No products in the cart.
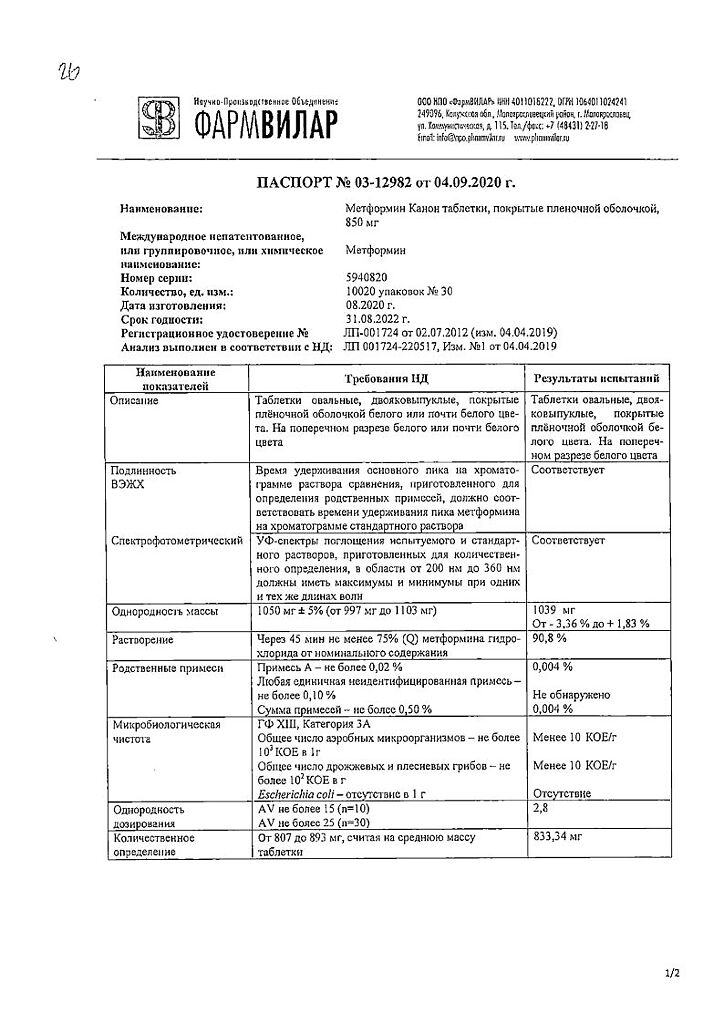
Metformin Canon, 850 mg 30 pcs
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Metformin is a substance of biguanide class, its mechanism of action is manifested by inhibition of gluconeogenesis process in the liver, it reduces glucose absorption from the intestine, enhances the process of peripheral glucose utilization, increases the degree of tissue sensitivity to the action of insulin. It does not affect the process of insulin secretion by beta-cells of the pancreas; it does not provoke hypoglycemic reactions. As a consequence, it stops hyperinsulinemia, which is an important factor contributing to weight gain and the progression of vascular complications in diabetes. Under its influence the body weight stabilizes or decreases.
The drug decreases the content of triglycerides and low-density linoproteins in the blood. It reduces the intensity of fat oxidation and inhibits the production of free fatty acids. It is marked by its fibrinolytic effect, inhibiting RAL-1 and t-PA.
After Metformin is taken orally, the highest concentration is noted in plasma after 2.5 hours. In people who receive the drug at maximum doses, the highest plasma content of the active ingredient was not higher than 4 mcg/ml.
The absorption of the active ingredient stops 6 hours after administration. As a consequence, the plasma concentration decreases. If the patient takes the recommended doses of the drug, a steady steady plasma concentration of the active ingredient in the range of 1 µg/ml or less is noted after 1 to 2 days.
If the drug is taken while eating, absorption of the active ingredient is reduced. It cumulates mainly in the walls of the digestive tube.
His half-life is approximately 6.5 hours. The bioavailability level in healthy people is 50-60%. Its binding to plasma proteins is insignificant. Through the kidneys about 20-30% of the dose is excreted.
Indications
Indications
Diabetes mellitus type 1 and type 2
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
Tablets
Active substance:
metformin hydrochloride 850 mg;
Auxiliary substances:
Pregelatinized starch 66.3 mg,
sodium carboxymethyl starch (primogel) 13.6 mg,
sodium stearyl fumarate 5.1 mg,
povidone 79.9 mg,
talc 5.1 mg;
Composition of the film coating:
Opadray II white 30 mg, including: polyvinyl alcohol 14.07 mg, macrogol (polyethylene glycol) 7.08 mg, titanium dioxide 3.63 mg, talc 5.22 mg.
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
The tablets should be taken orally, swallowed whole, without chewing, during or immediately after a meal, with plenty of water.
Adults:
Monotherapy and combined therapy with other oral hypoglycemic agents
The recommended starting dose is 1000-1500 mg/day. To reduce gastrointestinal side effects, the dose should be divided into 2-3 doses. In 10-15 days in absence of adverse effects of gastrointestinal tract further gradual dose increase depending on blood glucose concentration is possible. Slow increase in dose may improve gastrointestinal tolerance of the drug.
The maintenance daily dose is 1500-2000 mg. The maximum daily dose is 3000 mg divided into 3 doses.
If planning to switch from another oral hypoglycemic drug to Metformin Canon, discontinue the other hypoglycemic drug and start Metformin Canon in the above doses.
Combination therapy with insulin
The recommended starting dose of Metformin Canon 500 mg and 850 mg is 1 tablet 2-3 times daily, Metformin Canon 1000 mg is 1 tablet once daily, the dose of insulin is chosen on the basis of blood glucose values.
Children over 10 years:
Metformin Canon is used in monotherapy and in combination therapy with insulin.
