No products in the cart.
Description
Lozartan is a specific angiotensin II receptor antagonist (AT1 tin) for oral administration. Angiotensin II selectively binds to AT1 receptors located in many tissues (vascular smooth muscle tissues, adrenal glands, kidneys and heart) and has several important biological functions including vasoconstriction and aldosterone release. Angiotensin II also stimulates smooth muscle cell overgrowth.
Lozartan and its pharmacologically active metabolite (E 3174) both in vitro and in vivo block all physiological effects of angiotensin II regardless of the source or synthesis route.
Lozartan selectively binds to AT1 receptors: it neither binds nor blocks receptors for other hormones and ion channels that play an important role in the regulation of cardiovascular function. In addition, losartan does not inhibit angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), which promotes bradykinin degradation, so bradykinin-mediated side effects (e.g., angioedema) are quite rare.
When using losartan, the lack of negative feedback effects on renin secretion results in increased plasma renin activity. Increased renin activity results in increased plasma angiotensin II concentrations. However, antihypertensive activity and decreased plasma aldosterone concentration persist, indicating effective angiotensin II receptor blockade. After discontinuation of losartan, plasma renin activity and angiotensin II concentration decreased within 3 days to baseline values observed before the start of the drug.
Lozartan and its active metabolite have a high affinity for angiotensin II receptors (AT1 type).
The plasma concentrations of losartan and its active metabolite and the antihypertensive effect of losartan increase with increasing drug dose.
The maximum antihypertensive effect develops 3-6 weeks after initiation of the drug.
In patients with arterial hypertension, proteinuria (more than 2 g per day), without diabetes mellitus, use of the drug significantly reduces proteinuria, albumin and immunoglobulin G (IgG) excretion.
In postmeonasal women with arterial hypertension taking losartan at a dose of 50 mg/day for 4 weeks, no effect of therapy on renal and systemic prostaglandin levels was detected.
Lozartan has no effect on autonomic reflexes and no lasting effect on plasma norepinephrine levels.
In patients with arterial hypertension, losartan in doses up to 150 mg daily does not cause clinically significant changes in triglyceride, total cholesterol and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol concentrations. At the same doses, losartan has no effect on fasting blood glucose concentration.
Lozartan has been shown to decrease serum uric acid concentrations (typically less than 0.4 mg/dL) that persist during long-term therapy. In controlled clinical trials involving patients with arterial hypertension, there have been no cases of drug withdrawal due to an increase in serum creatinine or potassium.
Indications
Indications
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
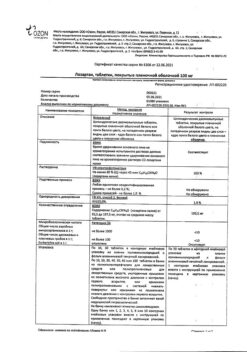
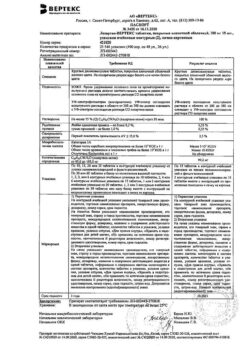
Composition
Composition
1 tablet contains:
Active ingredient:
losartan potassium 12.5 mg;
Associates:
MCC;
mannitol;
croscarmellose sodium;
povidone 30;
magnesium stearate;
hypromellose;
titanium dioxide;
t talc;
propylene glycol
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Lozartan is taken orally, in adults, regardless of meals, once daily.
In arterial hypertension – 50 mg, if necessary, the dose may be gradually increased (in some cases up to a maximum daily dose of 100 mg).
In chronic heart failure – 12.5 mg with gradual increase in 2 steps (after 1 week to 25 mg and after another 1 week to 50 mg) to the usual maintenance dose of 50 mg.
Interaction
Interaction
It enhances (mutually) the effect of other hypotensive drugs (diuretics, beta-adrenoblockers, sympatholytics).
It increases the risk of hyperkalemia when combined with potassium-saving diuretics and K+ preparations.
In patients with dehydration (prior treatment with high doses of diuretics), symptomatic hypotension may occur.
No clinically significant interaction with hydrochlorothiazide, digoxin, indirect anticoagulants, cimetidine, phenobarbital was noted.
May be administered with other hypotensive drugs.
Side effects
Side effects
Nervous system and sensory organs: â¥1% – dizziness, asthenia/fatigue, headache, insomnia;
Respiratory system: â¥1% – nasal congestion, cough, upper respiratory tract infections (elevated body temperature, sore throat, etc.), sinusopathy, sinusitis, pharyngitis;
Gastrointestinal system disorders: â¥1% – nausea, diarrhea, dyspeptic phenomena, abdominal pain;
Motor system disorders: â¥1% – cramps, myalgia, pain in the back, chest, legs;
Cardiovascular system and blood (hematopoiesis, hemostasis):
Side of the genitourinary system:
Side of the skin:
Allergic reactions:
Others: â¥1% – hyperkalemia;
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: decreased BP, changes in HR (tachycardia or bradycardia due to excitation of n.vagus).
Treatment: forced diuresis, symptomatic therapy; hemodialysis is ineffective.
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
| Conditions of storage | In a light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Vertex, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Vertex |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Lozartan 12.5mg, 30 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.