No products in the cart.
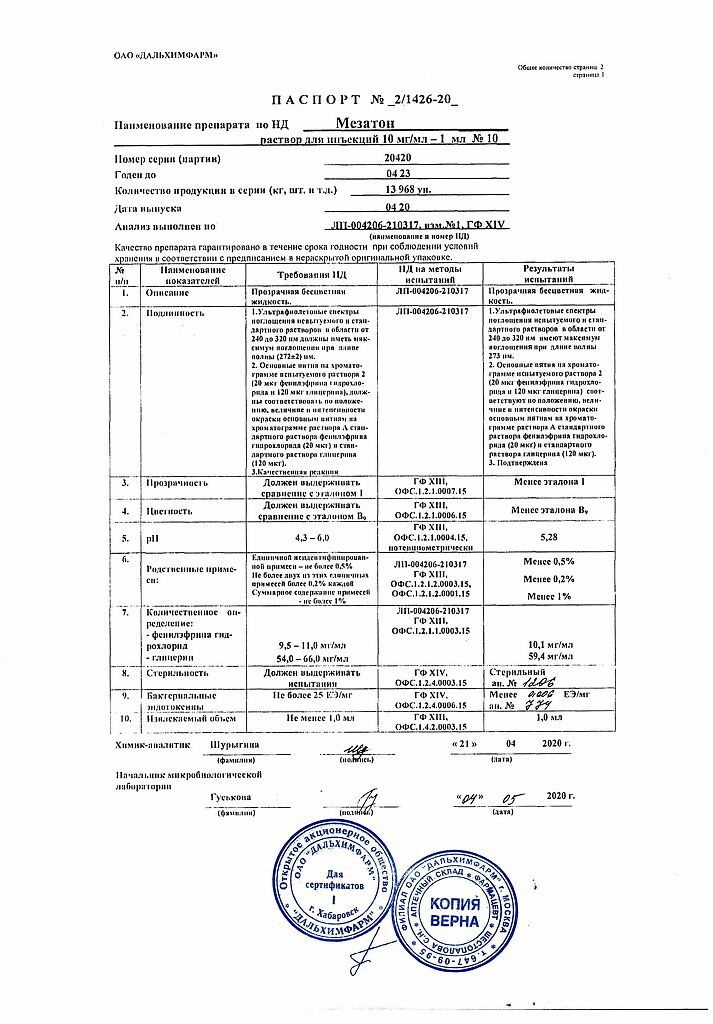
Mesaton, 10 mg/ml 1 ml 10 pcs
€5.31 €4.43
EAN: 4602824022983
SKU: 54028
Categories: Anesthesia and resuscitation, Anesthesia solutions, Medicine
Description
PharmacoDynamics
Phenylephrine is an alpha1-adrenergic stimulant that slightly affects the beta-adrenoceptors of the heart; it is not a catecholamine because it contains only one hydroxyl group in the aromatic core. Causes narrowing of the arterioles and an increase in arterial pressure (BP) (with possible reflex bradycardia), but is more prolonged because it is less prone to the action of catechol()-methyltransferase.
It does not cause an increase in the minute blood volume.
After intravenous administration, the action of the drug develops immediately and lasts for 5-20 minutes. When administered subcutaneously and intramuscularly the action of the drug starts 10-15 min and lasts 1-2 hours after injection.
Pharmacokinetics
After intramuscular administration the drug is quickly absorbed into the systemic blood flow. Volume of distribution after single administration is 340 l. Binding to plasma proteins is low. It is almost completely metabolized in the liver by monoaminoxidase (without catechol()-methyltransferase). The terminal elimination half-life is about 3 hours. It is excreted by the kidneys as metabolites.
Indications
Indications
Acute arterial hypotension;
Vascular insufficiency due to overdose of vasodilators;
Shock (traumatic, toxic);
As a vasoconstrictor during local anesthesia.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacodynamics
Phenylephrine is an alpha1-adrenergic stimulant that has a slight effect on beta-adrenergic receptors of the heart; is not a catecholamine because it contains only one hydroxyl group in the aromatic ring. Causes a constriction of arterioles and an increase in blood pressure (BP) (with possible reflex bradycardia), but lasts longer because it is less prone to the action of catechol-()-methyltransferase.
Does not cause an increase in minute blood volume.
After intravenous administration, the effect of the drug develops immediately and lasts for 5-20 minutes. When administered subcutaneously and intramuscularly, the effect of the drug begins within 10-15 minutes and continues for 1-2 hours after administration.
