No products in the cart.
Levofloxacin-Vertex, 500 mg 5 pcs
€9.72 €8.00
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Antimicrobial, fluoroquinolone
Pharmacological action
Indications
Indications
Infectious and inflammatory diseases caused by microorganisms sensitive to levofloxacin:
– lower respiratory tract infections (exacerbations of chronic bronchitis, community-acquired pneumonia);
– acute maxillary sinusitis;
– uncomplicated urinary tract infections;
– complicated urinary tract infections (including acute pyelonephritis);
– infections of the skin and soft tissues (festering atheromas, abscess, boils);
– chronic bacterial prostatitis;
– intra-abdominal infection;
– complex therapy of drug-resistant forms of tuberculosis.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Antimicrobial agent, fluoroquinolone
Pharmacological action
Special instructions
Special instructions
The drug should be used at least 2 hours before or 2 hours after taking iron salts, zinc, antacids and sucralfate.
During treatment with the drug, it is necessary to avoid solar and artificial UV irradiation to avoid damage to the skin (photosensitization).
If signs of tendonitis, pseudomembranous colitis, or allergic reactions appear, the drug is immediately discontinued.
It should be borne in mind that in patients with a history of brain damage (stroke, severe trauma), seizures may develop; with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, there is a risk of hemolysis.
When levofloxacin and warfarin are used simultaneously, careful monitoring of prothrombin time and other coagulation parameters is necessary.
Careful monitoring of plasma glucose concentrations is recommended when using the drug simultaneously with hypoglycemic drugs.
Since levofloxacin is excreted mainly by the kidneys, patients with impaired renal function require mandatory monitoring of renal function, as well as adjustment of the dosage regimen. Cases of QT prolongation have been reported in patients receiving fluoroquinolones, including levofloxacin. When using fluoroquinolones, including levofloxacin, caution should be exercised in patients with known risk factors for QT interval prolongation: advanced age; electrolyte imbalance (hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia); congenital long QT syndrome; heart disease (heart failure, myocardial infarction, bradycardia); simultaneous use of medications that can prolong the QT interval.
Sensory and sensorimotor peripheral neuropathy, which may have a rapid onset, has been reported in patients receiving fluoroquinolones, including levofloxacin. If the patient develops symptoms of neuropathy, levofloxacin should be discontinued. This minimizes the possible risk of developing irreversible changes.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Levofloxacin
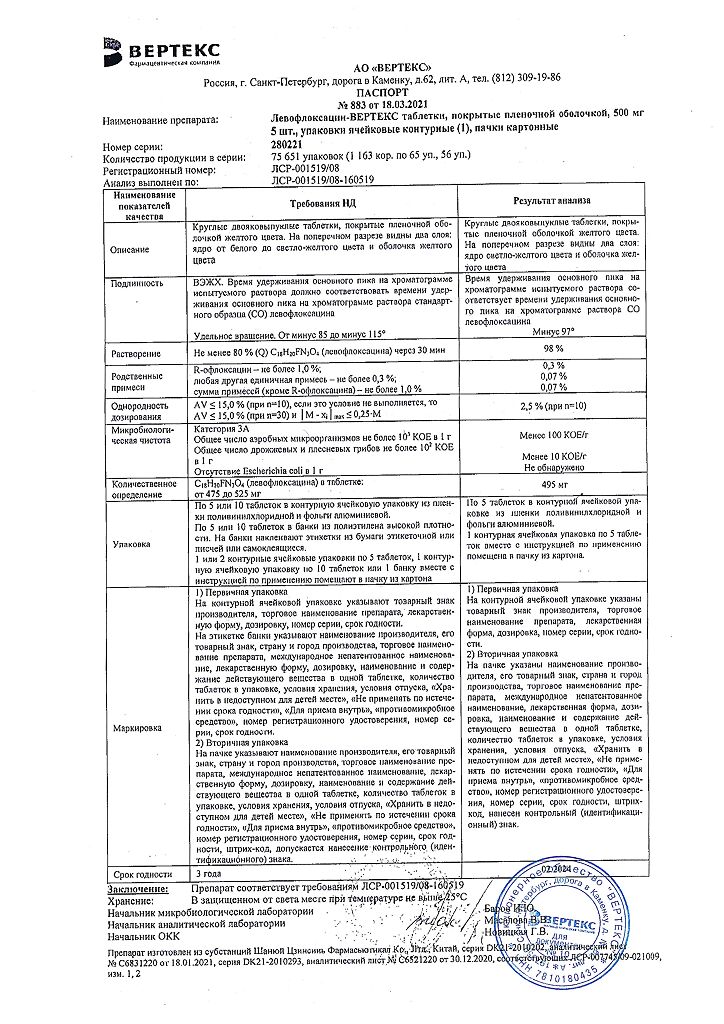
Composition
Composition
1 film-coated tablet contains
Active substance:
levofloxacin hemihydrate in terms of levofloxacin – 500.00 mg
Excipients (core):
microcrystalline cellulose – 60.00 mg,
sodium carboxymethyl starch – 35.00 mg,
povidone (polyvinylpyrrolidone) – 30.00 mg,
magnesium stearate – 10.00 mg,
croscarmellose sodium – 16.54 mg,
colloidal silicon dioxide – 6.00 mg.
