No products in the cart.
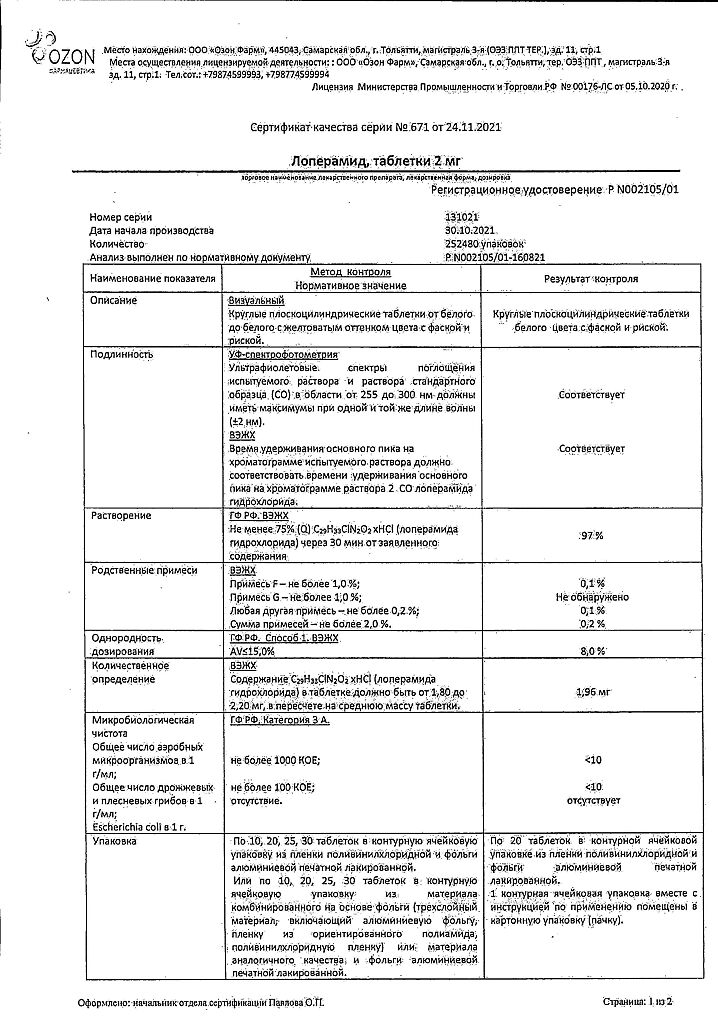
Loperamide, tablets 2 mg 20 pcs
€1.12 €1.02
Description
Loperamide interacts with opiate receptors located in the ring and longitudinal muscles of the intestinal wall and inhibits the release of prostaglandins and acetylcholine. Loperamide inhibits intestinal peristalsis and increases the passage time of intestinal contents. Loperamide increases the tone of the anal sphincter and helps to reduce the urge to defecation and to retain feces.
Loperamide inhibits exit of electrolytes and fluids into the intestinal lumen or/and stimulates their absorption from the intestine. In high doses, loperamide may reduce the formation of hydrochloric acid in the stomach. The action of loperamide develops quickly and lasts 4-6 hours.
There have been no cases of drug dependence or tolerance after loperamide administration. But morphine-like dependence has been observed in monkeys when using high doses of loperamide.
The gastrointestinal tract is poorly absorbed (approximately 40% of the dose). Due to the high degree of biotransformation during the “first passage” through the liver and the high affinity of the drug to the intestinal wall receptors, the unchanged content of loperamide after using 2 mg of the drug is less than 2 ng/ml.
The maximum concentration in the blood is reached 2.5 hours after taking the solution and 5 hours after taking the capsules. Loperamide binds 97% to proteins. The elimination half-life is 9.1-14.4 hours (on average about 10.8 hours). Loperamide is metabolized in the liver, mainly excreted as metabolites in the bile and feces, partially excreted in the urine. In a study in rats (duration 1.5 years), no carcinogenic effects of loperamide were found when doses exceeding the MRDH up to 133 times were used.
Loperamide mutagenicity studies have not been performed. Reproduction studies in rats have found that loperamide can cause decreased fertility in males and infertility in females when using high doses of the drug (150-200 times the MRDH).
In reproduction studies in rabbits and rats, it has been shown that when doses of loperamide not more than 30 times the MRDH are used, the drug is not harmful to offspring and has no teratogenic effects. It is not known whether loperamide passes into breast milk. In a study of post- and prenatal development of rat offspring, reduced offspring survival was observed when 40 mg/kg loperamide was used in lactating females.
Indications
Indications
Symptomatic therapy of chronic and acute diarrhea due to changes in the qualitative composition of food and diet, disorders of absorption and metabolism, as well as emotional, allergic, radiation, drug origin; in diarrhea of infectious origin, as an adjuvant; ileostomy (to reduce the volume and frequency of stool, to make its consistency dense).
