No products in the cart.
Metformin, 1000 mg 60 pcs
€5.79 €5.15
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Hypoglycemic drug of oral biguanide group.
ATX code: A10BA02
Pharmacological properties
.Pharmacodynamics
Metformin reduces hyperglycemia without leading to hypoglycemia. Unlike sulfonylurea derivatives, it does not stimulate insulin secretion and has no hypoglycemic effect in healthy individuals. Increases the sensitivity of peripheral receptors to insulin and glucose utilization by cells. Inhibits gluconeogenesis in the liver, delays carbohydrate absorption in the intestine. Stimulates glycogen synthesis by activating glycogen synthase. Increases the transport capacity of all types of membrane glucose transporters.
In addition, it has favorable effects on lipid metabolism: it reduces the levels of total cholesterol, low-density lipoproteins and triglycerides.
By taking metformin, a patient’s body weight either remains stable or decreases moderately.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption<
Metformin is rapidly absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). Absolute bioavailability is 50-60%. Maximum concentration (Cmax) in blood plasma is approximately 2 µg/ml. Time to reach Cmax is 2.5 h. Absorption of metformin is decreased and delayed with concomitant food intake.
Distribution
Metformin is rapidly distributed in tissues, almost does not bind to plasma proteins.
Metabolism and excretion
It is metabolized to a very low degree and excreted by the kidneys. Metformin clearance in healthy subjects is 400 ml/min (4 times greater than creatinine clearance), indicating the presence of active tubular secretion. The elimination half-life (T1/2) is about 6.5 h.
Pharmacokinetics in special groups of patients
In patients with renal impairment the T1/2 increases, there is a risk of metformin cumulation in the body.
Indications
Indications
Type 2 diabetes mellitus, especially in obese patients, with ineffective diet therapy and exercise:
in adults as monotherapy or in combination with other oral hypoglycemic drugs, or with insulin;
in children over 10 years of age as monotherapy or in combination with insulin.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Hypoglycemic agent of the biguanide group for oral use.
ATX code: A10BA02
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Metformin reduces hyperglycemia without leading to the development of hypoglycemia. Unlike sulfonylurea derivatives, it does not stimulate insulin secretion and does not have a hypoglycemic effect in healthy individuals. Increases the sensitivity of peripheral receptors to insulin and the utilization of glucose by cells. Inhibits gluconeogenesis in the liver, delays the absorption of carbohydrates in the intestine. Stimulates glycogen synthesis by activating glycogen synthase. Increases the transport capacity of all types of membrane glucose transporters.
In addition, it has a beneficial effect on lipid metabolism: it reduces the content of total cholesterol, low-density lipoproteins and triglycerides.
While taking metformin, the patient’s body weight either remains stable or decreases moderately.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Metformin is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). Absolute bioavailability is 50-60%. The maximum concentration (Cmax) in blood plasma is approximately 2 mcg/ml. The time to reach Cmax is 2.5 hours. With simultaneous food intake, the absorption of metformin is reduced and delayed.
Distribution
Metformin is quickly distributed into tissues and practically does not bind to blood plasma proteins.
Metabolism and excretion
It is metabolized to a very weak extent and is excreted by the kidneys. Metformin clearance in healthy subjects is 400 ml/min (4 times greater than creatinine clearance), indicating the presence of active tubular secretion. The half-life (T1/2) is about 6.5 hours.
Pharmacokinetics in special groups of patients
In patients with renal failure, T1/2 increases, and there is a risk of metformin accumulation in the body.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Lactic acidosis
Lactic acidosis is a rare but serious (high mortality unless promptly treated) complication that may occur due to accumulation of metformin. Cases of lactic acidosis when taking metformin occurred mainly in patients with diabetes mellitus with severe renal failure.
Other associated risk factors should be taken into account, such as decompensated diabetes mellitus, ketosis, prolonged fasting, alcoholism, liver failure and any condition associated with severe hypoxia. This may help reduce the incidence of lactic acidosis.
The risk of developing lactic acidosis should be taken into account when nonspecific signs appear, such as muscle cramps accompanied by dyspeptic symptoms, abdominal pain and severe asthenia. Lactic acidosis is characterized by acidotic shortness of breath, abdominal pain and hypothermia followed by coma. Diagnostic laboratory parameters are a decrease in blood pH (less than 7.25), lactate content in the blood plasma over 5 mmol/l, increased anion gap and lactate/pyruvate ratio.
If metabolic acidosis is suspected, stop taking the drug and consult a doctor immediately.
Surgical operations
The use of metformin should be discontinued 48 hours before elective surgery and can be continued no earlier than 48 hours after, provided that renal function was found to be normal during the examination.
Metformin should be replaced with another hypoglycemic drug (for example, insulin) 48 hours before an x-ray examination with intravenous contrast agents and continued for another 48 hours after this examination.
