No products in the cart.
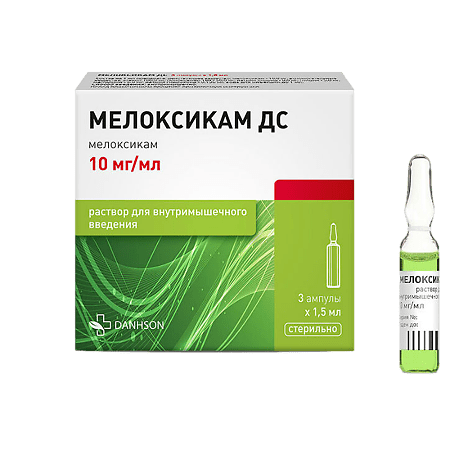
Meloxicam DS, 10 mg/ml 1.5 ml 3 pcs
€6.08 €5.32
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
ATC code: M01AC06
Pharmacodynamics:
Meloxicam is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug with analgesic anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effect. Anti-inflammatory activity is associated with inhibition of enzymatic activity of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), involved in the biosynthesis of prostaglandins in the inflammation. To a lesser extent meloxicam acts on cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) involved in the synthesis of prostaglandin protecting the mucosa of the gastrointestinal tract and is involved in the regulation of blood flow in the kidneys.
Pharmacokinetics:
Relative bioavailability is nearly 100%. After an intravenous injection of 5 mg, the Cmax is 1.62 mcg/mL and is reached within approximately 60 minutes. Meloxicam binds well to plasma proteins, especially to albumin (99%). Penetrates into synovial fluid The concentration in synovial fluid is approximately 50% of the plasma concentration. Vd is low, averaging 11 L. Interindividual variation is 30-40%.
Meloxicam is almost completely metabolized in the liver to form 4 pharmacologically inactive derivatives. The main metabolite 5′-carboxymeloxicam (60% of the dose value) is formed by oxidation of the intermediate metabolite 5′-hydroxymethylmeloxicam which is also excreted but to a lesser extent (9% of the dose value). In vitro studies have shown that CYP2C9 isoenzyme plays an important role in this metabolic transformation, and CYP3A4 isoenzyme has additional importance. Peroxidase activity of which probably varies individually takes part in the formation of two other metabolites (which are 16% and 4% of the drug dose, respectively).
It is excreted equally in the feces and urine, mainly as metabolites. Less than 5% of daily dose is excreted unchanged in the feces, and only trace amounts of the drug are excreted in the urine. Mean T1/2 is 20 hours. Plasma clearance averages 8 ml/min.
Meloxicam exhibits linear pharmacokinetics at doses of 7.5-15 mg when administered by injection.
Hepatic or renal insufficiency of moderate severity has no significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of meloxicam.
Indications
Indications
– Symptomatic treatment of osteoarthritis;
– Symptomatic treatment of rheumatoid arthritis;
– Symptomatic treatment of ankylosing spondylitis (Bechterew’s disease).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
ATX code: M01AC06
Pharmacodynamics:
Meloxicam is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug with analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects. The anti-inflammatory effect is associated with inhibition of the enzymatic activity of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), which is involved in the biosynthesis of prostaglandins in the area of inflammation. To a lesser extent, meloxicam acts on cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1), which is involved in the synthesis of prostaglandin, which protects the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract and is involved in the regulation of blood flow in the kidneys.
Pharmacokinetics:
Relative bioavailability is almost 100%. After intramuscular administration of the drug at a dose of 5 mg, Cmax is 1.62 μg/ml and is achieved within approximately 60 minutes. Meloxicam binds well to plasma proteins, especially albumin (99%). Penetrates into synovial fluid; the concentration in synovial fluid is approximately 50% of the concentration in plasma. Vd low averages 11 liters. Interindividual differences are 30-40%.
Meloxicam is almost completely metabolized in the liver to form 4 pharmacologically inactive derivatives. The main metabolite 5′-carboxymeloxicam (60% of the dose) is formed by oxidation of the intermediate metabolite 5′-hydroxymethylmeloxicam, which is also excreted but to a lesser extent (9% of the dose). In vitro studies have shown that the CYP2C9 isoenzyme plays an important role in this metabolic transformation; the CYP3A4 isoenzyme plays an additional role. In the formation of the other two metabolites (constituting 16% and 4% of the drug dose, respectively), peroxidase takes part, the activity of which probably varies individually.
It is excreted equally in feces and urine, mainly in the form of metabolites. In unchanged form, less than 5% of the daily dose is excreted in the urine; in unchanged form, the drug is found only in trace amounts. The average T1/2 is 20 hours. Plasma clearance averages 8 ml/min.
Meloxicam exhibits linear pharmacokinetics in doses of 7.5-15 mg when administered intramuscularly.
Moderate hepatic or renal impairment does not significantly affect the pharmacokinetics of meloxicam.
Special instructions
Special instructions
– Caution should be exercised when using the drug in patients with a history of gastric or duodenal ulcers, as well as in patients on anticoagulant therapy. Such patients have an increased risk of erosive and ulcerative diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
– Caution should be exercised and monitoring of renal function indicators when using the drug in elderly patients, patients with chronic heart failure with symptoms of circulatory failure, patients with cirrhosis of the liver, as well as in patients with hypovolemia as a result of surgical interventions.
– In patients with renal failure, if creatinine clearance is more than 30 ml/min, no dosage adjustment is required.
– In patients on dialysis, the dosage of the drug should not exceed 75 mg/day.
– Patients taking diuretics and meloxicam simultaneously should take sufficient fluids.
– If allergic reactions occur during treatment (itching, skin rash, urticaria, photosensitivity), you must consult a doctor to decide whether to stop taking the drug.
