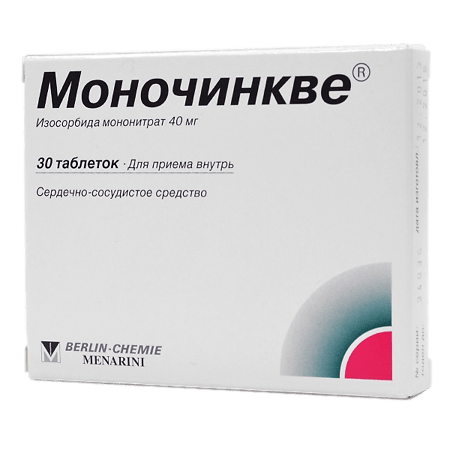
Monochinqué, tablets 40 mg 30 pcs
€5.63 €5.00
Description
Pharmacodynamics
Peripheral vasodilator with predominant effect on the venous vessels. It has a vasodilator and antianginal action.
Limits preload (due to the expansion of peripheral veins) and postload (due to the reduction of total peripheral vascular resistance), reduces myocardial oxygen demand, dilates coronary arteries and improves coronary blood flow, promotes its redistribution in ischemic areas, reduces left ventricular end diastolic volume and reduces systolic tension of its walls. Increases exercise tolerance in patients with coronary artery disease, reduces the pressure in the small circle of the circulation.
Isosorbide mononitrate causes relaxation of the muscles of the bronchi, urinary tract, muscles of the gallbladder, biliary tract and esophagus, as well as the small and large intestine, including sphincters.
At a molecular level, nitrates act by producing nitric oxide (NO) and cyclic guanosylmonophosphate (cGMP), which is considered a mediator of relaxation. When administered orally, isosorbide-5-monononitrate has an antianginal effect as early as 30 minutes and lasts for 2-6 hours.
Pharmacokinetics
It is quickly and completely absorbed after oral administration. Bioavailability is 90 to 100%. The maximum concentration in plasma is reached after approximately 1-1.5 hours.
Therapeutic concentration of isosorbide-5-monononitrate in blood is reached after 30 minutes and is 250 ng/ml, during the 4th hour – 414 ng/ml, during the 12th hour -199 ng/ml (i.e. the concentration drop is slow). Isosorbide-5-mononitrate is almost completely metabolized in the liver, and undergoes a “first pass” effect through the liver (in contrast to isosorbium dinitrate). Metabolites are pharmacologically inactive.
Isosorbide-5-monononitrate is excreted by the kidneys almost exclusively as metabolites. Approximately 2% is excreted unchanged. The elimination half-life is 4-5 hours, which is 8 times higher than that of isosorbide dinitrate.
The development of tolerance as well as cross-tolerance with other nitro compounds during long-term continuous treatment with high doses of isosorbide – 5 -mononitrate has been described. To prevent reduction or loss of efficacy, continuous administration of high doses of the drug should be avoided.
Indications
Indications
Prevention of angina attacks in patients with coronary artery disease, incl. after myocardial infarction.
Treatment of chronic heart failure (as part of combination therapy).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacodynamics
Peripheral vasodilator with a predominant effect on venous vessels. Has a vasodilator and antianginal effect.
Reduces preload (due to the expansion of peripheral veins) and afterload (due to a decrease in total peripheral vascular resistance), reduces myocardial oxygen demand, dilates the coronary arteries and improves coronary blood flow, promotes its redistribution to ischemic areas, reduces the end-diastolic volume of the left ventricle and reduces the systolic tension of its walls. Increases tolerance to physical activity in patients with coronary artery disease, reduces pressure in the pulmonary circulation.
Isosorbide mononitrate causes relaxation of the muscles of the bronchi, urinary tract, gallbladder muscles, bile ducts and esophagus, as well as the small and large intestines, including sphincters.
At the molecular level, nitrates act through the formation of nitric oxide (NO) and cyclic guanosyl monophosphate (cGMP), which is considered a relaxation mediator. When isosorbide-5-mononitrate is taken orally, the antianginal effect appears within 30 minutes and lasts 2-6 hours.
Pharmacokinetics
Quickly and completely absorbed after oral administration. Bioavailability ranges from 90 to 100%. The maximum concentration in blood plasma is reached after approximately 1-1.5 hours.
The therapeutic concentration of isosorbide-5-mononitrate in the blood is achieved after 30 minutes and is 250 ng/ml, during the 4th hour – 414 ngml, during the 12th hour -199 ng/ml (i.e., the concentration drop is slow). Isosorbide-5-mononitrate is almost completely metabolized in the liver and is subject to a “first pass” effect through the liver (unlike isosorbide dinitrate). Metabolites are pharmacologically inactive.