Excipients (shell):
Opadry White – 30.00 mg, incl. polyvinyl alcohol – 14.070 mg, macrogol 3350 – 7.080 mg, talc – 5.220 mg, titanium dioxide – 3.630 mg.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to levofloxacin and other fluoroquinolones, epilepsy, tendon damage during previous treatment with quinolones, pregnancy, breastfeeding, childhood and adolescence (up to 18 years).
With caution
Old age (high probability of concomitant decline in renal function), deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the digestive system: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea (including blood), indigestion, loss of appetite, abdominal pain, pseudomembranous colitis, increased activity of “liver” transaminases, hyperbilirubinemia, hepatitis, dysbacteriosis.
From the cardiovascular system: decreased blood pressure, vascular collapse, tachycardia, increased Q-T interval on the cardiogram, atrial fibrillation.
Metabolism: hypoglycemia (increased appetite, increased sweating, trembling, nervousness), hyperglycemia (dry mouth, thirst, increased urination, fatigue, blurred vision, dry or itchy skin, arrhythmia).
From the nervous system: headache, dizziness, weakness, drowsiness, insomnia, anxiety, paresthesia in the hands, fear, hallucinations, confusion, depression, movement disorders, convulsions, peripheral sensory neuropathy, peripheral sensorimotor neuropathy, mental disorders with behavioral disorders with self-harm, including suicidal thoughts and suicide attempts, extrapyramidal disorders, agitation (excitement), nightmares.
From the senses: disturbances of vision, hearing, smell, taste and tactile sensitivity, ringing in the ears.
From the musculoskeletal system: arthralgia, muscle weakness, myalgia, tendon rupture, tendinitis, rhabdomyolysis.
From the urinary system: hypercreatininemia, interstitial nephritis, acute renal failure.
From the hematopoietic organs: eosinophilia, hemolytic anemia, leukopenia, neutropenia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, hemorrhages.
Allergic reactions: itching and redness of the skin, swelling of the skin and mucous membranes, urticaria, malignant exudative erythema (Stevens-Johnson syndrome), toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell’s syndrome), bronchospasm, anaphylactic shock, allergic pneumonitis, vasculitis.
Other: asthenia, exacerbation of porphyria, photosensitivity, persistent fever, leukocytoclastic vasculitis, development of superinfection.
Interaction
Interaction
Quinolones may enhance the ability of drugs, including theophylline, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to lower the seizure threshold. When taken simultaneously with fenbufen, higher concentrations of levofloxacin are observed than with motor therapy.
The effect of levofloxacin is reduced by drugs that inhibit intestinal motility, sucralfate, magnesium- or aluminum-containing antacids, iron and zinc salts.
Taking glucocorticosteroids increases the risk of tendon rupture.
Levofloxacin enhances the anticoagulant activity of warfarin.
The elimination (renal clearance) of levofloxacin is slightly slowed down by cimetidine and probenecid due to the possible blocking of tubular secretion of levofloxacin in the kidneys. It should be noted that this interaction is of clinical significance, primarily for patients with impaired renal function.
Levofloxacin increases the half-life of cyclosporine.
The simultaneous use of levofloxacin and hypoglycemic agents leads to changes in the concentration of glucose in the blood plasma (hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia).
When used simultaneously with drugs that prolong the Q-T interval (class IA and III antiarrhythmics, tricyclic and tetracyclic antidepressants, neuroleptics, macrolides, antifungals, imidazole derivatives, some antihistamines, including astemizole, terfenadine, ebastine), the Q-T interval may be prolonged.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms:
confusion, dizziness, disturbances of consciousness, convulsions, possible nausea, vomiting and erosive lesions of the mucous membranes. Studies have shown that when levofloxacin is used in doses exceeding the average therapeutic dose, the QT interval may prolong.
Treatment:
If necessary, carry out symptomatic therapy. Levofloxacin is not eliminated by hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis and continuous peritoneal dialysis. There is no specific antidote.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
Store the drug in a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Vertex, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store the drug in a dry place protected from light at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. Keep out of reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Vertex, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Vertex |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Levofloxacin-Vertex, 500 mg 5 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.