Pharmacokinetics
After intramuscular administration, it is quickly absorbed into the systemic circulation. The volume of distribution after a single administration is 340 liters. The connection with blood plasma proteins is low. Almost completely metabolized in the liver by monoamine oxidase (without the participation of catechol-()-methyltransferase). The terminal half-life is approximately 3 hours. Excreted by the kidneys in the form of metabolites.
Special instructions
Special instructions
During treatment, electrocardiogram indicators, blood pressure, minute blood volume, blood circulation in the extremities and at the injection site should be monitored.
In patients with arterial hypertension in the event of drug-induced collapse, it is sufficient to maintain systolic blood pressure at a level lower than usual by 30-40 mm Hg. A sharp increase in blood pressure, severe bradycardia or tachycardia, persistent cardiac arrhythmias require discontinuation of treatment.
Before or during shock therapy, correction of hypovolemia, hypoxia, acidosis and hypercapnia is mandatory.
The drug is used with caution in cases of arterial hypertension in the pulmonary circulation, hypovolemia, and ventricular arrhythmia.
In old age, the number of adrenergic receptors sensitive to phenylephrine decreases.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery During the treatment period, it is necessary to refrain from driving vehicles and engaging in potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Phenylephrine
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient:
phenylephrine hydrochloride – 10 mg
Excipients:
glycerol (distilled glycerin) – 60 mg;
water for injection – up to 1 ml
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Adequate and strictly controlled studies of the use of the drug during pregnancy and breastfeeding have not been conducted.
In animals in late pregnancy, phenylephrine caused fetal growth retardation and stimulated early onset of labor.
Use of the drug Mezaton Adverse reactions (ARs) are distributed in accordance with the classification of damage to organs and organ systems according to the MedDRA dictionary and the frequency of development of WHO ADRs: very often: (2 1/10); often: (2 1/100 and < 1/10); uncommon: (2 1/1000 and <1/100); rare: (2 1/10000 and <1/1000); very rare: (< 1/10000); frequency unknown (it is not possible to determine the frequency of occurrence based on available data).
Immune system disorders: rarely – allergic reactions (skin rash, urticaria).
Endocrine system disorders: frequency unknown – hyperglycemia. Metabolic and nutritional disorders: frequency unknown – increased sweating.
Nervous system disorders: very rarely – insomnia, nervousness, tremor, anxiety, increased excitability, confusion, irritability and headache, dizziness, cerebral hemorrhage, paresthesia, weakness.
Visual disturbances: very rarely – pain in the eyes, mydriasis.
Cardiac disorders: rarely – palpitations, bradycardia, tachycardia, ventricular arrhythmias (especially when used in high doses), angina pectoris, frequency unknown – pulmonary edema, cardiac arrest.
Vascular disorders: rarely – increased or decreased blood pressure, frequency unknown – pale facial skin, tingling sensation and coldness of the extremities.
Disorders of the respiratory system, chest and mediastinal organs: rarely – dyspnea.
Gastrointestinal disorders: often nausea, vomiting, frequency unknown – increased salivation.
Renal and urinary tract disorders: very rarely – dysuria, urinary retention.
General disorders and disorders at the injection site: in some cases, necrosis and scab formation are possible when ingested into tissues or during subcutaneous injections. Contraindicated during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
There are no data on the excretion of phenylephrine into breast milk.
If it is necessary to use the drug during lactation, breastfeeding should be stopped.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to any of the components of the drug;
Diseases accompanied by obstruction of the outflow tract of the left ventricle (severe aortic stenosis, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy);
Pheochromocytoma;
Arterial hypertension of any severity;
Ventricular fibrillation;
Glucose-b-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency;
Porphyria;
Thyrotoxicosis;
Angle-closure glaucoma;
Acute myocardial infarction;
Use simultaneously with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAO) and within 14 days after stopping therapy with MAO inhibitors;
Halothane or cyclopropane anesthesia;
Pregnancy and breastfeeding period;
Age up to 18 years.
