No products in the cart.
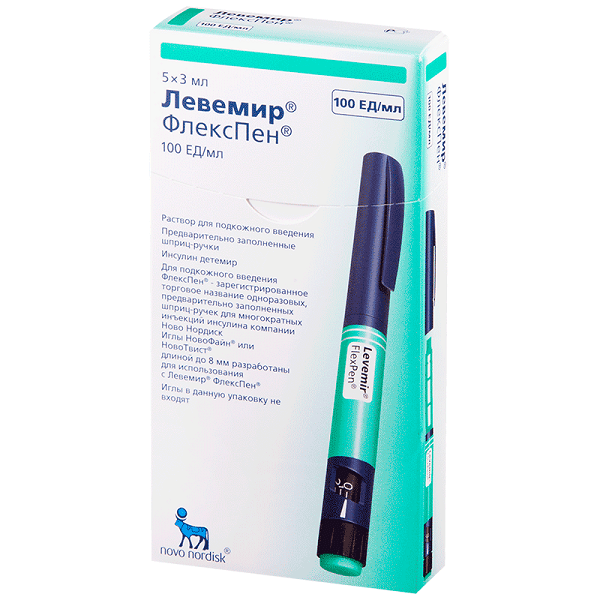
Levemir FlexPen, 100 me/ml 3 ml cartridges in syringe pens 5 pcs
€70.99 €61.53
Description
The drug Levemir® FlexPen® is produced by recombinant DNA biotechnology using Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain. It is a soluble analog of basal human prolonged-acting insulin with a flat action profile.
The profile of action of Levemir® FlexPen® is much less variable than isophan insulin and insulin glargine.
The prolonged action of Levemir® FlexPen® is due to the marked self-association of insulin detemir molecules at the injection site and the binding of drug molecules to albumin via a side-chain fatty acid bond. Insulin detemir is slower to reach peripheral target tissues than isophan insulin. These combined delayed-distribution mechanisms provide a more reproducible absorption and action profile of Levemir® FlexPen® compared to isophane insulin.
For doses of 0.2-0.4 IU/kg, 50% of the drug’s maximum effect occurs between 3 and 4 and 14 hours after administration. The duration of action is up to 24 hours, depending on the dose, which provides the possibility of single and double daily administration. When administered twice daily, Css of the drug is achieved after administering 2-3 doses of the drug.
After p/q administration, a pharmacodynamic response proportional to the dose administered was observed (maximal effect, duration of action, overall effect).
Long-term studies have demonstrated low day-to-day variability in fasting plasma glucose concentrations when treating patients with Levemir® FlexPen® compared to isophane insulin.
In long-term studies in patients with type 2 diabetes who received basal insulin therapy in combination with oral hypoglycemic agents, it has been demonstrated that glycemic control (as measured by glycosylated hemoglobin – HbA1C) on therapy with Levemir® FlexPen® was comparable to that on treatment with isophane insulin and insulin glargine, with a low increase in body weight.
In studies, use of combination therapy with Levemir® FlexPen® and oral hypoglycemic agents resulted in a 61-65% reduction in the risk of mild nocturnal hypoglycemia compared with isophane insulin.
An open randomized clinical trial was conducted involving patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who did not achieve glycemic targets on therapy with oral hypoglycemic agents. The study began with a 12-week preparatory period, during which patients received liraglutide combination therapy with metformin, during which 61% of patients reached their HbA1c ® FlexPen® at a daily single dose; patients in the other continued to receive liraglutide in combination with metformin for the next 52 weeks.
While this period, the treatment group that received in addition to liraglutide therapy with metformin a daily single injection of Levemir®FlexPen®, demonstrated a further decrease in HbA1c from an initial 7.6% to 7.1% at the end of the 52-week period, with no episodes of severe hypoglycemia. When a dose of Levemir® FlexPen® was added to liraglutide therapy, the advantage of the latter in terms of statistically significant weight reduction in patients persisted.
In long-term studies (≥6 months) involving patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus, fasting plasma glucose concentrations were better on treatment with Levemir® FlexPen® compared to the use of isofan-insulin in base-bolus therapy. Glycemic control (HbA1c) on therapy with Levemir®FlexPen® was comparable to that of isofan-insulin treatment, with a lower risk of nocturnal hypoglycemia and no increase in body weight on Levemir® FlexPen®.