– Meloxicam, like other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, can mask the symptoms of infectious diseases.
– The use of meloxicam, like other drugs that block prostaglandin synthesis, can affect fertility and is therefore not recommended for women planning pregnancy.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles. Wed and fur.:
The use of the drug may cause undesirable effects such as headache and dizziness and drowsiness. You should refrain from driving vehicles and servicing machines and mechanisms that require concentration.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Meloxicam
Composition
Composition
1 ampoule contains:
Active ingredient:
meloxicam – 15 mg;
Auxiliary components: ethanol, poloxamer 188, sodium chloride, glycine, meglumine, sodium hydroxide, water for injection.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Use during pregnancy and lactation is contraindicated.
Contraindications
Contraindications
– Hypersensitivity to the active substance or auxiliary components;
– contraindicated in the period after coronary artery bypass surgery;
– decompensated heart failure;
– complete or incomplete combination of bronchial asthma, recurrent polyposis of the nasal mucosa and paranasal sinuses and intolerance to acetylsalicylic acid and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (including a history);
– erosive and ulcerative changes in the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum; active gastrointestinal bleeding;
– exacerbation of inflammatory bowel diseases (nonspecific ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease);
– cerebrovascular bleeding or other bleeding;
– severe liver failure or active liver disease;
– severe renal failure in patients not undergoing dialysis (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min) progressive kidney diseases, incl. confirmed hyperkalemia;
– pregnancy, breastfeeding period;
– children under 18 years of age.
With caution:
Coronary heart disease cerebrovascular diseases chronic heart failure dyslipidemia/hyperlipidemia diabetes mellitus peripheral arterial disease smoking creatinine clearance from 30 to 60 ml/min. Anamnestic data on the development of ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection, old age, long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), frequent alcohol consumption, severe somatic diseases, concomitant therapy with the following drugs:
– Anticoagulants (for example warfarin);
– antiplatelet agents (for example acetylsalicylic acid clopidogrel);
– oral glucocorticosteroids (for example prednisolone);
– selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (for example, citalopram fluoxetine paroxetine sertraline);
To reduce the risk of developing adverse events from the gastrointestinal tract, the minimum effective dose should be used for the shortest possible short course.
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the digestive system: more than 1% – dyspepsia, incl. nausea vomiting abdominal pain constipation flatulence diarrhea; 0.1-1% – transient increase in the activity of “liver” transaminases hyperbilirubinemia belching esophagitis gastroduodenal ulcer bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract (including hidden) stomatitis; <0.1% - gastrointestinal perforation colitis; hepatitis gastritis.
From the hematopoietic system: more than 1% – anemia; 0.1-1% – change in blood formula, incl. leukopenia thrombocytopenia.
From the skin: more than 1% – itching, skin rash; 0.1-1% – urticaria; less than 0.1% – photosensitivity, bullous rashes, erythema multiforme, incl. Stevens-Johnson syndrome toxic epidermal necrolysis.
From the respiratory system: less than 0.1% – bronchospasm.
From the side of the central nervous system: more than 1% – dizziness, headache; 0.1-1% – vertigo, tinnitus, drowsiness; less than 0.1% – confusion, disorientation, emotional lability.
From the cardiovascular system: more than 1% – peripheral edema; 0.1-1% – increased blood pressure, heartbeat, “flushes” of blood to the skin of the face.
From the urinary system: 0.1-1% – hypercreatininemia and/or increased urea in the blood serum; less than 0.1% – acute renal failure; The connection with taking meloxicam has not been established – interstitial nephritis, albuminuria, hematuria.
From the senses: less than 0.1% – conjunctivitis, visual impairment, incl. blurred vision.
Allergic reactions: less than 0.1% – angioedema, anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions.
Local reactions: more than 1% – swelling at the injection site; less than 1% – pain at the injection site.
Interaction
Interaction
– When used simultaneously with other NSAIDs (as well as acetylsalicylic acid), it increases the risk of erosive and ulcerative lesions and bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract;
– When used simultaneously with antihypertensive drugs, the effectiveness of the latter may decrease;
– When used simultaneously with lithium preparations, the development of cumulation of lithium and an increase in its toxic effect is possible (monitoring the concentration of lithium in the blood is recommended);
– When used simultaneously with methotrexate, the side effect of the latter on the hematopoietic system increases (the risk of anemia and leukopenia requires periodic monitoring of a general blood test);
– When used simultaneously with diuretics and cyclosporine, the risk of developing renal failure increases;
– When used simultaneously with intrauterine contraceptives, the effectiveness of the latter may decrease;
– When used simultaneously with anticoagulants (heparin ticlopidine warfarin), antiplatelet agents (acetylsalicylic acid clopidogrel) as well as fibrinolytic drugs (streptokinase fibrinolysin), the risk of bleeding increases (periodic monitoring of blood clotting parameters is necessary);
– When used simultaneously with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding increases.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: impaired consciousness nausea vomiting epigastric pain gastrointestinal bleeding acute renal failure liver failure respiratory arrest asystole.
Treatment: there is no specific antidote; symptomatic therapy. Forced diuresis, alkalization of urine, hemodialysis – are ineffective due to the high connection of the drug with blood proteins.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
Store in a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
Keep out of the reach of children!
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years.
Do not use after expiration date.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Vetprom AD, Bulgaria
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years. Do not use after the expiration date. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store in a dry place protected from light at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. Store out of the reach of children! |
| Manufacturer | VetProm AD, Bulgaria |
| Medication form | solution |
| Brand | VetProm AD |
Related products
Buy Meloxicam DS, 10 mg/ml 1.5 ml 3 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.