With caution
Coronary heart disease (especially after a recent myocardial infarction), angina pectoris, coronary thrombosis, mesenteric and other visceral or peripheral vessels, diabetes mellitus, pulmonary hypertension, ventricular arrhythmias, occlusive vascular diseases: arterial thromboembolism, atherosclerosis, thromboangiitis obliterans (Buerger’s disease), Raynaud’s disease, vascular tendency to spasms frostbite, diabetic endarteritis, thyroid dysfunction, metabolic acidosis, hypercapnia, hypoxia, old age, renal and/or liver dysfunction, use in patients with prostate diseases who have an increased risk of urinary retention.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Adverse reactions (ARs) are distributed according to the classification of damage to organs and organ systems according to the MedDRA dictionary and the frequency of development of WHO ADRs: very often: (2 1/10); often: (2 1/100 and < 1/10); uncommon: (2 1/1000 and <1/100); rare: (2 1/10000 and <1/1000); very rare: (< 1/10000); frequency unknown (it is not possible to determine the frequency of occurrence based on available data).
Immune system disorders: rarely – allergic reactions (skin rash, urticaria).
Endocrine system disorders: frequency unknown – hyperglycemia. Metabolic and nutritional disorders: frequency unknown – increased sweating.
Nervous system disorders: very rarely – insomnia, nervousness, tremor, anxiety, increased excitability, confusion, irritability and headache, dizziness, cerebral hemorrhage, paresthesia, weakness.
Visual disturbances: very rarely – pain in the eyes, mydriasis.
Cardiac disorders: rarely – palpitations, bradycardia, tachycardia, ventricular arrhythmias (especially when used in high doses), angina pectoris, frequency unknown – pulmonary edema, cardiac arrest.
Vascular disorders: rarely – increased or decreased blood pressure, frequency unknown – pale facial skin, tingling sensation and coldness of the extremities.
Disorders of the respiratory system, chest and mediastinal organs: rarely – dyspnea.
Gastrointestinal disorders: often nausea, vomiting, frequency unknown – increased salivation.
Renal and urinary tract disorders: very rarely – dysuria, urinary retention.
General disorders and disorders at the injection site: in some cases, necrosis and scab formation are possible when ingested into tissues or during subcutaneous injections.
Interaction
Interaction
Phenylephrine reduces the antihypertensive effect of diuretics and antihypertensive drugs, beta-blockers (the risk of developing arterial hypertension and disorders of the cardiovascular system).
Neuroleptics and phenothiazide derivatives reduce the hypertensive effect of the drug. MAO inhibitors, oxytocin, ergot alkaloids, tricyclic antidepressants, methylphenidate, adrenomimetics enhance the pressor effect and arrhythmogenic effect of phenylephrine.
Beta blockers reduce the cardiac stimulating activity of the drug.
The use of the drug against the background of previous use of reserpine can cause the development of a hypertensive crisis due to depletion of catecholamine reserves in adrenergic endings and increased sensitivity to adrenergic agonists.
Inhalation anesthetics (including chloroform, enflurane, halothane, isoflurane, methoxyflurane) increase the risk of severe atrial and ventricular arrhythmias (including ventricular fibrillation) because they sharply increase the sensitivity of the myocardium to sympathomimetics. Ergometrine, ergotamine, methylergometrine, oxytocin, doxapram increase the severity of the vasoconstrictor effect.
Phenylephrine reduces the antianginal effect of nitrates, which, in turn, can reduce the pressor effect of Mezaton@ and the risk of arterial hypotension (simultaneous use is allowed depending on the achievement of the required therapeutic effect).
Thyroid hormones mutually increase the effectiveness of the drug and the associated risk of coronary insufficiency (especially with coronary atherosclerosis).
The pressor effect of phenylephrine hydrochloride is increased in patients receiving tricyclic antidepressants.
Phenylephrine, when used simultaneously with digoxin or other cardiac glycosides, increases the risk of developing heart rhythm disturbances and myocardial infarction.
The use of the drug Mezaton during childbirth to correct arterial hypotension against the background of the use of drugs that stimulate labor (vasopressin, ergotamine, ergometrine, methylergometrine) can cause a persistent increase in blood pressure in the postpartum period.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: headache, significant increase in blood pressure, reflex bradycardia, ventricular extrasystole, short paroxysms of ventricular tachycardia, feeling of heaviness in the head and limbs. In case of significant overdose, confusion, hallucinations and convulsions may occur.
Treatment: intravenous administration of short-acting alpha-blockers (phentolamine at a dose of 5-60 mg intravenously over 10-30 minutes) and beta-blockers (for heart rhythm disturbances).
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a place protected from light at a temperature not exceeding 25 o C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
4 years.
Do not use after expiration date.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Dalkhimfarm, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 4 years. Do not use after the expiration date. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 o c, Keep out of reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Dalkhimpharm, Russia |
| Medication form | solution for injection |
| Brand | Dalkhimpharm |
Related products
Buy Mesaton, 10 mg/ml 1 ml 10 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.