No products in the cart.
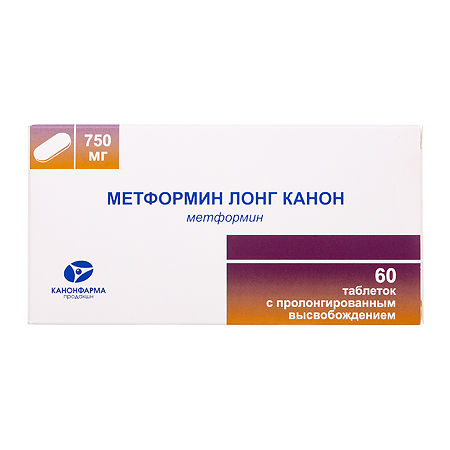
Metformin Long Canon, 750 mg 60 pcs
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Orally administered hypoglycemic drug from the group of biguanides (dimethylbiguanide). The mechanism of action of metformin is related to its ability to inhibit gluconeogenesis, as well as the formation of free fatty acids and fat oxidation. It increases the sensitivity of peripheral receptors to insulin and glucose utilization by cells.
Metformin does not affect the amount of insulin in the blood, but changes its pharmacodynamics by reducing the ratio of bound to free insulin and increasing the ratio of insulin to proinsulin.
Metformin stimulates glycogen synthesis by acting on glycogen synthetase. It increases transport capacity of all types of membrane glucose transporters. Delays absorption of glucose in the intestine.
Limits triglycerides, LDL, LDLNP. Metformin improves blood fibrinolytic properties by inhibiting tissue-type plasminogen activator inhibitor.
A patient’s body weight either remains stable or decreases moderately while taking metformin.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration metformin is slowly and partially absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Cmax in plasma is reached after approximately 2.5 hours. At a single dose of 500 mg absolute bioavailability is 50-60%. Absorption of metformin is decreased and delayed with concomitant food intake.
Metformin is rapidly distributed in body tissues. Practically does not bind with plasma proteins. It accumulates in the salivary glands, liver and kidneys.
Extracted by the kidneys unchanged. T1/2 from plasma is 2-6 hours.
In impaired renal function, metformin may be cumulated.
Indications
Indications
Diabetes mellitus type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) with ineffective diet therapy and physical activity, in obese patients: in adults – as monotherapy or in combination with other oral hypoglycemic agents or with insulin;
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
An oral hypoglycemic agent from the biguanide group (dimethylbiguanide). The mechanism of action of metformin is associated with its ability to suppress gluconeogenesis, as well as the formation of free fatty acids and fat oxidation. Increases the sensitivity of peripheral receptors to insulin and the utilization of glucose by cells.
Metformin does not affect the amount of insulin in the blood, but changes its pharmacodynamics by reducing the ratio of bound to free insulin and increasing the ratio of insulin to proinsulin.
Metformin stimulates glycogen synthesis by acting on glycogen synthetase. Increases the transport capacity of all types of membrane glucose transporters. Delays the absorption of glucose in the intestines.
Reduces the level of triglycerides, LDL, VLDL. Metformin improves the fibrinolytic properties of blood by suppressing tissue-type plasminogen activator inhibitor.
While taking metformin, the patient’s body weight either remains stable or decreases moderately.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration, metformin is slowly and incompletely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Cmax in plasma is reached after approximately 2.5 hours. With a single dose of 500 mg, absolute bioavailability is 50-60%. With simultaneous food intake, the absorption of metformin is reduced and delayed.
Metformin is rapidly distributed into body tissues. Practically does not bind to plasma proteins. Accumulates in the salivary glands, liver and kidneys.
It is excreted unchanged by the kidneys. T1/2 from plasma is 2-6 hours.
In case of impaired renal function, accumulation of metformin is possible.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Use is not recommended for acute infections, exacerbation of chronic infectious and inflammatory diseases, injuries, acute surgical diseases, or danger of dehydration.
