No products in the cart.
Losartan, 50 mg 90 pcs
€11.17 €9.77
Description
Lozartan is an oral specific angiotensin II receptor antagonist (type AT1). Angiotensin II selectively binds to AT1 receptors located in many tissues (vascular smooth muscle tissues, adrenal glands, kidneys, and heart) and has several important biological functions including vasoconstriction and aldosterone release. Angiotensin II also stimulates smooth muscle cell overgrowth.
Lozartan and its pharmacologically active metabolite (E 3174) both in vitro and in vivo block all physiological effects of angiotensin II regardless of source or synthesis route. Losartan selectively binds to AT1 receptors; it does not bind to or block receptors for other hormones and ion channels that play an important role in the regulation of cardiovascular function. In addition, losartan does not inhibit angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), which promotes bradykinin degradation, so bradykinin-mediated side effects (such as angioedema) are quite rare.
When using losartan, the lack of negative feedback effects on renin secretion results in increased plasma renin activity. Increased renin activity leads to increased plasma angiotensin II concentration.
However, antihypertensive activity and decreased plasma aldosterone concentration persist, indicating effective blockade of angiotensin II receptors. After discontinuation of losartan, plasma renin activity and angiotensin II concentrations decreased within 3 days to baseline values observed before starting the drug.
Losartan and its active metabolite have a high affinity for angiotensin II receptors (type AT1).
The plasma concentrations of losartan and its active metabolite and the antihypertensive effect of losartan increase with increasing drug dose.
The maximum antihypertensive effect develops 3-6 weeks after initiation of the drug.
In patients with arterial hypertension, proteinuria (more than 2 g per day), without diabetes mellitus, use of the drug significantly reduces proteinuria, albumin and immunoglobulin G (IgG) excretion.
In postmenopausal women with arterial hypertension taking losartan at a dose of 50 mg/day for 4 weeks, no effect of therapy on renal and systemic prostaglandin levels was found.
Lozartan has no effect on autonomic reflexes and no lasting effect on plasma norepinephrine levels.
In patients with arterial hypertension, losartan at doses up to 150 mg daily does not cause clinically significant changes in triglyceride, total cholesterol and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol concentrations. At similar doses, losartan has no effect on fasting blood glucose concentration.
Lozartan has been shown to reduce serum uric acid concentrations (typically less than 0.4 mg/dL) that persist during long-term therapy. In controlled clinical trials involving patients with arterial hypertension, no cases of drug withdrawal due to an increase in serum creatinine or potassium were noted.
Indications
Indications
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
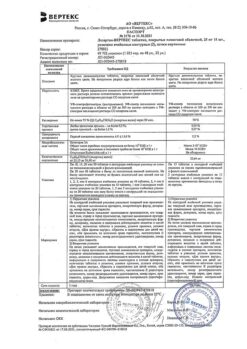
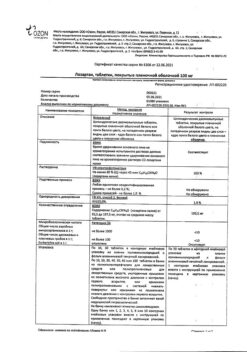
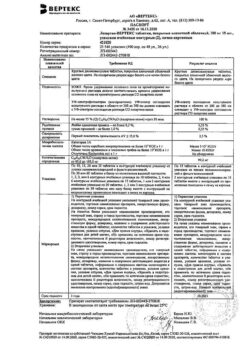
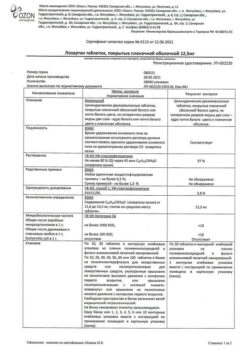
One tablet contains:
active ingredient:
losartan potassium – 50,000 mg;
excipients:
Lactose monohydrate – 57,500 mg,
microcrystalline cellulose – 20,000 mg,
croscarmellose sodium – 5,600 mg,
povidone (polyvinylpyrrolidone low molecular weight) – 4,500 mg,
silicon dioxide colloid – 1,000 mg,
magnesium stearate – 1,400 mg;
coating:
[hypromellose – 2,400 mg, talc – 0,800 mg, titanium dioxide – 0,440 mg, macrogol 4000 (polyethylene glycol 4000) – 0,360 mg] or [dry film coating mixture containing hypromellose (60%), talc (20%), titanium dioxide (11%), macrogol 4000 (polyethylene glycol 4000) (9%)] – 4,000 mg.
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Ingestion, regardless of meals.
The drug can be taken both as monotherapy and in combination with other hypotensive drugs.
