No products in the cart.
Milgamma compositum, 100 mg+100 mg 60 pcs.
€41.70 €36.14
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group: vitamins.
ATC code: A11DB02
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics:
Benfothiamine, a fat-soluble derivative of thiamine (vitamin B1), is phosphorylated in the body to the biologically active coenzymes thiamine diphosphate and thiamine triphosphate. Thiamine diphosphate is a coenzyme of pyruvate decarboxylase, 2-oxyglutarate dehydrogenase and transketolase, thus participating in the pentose phosphate cycle of glucose oxidation (in the transfer of the aldehyde group).
The phosphorylated form of pyridoxine (vitamin B6), pyridoxalphosphate, is a coenzyme of several enzymes that affect all stages of non-oxidative metabolism of amino acids. Pyridoxal phosphate is involved in the decarboxylation of amino acids and therefore in the formation of physiologically active amines (e.g., adrenaline, serotonin, dopamine, tyramine). Pyridoxal phosphate is involved in anabolic and catabolic processes (e.g. as a coenzyme of such transaminases as glutamate oxalocetate transaminase, glutamate pyruvate transaminase, GABA, α-ketoglutarate transaminase) as well as in various amino acid degradation and synthesis reactions. Vitamin B6 is involved in 4 different steps of tryptophan metabolism.
Pharmacokinetics:
When taken orally, most of benfothiamine is absorbed in the duodenum, less in the upper and middle small intestine. Benfotiamine is absorbed due to active resorption at concentrations ≤ 2 µmol and due to passive diffusion at concentrations ≥2 µmol. As a fat-soluble derivative of thiamine (vitamin B1), benfothiamine is absorbed faster and more completely than water-soluble thiamine hydrochloride. In the gut, benfothiamine is converted to S-benzoylthiamine as a result of dephosphorylation by