Do not use before surgery and within 2 days after surgery.
Metformin should be used with caution in elderly patients and people performing heavy physical work, which is associated with an increased risk of developing lactic acidosis. Elderly patients often experience asymptomatic renal dysfunction. Particular caution is required if renal dysfunction is caused by taking antihypertensive drugs or diuretics, as well as NSAIDs.
If during treatment the patient develops muscle cramps, indigestion (abdominal pain) and severe asthenia, it should be borne in mind that these symptoms may indicate the onset of lactic acidosis.
During treatment, it is necessary to monitor renal function; Determination of lactate content in plasma should be carried out at least 2 times a year, as well as when myalgia appears.
When metformin is used as monotherapy in accordance with the dosage regimen, hypoglycemia, as a rule, does not occur. However, when combined with insulin or sulfonylurea derivatives, there is a risk of developing hypoglycemia. In such cases, particularly careful monitoring of blood glucose concentrations is necessary.
During treatment, patients should avoid drinking alcohol due to the risk of developing lactic acidosis.
Preclinical studies have shown that metformin does not have carcinogenic potential.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Metformin
Composition
Composition
Extended-release tablets are white or off-white, oval, biconvex.
1 tab.
metformin hydrochloride
750 mg
Excipients:
hypromellose 2208 (hydroxypropyl methylcellulose 2208),
hypromellose (hydroxypropyl methylcellulose) 2910,
colloidal silicon dioxide,
magnesium stearate,
microcrystalline cellulose.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Acute or chronic metabolic acidosis, diabetic ketoacidosis, diabetic precoma and coma;
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the digestive system: possible (usually at the beginning of treatment) nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, flatulence, discomfort in the abdomen; in isolated cases – impaired liver function indicators, hepatitis (disappear after cessation of treatment).
From the side of metabolism: very rarely – lactic acidosis (cessation of treatment is required).
From the hematopoietic system: very rarely – impaired absorption of vitamin B12.
The profile of adverse reactions in children aged 10 years and older is the same as in adults.
Interaction
Interaction
When used simultaneously with sulfonylurea derivatives, acarbose, insulin, salicylates, MAO inhibitors, oxytetracycline, ACE inhibitors, clofibrate, cyclophosphamide, the hypoglycemic effect of metformin may be enhanced.
When used simultaneously with GCS, hormonal contraceptives for oral administration, danazol, epinephrine, glucagon, thyroid hormones, phenothiazine derivatives, thiazide diuretics, nicotinic acid derivatives, the hypoglycemic effect of metformin may be reduced.
In patients receiving metformin, the use of iodine-containing contrast agents for the purpose of diagnostic studies (including IV urography, IV cholangiography, angiography, CT) increases the risk of developing acute renal dysfunction and lactic acidosis. These combinations are contraindicated.
Injectable beta2-agonists increase blood glucose concentrations due to stimulation of beta2-adrenergic receptors. In this case, monitoring of blood glucose concentration is necessary. If necessary, it is recommended to prescribe insulin.
Concomitant use of cimetidine may increase the risk of developing lactic acidosis.
Concomitant use of loop diuretics may lead to the development of lactic acidosis due to possible functional renal failure.
When taken simultaneously with ethanol, the risk of developing lactic acidosis increases.
Nifedipine increases the absorption and Cmax of metformin.
Cationic drugs (amiloride, digoxin, morphine, procainamide, quinidine, quinine, ranitidine, triamterene, trimethoprim and vancomycin) secreted in the renal tubules compete with metformin for tubular transport systems and may lead to an increase in its Cmax.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Kanonpharma production CJSC, Russia
Additional information
| Manufacturer | Kanonfarma Production ZAO, Russia |
|---|---|
| Medication form | sustained release tablets |
| Brand | Kanonfarma Production ZAO |
Related products
Buy Metformin Long Canon, 750 mg 60 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.