The recommended initial dose of the drug Metformin Canon is 500 mg 1 time per day in the evening with a meal. After 10-15 days the dose of the drug should be adjusted on the basis of blood glucose concentration. The maintenance dose is 1000-1500 mg/day in 2-3 doses. The maximum daily dose is 2000 mg in 3 doses.
Patients in elderly patients
Because of possible decrease of renal function, the dose of Metformin Canon should be adjusted with regular control of renal function parameters (control of serum creatinine at least 2-4 times per year).
The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor. It is not recommended to interrupt the use of the drug without a physician’s indication.
Interaction
Interaction
Contraindicated combinations:
Radiological studies with iodine-containing radiopaque contrast agents may cause development of lactoacidosis in diabetic patients with functional renal insufficiency. Metformin administration should be discontinued 48 hours before and not resumed until 48 hours after radiological examination with contrast agents.
Unrecommended combinations:
Simultaneous use of metformin with alcohol and ethanol-containing drugs, during acute alcohol intoxication, starvation or adherence to a low-calorie diet, as well as liver failure increases the risk of lactoacidosis.
Combinations requiring special caution:
When concomitant use of metformin with danazol, development of hyperglycemic effects is possible. If treatment with danazolol is necessary and after discontinuation of its use, metformin dose adjustment is required under control of blood glucose concentrations.
Chlorpromazine at high doses (100 mg/day) decreases insulin release and increases blood glucose concentrations. When concomitant use with neuroleptics and after discontinuation of their use, correction of metformin dose is required under control of blood glucose concentration.
Glucocorticosteroids (GCS) when used parenterally and topically decrease glucose tolerance and increase blood glucose concentration, in some cases causing ketosis. If it is necessary to use such a combination and after discontinuation of GCS, metformin dose adjustment is required under control of blood glucose concentration.
In concomitant use of loop diuretics and metformin there is a risk of lactoacidosis due to possible functional renal failure.
The use of beta2-adrenomimetics in the form of injections decreases hypoglycemic effect of metformin due to stimulation of beta2-adrenoreceptors. In this case, blood glucose concentration should be monitored and insulin should be used, if necessary.
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and other antihypertensive drugs may decrease the blood glucose concentration. If necessary, the dose of metformin should be adjusted.
Concomitant use of metformin with sulfonylurea derivatives, insulin, acarbose and salicylates may increase the hypoglycemic effect.
Nifedipine increases absorption and Cmax of metformin, which should be considered when using them concomitantly.
“Loop” diuretics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) increase the risk of reduced renal function. In this case, caution should be exercised when using metformin.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
During treatment with metformin, blood glucose concentrations should be monitored regularly on an empty stomach and after meals.
The patient should be warned to stop taking the drug and seek medical attention if vomiting, abdominal pain, muscle aches, general weakness, and severe malaise occur. These symptoms may be a sign of early lactoacidosis.
Metformin should be discontinued 48 hours before and 48 hours after radiologic investigation (including urography, intravenous angiography) using radiographic contrast agents.
Because metformin is excreted by the kidneys, creatinine concentrations should be determined before initiating treatment and regularly thereafter: once per year in patients with preserved renal function; 2-4 times per year in patients with decreased CK and in elderly patients.
Particular caution should be exercised if renal function is impaired, e.g., during initial therapy with antihypertensive agents, diuretics, NSAIDs.
Patients should be advised to seek medical attention if they have symptoms of bronchopulmonary infection or urinary tract infections.
Alcohol should be withheld while using metformin due to the increased risk of hypoglycemia and disulfiram-like effects.
Hypovitaminosis B12 when taking metformin is due to impaired absorption and is reversible. Signs of hypovitaminosis of B12 quickly disappear when the drug is discontinued.
Impact on ability to drive and operate vehicles:
Metformin monotherapy does not cause hypoglycemia and therefore does not affect the ability to drive or operate machinery.
When using metformin with other hypoglycemic agents (sulfonylurea derivatives, insulin, etc.) hypoglycemic states may develop, in which the ability to drive vehicles and engage in other potentially dangerous activities requiring increased attention and quick psychomotor reactions is impaired.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Side effects
Side effects
Central nervous system: taste disorder (“metallic” taste in the mouth).
Gastrointestinal disorders: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain and lack of appetite.
The occurrence of these side effects is most likely during the initial period of treatment and in most cases they go away spontaneously. To prevent symptoms, it is recommended that metformin be taken with or after meals. Slowly increasing the dose may improve gastrointestinal tolerance.
Hepatobiliary system side: impaired liver function parameters, hepatitis. After withdrawal of metformin, adverse events usually disappear completely.
Allergic reactions: very rare – erythema, skin itching, rash, urticaria.
Metabolic disorders: very rare – lactoacidosis (requires cancellation of the drug).
Others: very rare – with long-term use hypovitaminosis of B12 (including megaloblastic anemia) and folic acid (malabsorption) develops.
Published data show that in a limited pediatric population aged 10 to 16 years, side effects are similar in nature and severity to those in adult patients.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: when using metformin at a dose of 85 g, no hypoglycemia was observed, but the development of lactoacidosis was noted. Early symptoms of lactocidosis are nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, decreased body temperature, abdominal pain, muscle pain; further on, rapid breathing, dizziness, impaired consciousness and development of coma may be noted.
Treatment: In case of signs of lactocidosis the drug treatment shall be stopped immediately, the patient shall be urgently hospitalized and after determining the lactate concentration the diagnosis shall be determined. The most effective measure for lactate and metformin elimination from the body is hemodialysis. Symptomatic treatment is also carried out.
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
| Manufacturer | Kanonfarma Production ZAO, Russia |
|---|---|
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Kanonfarma Production ZAO |
Related products
Buy Metformin Canon, 850 mg 30 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.