Arterial hypertension
The standard starting and maintenance dose for most patients is 50 mg once daily. Maximum antihypertensive effect is achieved after 3-6 weeks of therapy.
In some patients the dose may be increased to a maximum daily dose of 100 mg once daily for a greater effect.
In patients with decreased circulating blood volume (e.g., when taking high-dose diuretics), the starting dose of the drug should be reduced to 25 mg once daily (see section “Special Precautions”).
There is no need to adjust the starting dose in elderly patients and in patients with renal impairment, including dialysis patients.
Patientswith hepatic impairment (less than 9 points on the Child-Pugh scale) during hemodialysis procedure and patients older than 75 years are recommended to prescribe the drug in a lower starting dose of 25 mg once daily.
Risk reduction of associated cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in patients with arterial hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy
The standard initial dose of the drug is 50 mg once daily. Subsequently, it is recommended that hydrochlorothiazide be added or the dose of Lozartan be increased to 100 mg (depending on the degree of blood pressure (BP) reduction) in one or two doses.
Kidney protection in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and proteinuria
The standard starting dose of the drug is 50 mg once daily. Subsequently, it is recommended that the dose of Lozartan be increased to 100 mg once daily, taking into account the degree of BP reduction. Losartan may be combined with other hypotensive drugs (diuretics, slow calcium channel blockers, alpha- and beta-adrenoblockers, hypotensive drugs of central action), insulin and other hypoglycemic drugs (sulfonylurea derivatives, glitazones and glucosidase inhibitors).
Chronic heart failure
The initial dose of the drug is 12.5 mg once daily. Typically, the dose is titrated at weekly intervals (i.e., 12.5 mg once daily, 25 mg once daily, 50 mg once daily) to the usual maintenance dose of 50 mg once daily, depending on individual tolerance.
Interaction
Interaction
When concomitant use with diuretics in high doses, arterial hypotension is possible.
Concomitant use with potassium preparations, potassium-saving diuretics increases the risk of hyperkalemia.
Concomitant use with indomethacin may decrease the effectiveness of losartan.
Lithium intoxication has been reported with lithium carbonate.
Concomitant use with orlistat decreases the antihypertensive effect of losartan, which may result in a significant increase in BP, development of a hypertensive crisis.
Concomitant use with rifampicin increases the clearance of losartan and decreases its effectiveness.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
Caution should be exercised if there is arterial hypotension, decreased RBC, impaired water-electrolyte balance, bilateral renal artery stenosis or renal artery stenosis of the single kidney, renal/hepatic insufficiency.
Patients who have fluid and/or sodium deficiencies should have their water-electrolyte disturbances corrected or use a lower initial dose before starting treatment.
In patients who are dehydrated (e.g., treated with high-dose diuretics), symptomatic arterial hypotension may occur at the start of treatment with losartan.
In patients with impaired renal function, the dose of losartan may need to be reduced.
In patients with a history of liver disease, losartan should be used in low doses. In cirrhosis, plasma concentrations of losartan are significantly increased.
By treatment, blood potassium levels should be monitored regularly, especially in elderly patients with impaired renal function.
The concomitant use of losartan with potassium-saving diuretics should be avoided.
The safety and effectiveness of losartan in children have not been established.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Cautions
Liver failure (less than 9 points by Child-Pugh), arterial hypotension, reduced circulating blood volume (CBC), impaired water-electrolyte balance, hyperkalemia, bilateral renal artery stenosis or artery stenosis of the single kidney, renal failure, conditions after renal transplantation, aortic and mitral stenosis, obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, history of angioneurotic edema, severe heart failure (NYHA functional class IV), coronary heart disease, heart failure with life-threatening arrhythmias, cerebrovascular disease, primary aldosteronism, heart failure with concomitant severe renal failure.
Side effects
Side effects
Cardiovascular system disorders:dizziness, orthostatic hypotension.
Metabolic disorders:hyperkalemia.
Allergic reactions: angioedema (including swelling of the face, lips, pharynx and/or tongue), urticaria.
Digestive system disorders:diarrhea, increased ALT activity.
CNS side:headache.
Dermatological reactions: itching.
Others:renal dysfunction, myalgia.
Overdose
Overdose
There is limited information about overdose of the drug.
The most likely symptoms
A marked decrease in BP and tachycardia; bradycardia may occur due to parasympathetic (vagus) stimulation.
Treatment
Forced diuresis, symptomatic therapy.
Neither losartan nor its active metabolite is excreted by hemodialysis.
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
| Manufacturer | Vertex, Russia |
|---|---|
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Vertex |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Losartan, 50 mg 90 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.