Kidney function
Since metformin is excreted by the kidneys, before starting treatment and regularly thereafter, it is necessary to determine CK: at least once a year in patients with normal renal function, and 2-4 times a year in elderly patients, as well as in patients with CK at the lower limit of normal.
Particular caution should be exercised in case of possible impairment of renal function in elderly patients, with simultaneous use of antihypertensive drugs, diuretics or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Use in children and adolescents
The diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus must be confirmed before starting treatment with metformin.
In clinical studies lasting 1 year, metformin was shown to have no effect on growth and puberty. However, due to the lack of long-term data, careful monitoring of the subsequent effects of metformin on these parameters in children, especially during puberty, is recommended. The most careful monitoring is necessary in children aged 10-12 years.
Other Precautions
Patients are advised to continue to follow a diet with even carbohydrate intake throughout the day. Overweight patients are advised to continue to follow a hypocaloric diet (but not less than 1000 kcal/day).
It is recommended that routine laboratory tests be performed regularly to monitor diabetes mellitus.
It is not recommended to prescribe the drug if there is a risk of dehydration.
Metformin does not cause hypoglycemia when used alone, but caution is recommended when used in combination with insulin or other hypoglycemic agents (for example, sulfonylureas, repaglinide). When combined treatment requires careful monitoring of blood glucose concentrations.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
Monotherapy with the drug does not cause hypoglycemia and therefore does not affect the ability to drive vehicles and machines. Patients should be warned about the risk of developing hypoglycemia when using metformin in combination with other hypoglycemic drugs (sulfonylurea derivatives, insulin, repaglinide, etc.), which impair the ability to drive vehicles and engage in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased alertness and rapid psychomotor reactions.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Metformin
Composition
Composition
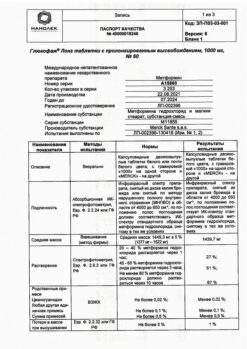
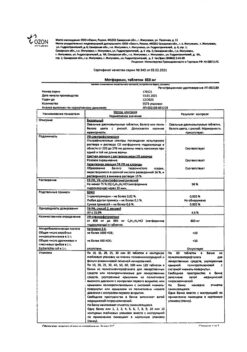
active substance: metformin hydrochloride 1000.0 mg;
excipients: potato starch 80.0 mg, lactose monohydrate 60.0 mg, povidone-KZO 36.0 mg, magnesium stearate 24.0 mg;
shell: film coating (polyvinyl alcohol 14.4 mg, titanium dioxide 9.0 mg, macrogol 7.3 mg, talc 5.3 mg) 36.0 mg.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Decompensated diabetes mellitus during pregnancy is associated with an increased risk of birth defects and perinatal mortality.
Limited evidence suggests that taking metformin in pregnant women does not increase the risk of birth defects in children.
When planning pregnancy or if pregnancy occurs while taking metformin for prediabetes or type 2 diabetes mellitus, the drug should be discontinued and insulin therapy prescribed. It is necessary to maintain the glucose level in the blood plasma at a level closest to normal to reduce the risk of fetal malformations.
Metformin passes into breast milk. No side effects were observed in breastfeeding newborns while taking metformin. However, due to limited data, the use of the drug during breastfeeding is not recommended. The decision to stop breastfeeding should be made taking into account the benefits of breastfeeding and the potential risk of side effects for the baby.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to metformin and/or any excipient of the drug;
diabetic ketoacidosis, diabetic precoma, coma;
renal failure (creatinine clearance (CC) less than 60 ml/min);
liver dysfunction;
clinically pronounced manifestations of acute and chronic diseases that can lead to the development of tissue hypoxia (including cardiac or respiratory failure, acute myocardial infarction);
use within less than 48 hours before and within 48 hours after radioisotope or x-ray studies with the introduction of an iodinated contrast agent;
lactose intolerance, lactase deficiency, glucose-galactose malabsorption;
chronic alcoholism, acute alcohol poisoning;
hypocaloric diet (less than 1000 kcal/day);
lactic acidosis (including history);
acute conditions with a risk of developing renal dysfunction: dehydration (with diarrhea, vomiting), severe infectious diseases, shock;
extensive surgical operations and injuries, when insulin therapy is indicated (see section “Special Instructions”);
pregnancy;
children under 10 years of age.
With caution
The drug should be used in people over 60 years of age who perform heavy physical work, which is associated with an increased risk of developing lactic acidosis; during breastfeeding.
Side Effects
Side Effects
The frequency of side effects of the drug is assessed as follows: very often: > 1/10; often: 1/10-1/100; uncommon: 1/100-1/1000; rare: 1/1000-1/10000; very rare: < 1/10000.
Metabolic and nutritional disorders
Very rare: lactic acidosis (see section “Special instructions”).