Isosorbide-5-mononitrate is excreted by the kidneys almost exclusively in the form of metabolites. Approximately 2% is excreted unchanged. The half-life is 4-5 hours, which is 8 times higher than that of isosorbide dinitrate.
The development of tolerance, as well as cross-tolerance with other nitro compounds, has been described during long-term continuous treatment with high doses of isosorbide 5-mononitrate. To prevent reduction or loss of effectiveness, continuous use of high doses of the drug should be avoided.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Monocinque® should not be used to relieve acute attacks of angina and acute myocardial infarction.
During therapy, monitoring of blood pressure and heart rate is necessary.
Abrupt withdrawal of the drug should be avoided (the dose should be reduced gradually).
It is possible to develop tolerance to Monocinque® or cross-tolerance to other nitro compounds (reduced effectiveness of the drug due to previous use of other nitro compounds). To prevent the development of tolerance to the action of Monocinque®, continuous use in high doses should be avoided.
Patients with circulatory instability may develop symptoms of acute circulatory failure already at the first dose of the drug.
“Nitrate” headaches can be largely prevented if you take 1/2 tablet at the beginning of therapy. Monocinque® morning and evening.
During treatment with the drug, the use of ethanol should be avoided.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and other mechanisms that require increased concentration
During treatment, it is not recommended to drive vehicles or engage in other potentially hazardous activities that require a quick psychomotor reaction.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Isosorbide mononitrate
Composition
Composition
Active ingredients:
isosorbide-5-mononitrate 40 mg.
Excipients:
lactose monohydrate – 160 mg,
microcrystalline cellulose – 82.5 mg,
corn starch – 10 mg,
talc – 5 mg,
magnesium stearate – 2.5 mg.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity (including to other organic nitrates), acute stage of myocardial infarction, acute circulatory disorders (shock, collapse), hemorrhagic stroke, severe arterial hypotension (less than 90/60 mm Hg), simultaneous use of the phosphodiesterase inhibitor sildenafil (Viagra), condition after traumatic brain injury, angle-closure glaucoma, children under 18 years of age.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Headache (at the beginning of treatment; decreases with continued therapy); after the first dose – a decrease in blood pressure and/or the development of orthostatic hypotension (accompanied by tachycardia, dizziness, weakness).
Very rarely – nausea, vomiting, facial redness, allergic skin reactions.
Interaction
Interaction
The hypotensive effect is enhanced by other vasodilators, antihypertensive drugs, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, antipsychotic drugs, phosphodiesterase inhibitors (sildenafil), and alcohol.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: decreased blood pressure with orthostatic dysregulation, reflex tachycardia and headache. Weakness, dizziness, hot flashes, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea may occur. At high doses (more than 20 mg/kg body weight), methemoglobinemia, cyanosis, dyspnea and tachypnea should be expected due to the formation of nitrite ions due to the metabolism of isosorbide mononitrate. Very high doses can lead to increased intracranial pressure with the occurrence of cerebral symptoms. In case of chronic overdose, an increase in the level of methemoglobin is possible. although the clinical significance of this has not yet been definitively established.
Treatment: gastric lavage, the patient should be placed in a horizontal position with legs raised. Vital signs should be monitored and adjusted if necessary. Patients with severe hypotension and/or shock should be given fluids; in exceptional cases, infusions of norepinephrine (norepinephrine) and/or dopamine can be administered to improve blood circulation. Administration of epinephrine (adrenaline) and related compounds is contraindicated.
Depending on the severity, the following antidotes are used in cases of methemoglobinemia:
Vitamin C: 1 g orally or in the form of sodium salt IV.
methylene blue: up to 50 ml of 1% solution of methylene blue intravenously.
toluidine blue: first 2-4 mg/kg body weight IV; then, if necessary, repeated administrations of 2 mg/kg body weight are possible with an interval between administrations of 1 hour.
Oxygen therapy, hemodialysis, and exchange blood transfusion are also performed.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
Store in a place protected from light, out of reach of children, at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
Shelf life
Shelf life
5 years.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Berlin-Chemie AG, Germany
Additional information
| Shelf life | 5 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store in a dark place out of the reach of children at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. |
| Manufacturer | Berlin-Chemie AG, Germany |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Berlin-Chemie AG |
Related products
Buy Monochinqué, tablets 40 mg 30 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.