The results of clinical studies evaluating the basal bolus mode of insulin therapy, indicate a comparable incidence of hypoglycemia in general on therapy with Levemir® FlexPen® and isophane insulin. Analysis of the development of nocturnal hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes demonstrated a significantly lower incidence of mild nocturnal hypoglycemia with Levemir® FlexPen®(when the patient is able to resolve hypoglycemia independently and hypoglycemia is confirmed by measuring capillary blood glucose concentration less than 2.8 mmol/L or plasma glucose less than 3.1 mmol/L) compared to that with isofan-insulin; and no differences were found between the two studied drugs in the frequency of occurrence of mild nocturnal hypoglycemic episodes in type 2 diabetic patients.
The nocturnal glycemic profile is flatter and flatter with Levemir® FlexPen® compared to isophane insulin, which is reflected in a lower risk of nocturnal hypoglycemia.
When using Levemir® FlexPen® antibody production was observed. However, this fact has no effect on glycemic control.
Pregnancy
A randomized controlled clinical trial including 310 pregnant women with type 1 diabetes evaluated the efficacy and safety of Levemir® FlexPen® in a baseline-bolus regimen of therapy (152 patients), compared with isophane insulin in combination with insulin aspart (158 patients) used as prandial insulin.
The results of the study showed that patients who received Levemir® FlexPen®, a similar decrease in the HbA1c index at 36 weeks of pregnancy was observed compared to the group receiving isofan-insulin. The group of patients treated with Levemir®FlexPen® and the group treated with isofan-insulin showed similar overall HbA1c profile throughout pregnancy.
Target HbA1c ® FlexPen® and 32% of patients in the isophane-insulin therapy group.
The fasting glucose concentration at gestational ages 24 and 36 weeks was statistically significantly lower in the group of women who received Levemir® FlexPen® compared to the group receiving isofan-insulin therapy.
There were no statistically significant differences between patients treated with Levemir® FlexPen® and isophan-insulin in the incidence of hypoglycemic episodes throughout pregnancy.
The two groups of pregnant women treated with Levemir® FlexPen® and isophan-insulin showed similar results on the frequency of their adverse events throughout the pregnancy; However, the rates of serious adverse events were found to be quantitatively higher in patients throughout pregnancy (61 (40%) versus 49 (31%), in children during fetal development and after birth (36 (24%) versus 32 (20%)) in the Levemir treatment group.sup>® FlexPen® compared to the isophane-insulin therapy group.
The number of live-born children from mothers who became pregnant after they were randomized to therapy groups to receive treatment with one of the test drugs was 50 (83%) in the Levemir treatment group® FlexPen® and 55 (89%) in the isophane-insulin treatment group. The number of children born with congenital malformations was 4 (5%) in the Levemir® FlexPen® treatment group and 11 (7%) in the isophane-insulin treatment group. Of these, serious congenital malformations were noted in 3 (4%) children in the Levemir® FlexPen® treatment group and 3 (2%) in the isophane-insulin treatment group.
Children and adolescents
The efficacy and safety of Levemir® FlexPen® in children was studied in two controlled 12-month clinical studies involving adolescents and children over 2 years of age with type 1 diabetes (694 patients in total); one of these studies included a total of 82 children with type 1 diabetes between the ages of two and five years. The results of these studies demonstrated that glycemic control (HbA1c) on therapy with Levemir®FlexPen® was comparable to that of isophane insulin when given as basal bolus therapy. In addition, a lower risk of nocturnal hypoglycemia (based on patients’ self-measured plasma glucose concentrations) and no weight gain (standard deviation for body weight adjusted for patient gender and age) was noted during treatment with Levemir® FlexPen®, compared to the use of isophane insulin. One of the clinical studies was extended for an additional 12 months (a total of 24 months of clinical data were obtained) to provide a more complete database to evaluate patient antibody formation during long-term treatment with Levemir® FlexPen®.