phosphatases. S-benzoylthiamine is fat-soluble, has high permeability and is absorbed mostly without being converted into thiamine. Due to enzymatic debenzoylation after absorption, thiamine and biologically active coenzymes thiamine diphosphate and thiamine triphosphate are formed. Especially high levels of these coenzymes are observed in the blood, liver, kidneys, muscles and brain.
Pyridoxine (vitamin B6) and its derivatives are absorbed primarily in the upper gastrointestinal tract by passive diffusion. In serum, pyridoxalphosphate and pyridoxal are bound to albumin. Before penetrating the cell membrane, pyridoxal phosphate bound to albumin is hydrolyzed by alkaline phosphatase to form pyridoxal.
The two vitamins are excreted mainly in the urine. Approximately 50% of thiamine is excreted unchanged or as sulfate. The remainder consists of several metabolites, among which are thiaminic acid, methylthiazo-acetic acid and pyramine. The average blood elimination half-life (t½) of benfothiamine is 3.6 h. The half-life of pyridoxine when taken orally is approximately 2-5 hours. The biological half-life of thiamine and pyridoxine is approximately 2 weeks.
Additional information
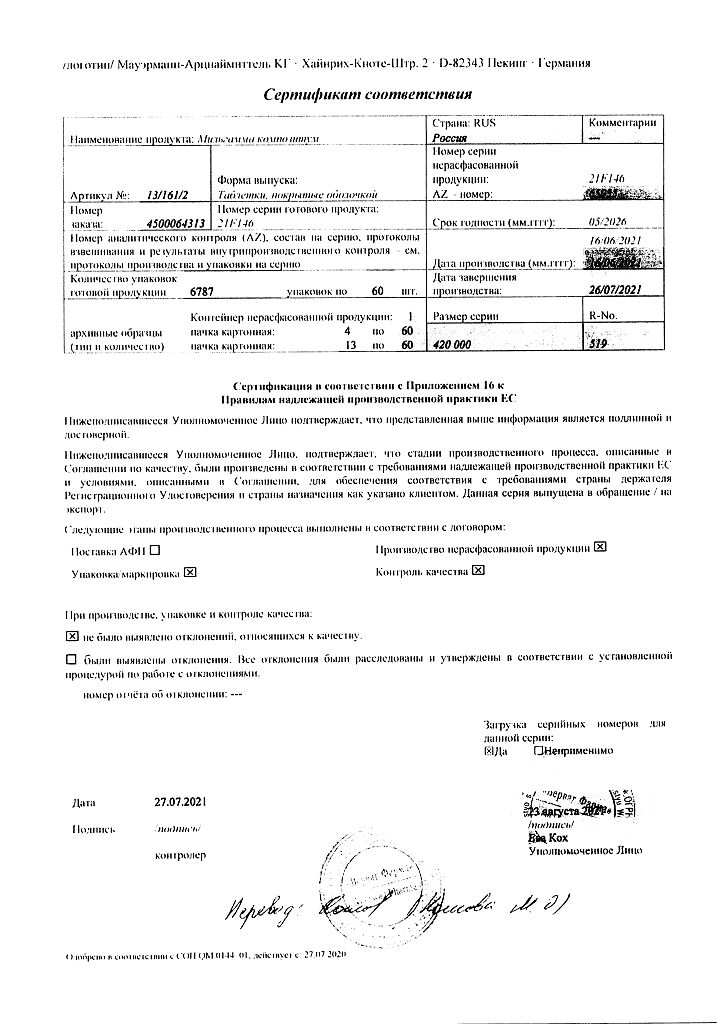
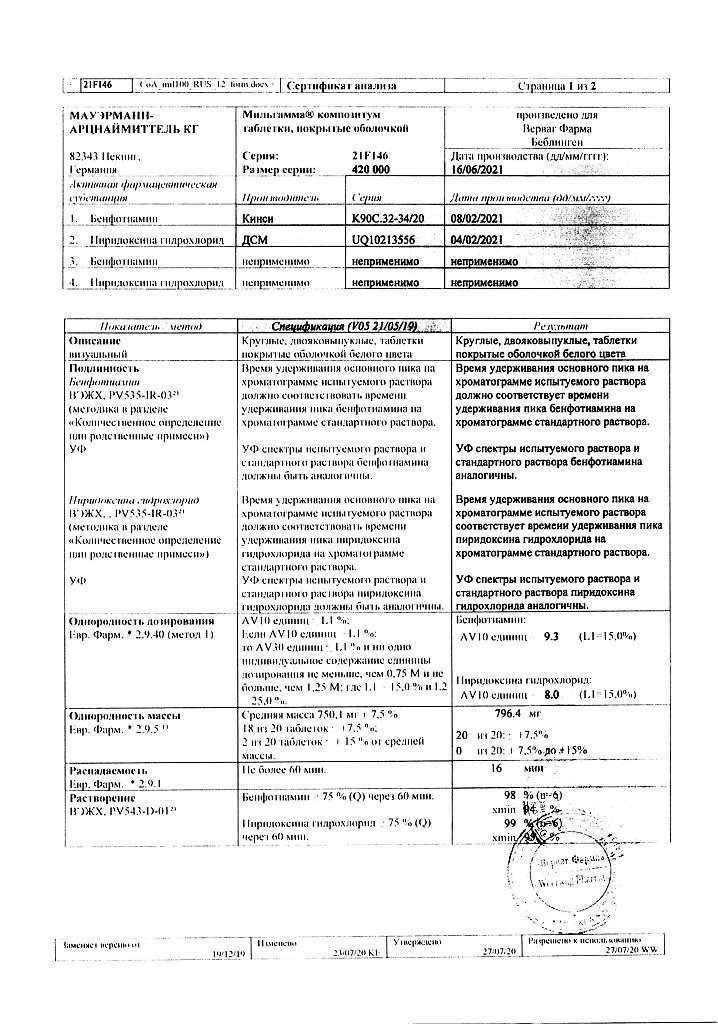
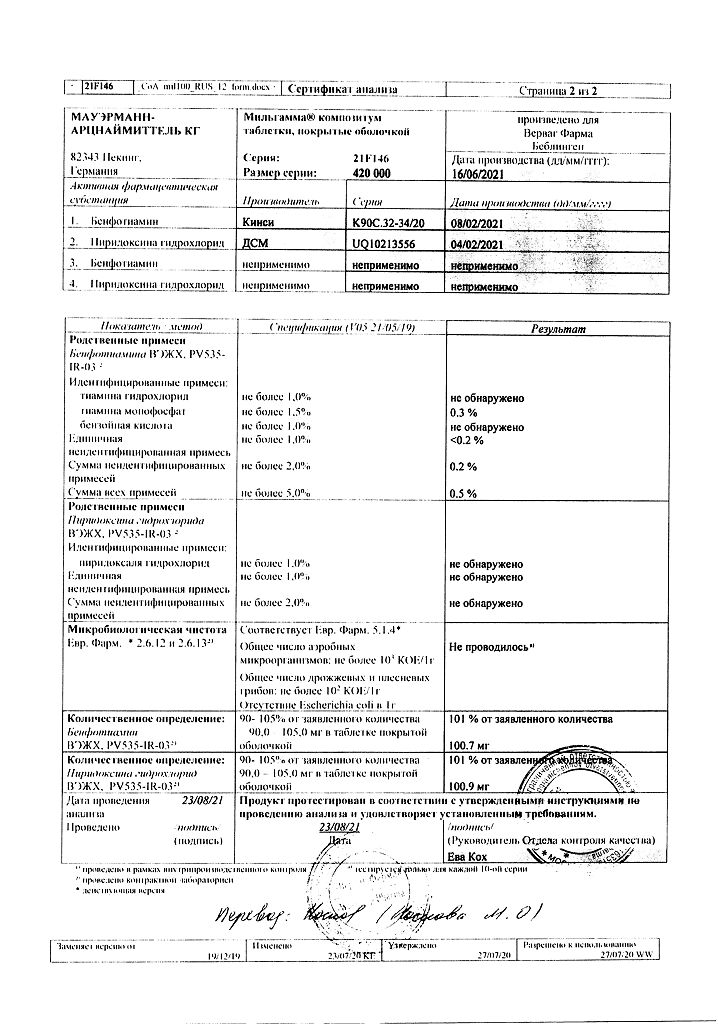
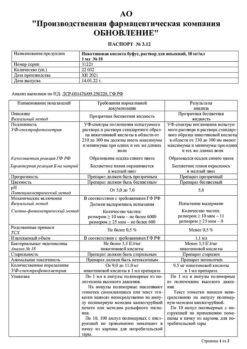
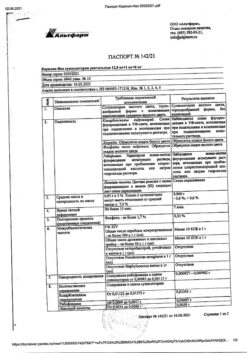
| Shelf life | 5 years. Do not use after the expiration date. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature not exceeding 25 ºC. Keep out of reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Mauermann-Arzneimittel KG, Germany |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Mauermann-Arzneimittel KG |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Milgamma compositum, 100 mg+100 mg 60 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.