With long-term use of metformin, a decrease in the absorption of vitamin B12 may be observed. When megaloblastic anemia is detected, the possibility of such an etiology must be taken into account.
Nervous system disorders
Common: taste disturbance.
Gastrointestinal disorders
Very common: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, lack of appetite, abdominal pain.
These side effects often occur during the initial period of treatment and in most cases, they disappear spontaneously with continued use. To reduce side effects, it is recommended to take the drug during or after meals. Slowly increasing the dose may improve gastrointestinal tolerability.
Disorders of the liver and biliary tract
Very rare: abnormal liver function tests and hepatitis. After discontinuation of metformin, these adverse effects completely disappear.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Very rare: skin reactions such as erythema, itching, rash.
Published post-marketing data as well as controlled clinical studies in a limited pediatric population in the age group of 10-16 years indicate that side effects in children are similar in nature and severity to those in adult patients.
Interaction
Interaction
Contraindicated combinations
Iodine-containing radiocontrast agents: against the background of functional renal failure in patients with diabetes mellitus, radiological examination using iodine-containing X-ray contrast agents can cause the development of lactic acidosis. Treatment with metformin should be discontinued depending on renal function 48 hours before or during an X-ray examination using iodinated contrast agents and not resumed earlier than 48 hours after, provided that during the examination renal function was found to be normal.
Combinations not recommended
Alcohol: with acute alcohol intoxication, the risk of developing lactic acidosis increases, especially in the case of malnutrition; following a low-calorie diet; in case of liver failure. While taking the drug, you should avoid drinking alcohol and medications containing ethanol.
Combinations requiring caution
Danazol: simultaneous use of danazol is not recommended to avoid the hyperglycemic effect of the latter; if treatment with danazol is necessary and after stopping the latter, a dose adjustment of metformin is required under the control of blood glucose concentrations.
Chlorpromazine, when taken in large doses (100 mg/day), increases the concentration of glucose in the blood, reducing the release of insulin. During treatment with antipsychotics and after stopping their use, dose adjustment of metformin is required under the control of blood glucose concentrations.
Glucocorticosteroids (GCS) of systemic and local action reduce glucose tolerance, increase the concentration of glucose in the blood, sometimes causing ketosis. During treatment with GCS and after stopping the latter, dose adjustment of metformin is required under the control of blood glucose concentrations.
Diuretics: Concomitant use of loop diuretics may lead to the development of lactic acidosis due to possible functional renal failure. You should not take metformin if CC is below 60 ml/min.
Beta2-adrenergic agonists, administered parenterally, increase blood glucose concentrations due to stimulation of beta-adrenergic receptors. In this case, monitoring of blood glucose concentration is necessary. If necessary, insulin administration is recommended.
When using the above drugs simultaneously, more frequent monitoring of blood glucose may be required, especially at the beginning of treatment. If necessary, the dose of metformin can be adjusted during treatment and after its cessation.
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and other antihypertensive drugs may decrease blood glucose concentrations. If necessary, the dose of metformin should be adjusted.
When metformin is used simultaneously with sulfonylurea derivatives, insulin, acarbose, and salicylates, hypoglycemia may develop.
Nifedipine increases the absorption and Cmax of metformin.
Cationic drugs (amiloride, digoxin, morphine, procainamide, quinidine, quinine, ranitidine, triamterene, trimethoprim and vancomycin) secreted in the renal tubules compete with metformin for tubular transport systems and may lead to an increase in its Cmax.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: when using metformin at a dose of 85 g (42.5 times the maximum daily dose), no hypoglycemia was observed, but the development of lactic acidosis was noted.
A significant overdose of metformin or associated risk factors can lead to the development of lactic acidosis (see “Special Instructions”).
Treatment: if signs of lactic acidosis appear, treatment with the drug must be stopped immediately, the patient must be urgently hospitalized and, after determining the lactate concentration, the diagnosis must be clarified. The most effective measure for removing lactate and metformin from the body is hemodialysis. Symptomatic treatment is also carried out.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years. Do not use after expiration date.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
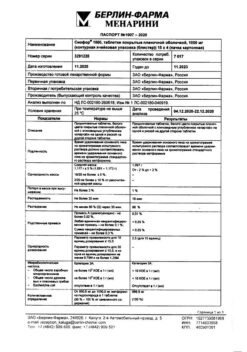
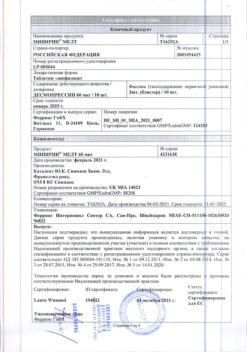
Rapharma JSC, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years. Do not use after the expiration date. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store in a dry, light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °С. Keep out of reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Rapharma AO, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Rapharma AO |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Metformin, 1000 mg 60 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.