The results obtained in the study indicate that during the first year of treatment with Levemir® FlexPen® there was an increase in the level of antibodies to insulin detemir; However, by the end of the second year of treatment, the level of antibodies to Levemir® FlexPen® decreased in patients to a level slightly higher than the baseline level at the start of therapy with Levemir® FlexPen®. Thus, it is proved that antibody formation in diabetic patients against the background of treatment with Levemir®FlexPen® has no adverse effect on the level of glycemic control and the dose of insulin detemir.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
The Cmax in serum is reached 6-8 h after administration. With twice daily administration, Css is reached after 2-3 administrations.
Interindividual variability in absorption is lower with Levemir® FlexPen® compared to other basal insulin preparations. No clinically significant intersex differences in the pharmacokinetics of Levemir® FlexPen® were found.
Distribution
The mean Vd of Levemir® FlexPen® (approximately 0.1 L/kg) indicates that a high proportion of insulin detemir is circulating in the blood.
Metabolism
The inactivation of Levemir® FlexPen is similar to that of human insulin preparations; all metabolites produced are inactive.
The results of in vitro and in vivo protein binding studies show no clinically significant interactions between insulin detemir and fatty acids or other protein-binding drugs.
Elimination
The terminal T1/2 after p/k injection is determined by the degree of absorption from the subcutaneous tissue and is 5-7 h depending on the dose.
Linearity
When administered p/k, plasma concentrations were proportional to the dose administered (Cmax, degree of absorption). No pharmacokinetic or pharmacodynamic interaction between liraglutide and Levemir® FlexPen® was detected., in equilibrium, when Levemir® FlexPen® was administered simultaneously to patients with type 2 diabetes at a single dose of 0.5 U/kg and liraglutide at a dose of 1.8 mg.
Particular patient groups
The pharmacokinetic properties of Levemir® FlexPen® were studied in children (6-12 years old) and adolescents (13-17 years old) and compared with pharmacokinetic properties in adults with type 1 diabetes. No differences were found.
There were no clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of Levemir® FlexPen® between elderly and younger patients or between patients with renal and hepatic impairment and healthy patients.
Preclinical safety data
In vitro studies in human cell lines, including insulin and IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor) receptor binding studies, have shown that insulin detemir has low affinity for both receptors and little effect on cell growth compared to human insulin. Preclinical data based on routine studies of pharmacological safety, repeated-dose toxicity, genotoxicity, carcinogenic potential, and toxic effects on reproduction showed no danger to humans.
Indications
Indications
Diabetes mellitus in adults, adolescents and children over 2 years of age.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Levemir® FlexPen® is produced by recombinant DNA biotechnology using the Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain. It is a soluble long-acting analogue of basal human insulin with a flat action profile.
The action profile of Levemir® FlexPen® is significantly less variable compared to isophane insulin and insulin glargine.
The prolonged effect of Levemir® FlexPen® is due to the pronounced self-association of insulin detemir molecules at the injection site and the binding of drug molecules to albumin through connection with the side fatty acid chain. Insulin detemir, compared to isophane insulin, reaches peripheral target tissues more slowly. These combined delayed distribution mechanisms provide a more reproducible absorption and action profile of Levemir® FlexPen® compared to isophane insulin.
For doses of 0.2–0.4 U/kg, 50% of the maximum effect of the drug occurs in the range from 3–4 to 14 hours after administration. The duration of action is up to 24 hours, depending on the dose, which allows for single or twice daily administration. With double administration, Css of the drug is achieved after administration of 2–3 doses of the drug.
After subcutaneous administration, a pharmacodynamic response proportional to the administered dose was observed (maximum effect, duration of action, overall effect).
Long-term studies have demonstrated low day-to-day variability in fasting plasma glucose concentrations when patients are treated with Levemir® FlexPen® as opposed to isophane insulin.
In long-term studies in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with basal insulin in combination with oral hypoglycemic drugs, it was demonstrated that glycemic control (measured by glycosylated hemoglobin – HbA1C) during treatment with Levemir® FlexPen® was comparable to that with treatment with isophane insulin and insulin glargine, while low body weight gain was observed.