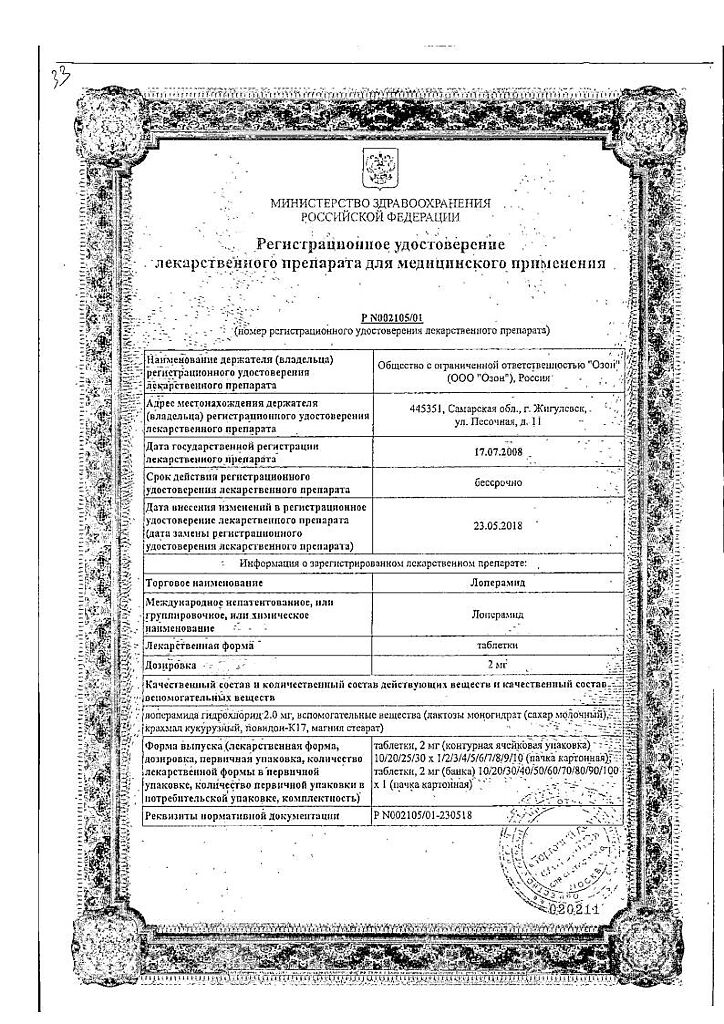
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient:
loperamide hydrochloride
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Loperamide is taken orally (regardless of meals; lingual tablet is placed on the tongue, after a few seconds it disintegrates, after which, without drinking water, it is swallowed with saliva; capsules are taken with water, without chewing). The dosing regimen depends on the indication. Acute diarrhea, adults: 4 mg – initial dose, then 2 mg after each shapeless stool, 16 mg – maximum daily dose; chronic diarrhea, adults: 4 mg/day. In absence of stool for more than 12 hours or normalization of stool consistency, therapy should be discontinued. In children 2-12 years old it is prescribed under the supervision of a physician, depending on age and body weight.
If during acute diarrhea within 2 days constipation, partial bowel obstruction, abdominal bloating develops or no clinical improvement is observed, loperamide should be stopped. In chronic diarrhea, loperamide may only be used if prescribed and supervised by a physician. Caution should be exercised when using loperamide in young children because of the high sensitivity to the opiate-like properties of loperamide – the effect on the central nervous system. During therapy of diarrhea (especially in children) it is necessary to compensate the loss of electrolytes and fluids.
Dehydration of the body may cause a change in response to loperamide. Caution should be used with loperamide in elderly patients (because variability in response to loperamide and concealment of dehydration symptoms are possible).
In patients with hepatic impairment, close monitoring for signs of toxic damage to the central nervous system should be performed (due to slowed metabolism of loperamide).
In patients with traveler’s diarrhea the decrease of intestinal motility caused by loperamide may cause prolonged temperature increase due to inhibition of excretion of microorganisms (Salmonella, Shigella, some strains of Escherichia coli and others) and their penetration into the intestinal mucosa. During therapy with loperamide, extreme caution should be exercised when driving vehicles or working with machinery.
Interaction
Interaction
Co-use of loperamide with opioid analgesics may increase the possibility of severe constipation. Co-use of loperamide and colestyramine may decrease the effectiveness of loperamide. Co-use of loperamide with ritonavir, co-trimoxazole increases the bioavailability of loperamide.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity, diverticulosis, intestinal obstruction, pseudomembranous colitis caused by taking broad-spectrum antibiotics; acute ulcerative colitis, other conditions in which intestinal peristalsis cannot be suppressed; acute dysentery (especially if blood is in the stool and accompanied by hyperthermia) and other gastrointestinal infections (caused by, among others, Shigella spp., Salmonella spp. and Campylobacter spp.); under 6 years of age.
Side effects
Side effects
Digestive system: bloating, constipation, intestinal colic, abdominal discomfort or pain, nausea, dry mouth, vomiting, intestinal obstruction, additionally for the lozenge tablets: tingling or burning sensation of the tongue that occurs immediately after using the tablets;
Nervous system: Drowsiness, fatigue, dizziness;
Allergic reactions: urticaria, skin rash, very rare – bullous rash, including toxic epidermal necrolysis; anaphylactic shock;
Other: urinary retention.
Overdose
Overdose
In case of loperamide overdose the following occurs: intestinal obstruction, central nervous system depression (drowsiness, miosis, stupor, muscle hypertonus, respiratory depression, movement coordination disorders).
Therapy: if necessary use of antidote – naloxone. Given that the duration of effect of loperamide is longer than that of naloxone, reuse of naloxone is possible. Also a thorough and prolonged (at least 1 day) observation of the patient and symptomatic treatment, gastric lavage, intake of activated charcoal, artificial lung ventilation (if necessary) is necessary.
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. |
| Manufacturer | Ozon, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Ozon |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Loperamide, tablets 2 mg 20 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.