In studies, the use of combination therapy with Levemir® FlexPen® and oral hypoglycemic drugs led to a reduction in the risk of mild nocturnal hypoglycemia by 61–65% compared with the use of isophane insulin.
An open-label, randomized clinical trial was conducted in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who did not achieve glycemic targets while receiving oral hypoglycemic agents. The study began with a 12-week run-in period during which patients received combination therapy with liraglutide plus metformin, during which 61% of patients achieved HbA1c ® FlexPen ® in a single daily dose; Another patient continued to receive liraglutide in combination with metformin for a further 52 weeks.
During this period, the treatment group receiving a daily single injection of Levemir® FlexPen® in addition to liraglutide plus metformin therapy demonstrated a further reduction in HbA1c from baseline 7.6% to 7.1% at the end of the 52-week period, with no episodes of severe hypoglycemia. When adding a dose of Levemir® FlexPen® to liraglutide therapy, the advantage of the latter in terms of statistically significant reduction in body weight in patients was maintained.
In long-term studies (≥6 months) in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus, fasting plasma glucose concentrations were better with Levemir® FlexPen® compared with isophane insulin in basal-bolus therapy. Glycemic control (HbA1c) during treatment with Levemir® FlexPen® was comparable to that during treatment with isophane insulin, with a lower risk of nocturnal hypoglycemia and no weight gain during use of Levemir® FlexPen®.
The results of clinical studies evaluating the basal-bolus insulin therapy regimen indicate a comparable incidence of hypoglycemia in general during therapy with Levemir® FlexPen® and isophane insulin. An analysis of the development of nocturnal hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus demonstrated a significantly lower incidence of mild nocturnal hypoglycemia with the use of the drug Levemir® FlexPen® (when the patient can independently eliminate the state of hypoglycemia, and hypoglycemia is confirmed by measuring the concentration of glucose in capillary blood – less than 2.8 mmol/l or glucose in the blood plasma – less than 3.1 mmol/l), compared with that with the use of isophane insulin; however, there were no differences between the two study drugs in the incidence of episodes of mild nocturnal hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
The nocturnal glycemic profile is flatter and more even with Levemir® FlexPen® compared to isophane insulin, which is reflected in a lower risk of developing nocturnal hypoglycemia.
When using the drug Levemir® FlexPen®, the production of antibodies was observed. However, this fact has no effect on glycemic control.
Pregnancy
A randomized controlled clinical trial involving 310 pregnant women with type 1 diabetes mellitus assessed the efficacy and safety of Levemir® FlexPen® in a basal-bolus regimen (152 patients) compared with isophane insulin in combination with insulin aspart (158 patients) used as prandial insulin.
The results of the study showed that patients receiving Levemir® FlexPen® had a similar decrease in HbA1c at the 36th week of pregnancy compared to the group receiving isophane insulin. The group of patients receiving therapy with Levemir® FlexPen® and the group receiving therapy with isophane insulin showed similarities in the general HbA1c profile throughout the entire pregnancy period.
Target level of HbA1c ® FlexPen ® and in 32% of patients in the isophane insulin therapy group.
Fasting glucose concentrations at 24 and 36 weeks of pregnancy were statistically significantly lower in the group of women who took Levemir® FlexPen® compared to the group who received isophane insulin therapy.
During the entire period of pregnancy, no statistically significant differences were found between patients receiving Levemir® FlexPen® and isophane insulin in the frequency of hypoglycemia episodes.
Both groups of pregnant women treated with Levemir® FlexPen® and isophane insulin showed similar results in terms of the incidence of adverse events throughout their pregnancy; however, it was found that in quantitative terms, the incidence of serious adverse events in patients throughout pregnancy (61 (40%) versus 49 (31%), in children during intrauterine development and after birth (36 (24%) versus 32 (20%)) was higher in the Levemir® FlexPen® treatment group compared with the isophane insulin therapy group.
The number of live births to mothers who became pregnant after being randomized to treatment with one of the study drugs was 50 (83%) in the Levemir FlexPen group and 55 (89%) in the isophane insulin group. The number of children born with congenital malformations was 4 (5%) in the Levemir® FlexPen® treatment group and 11 (7%) in the isophane insulin treatment group. Of these, serious congenital malformations were noted in 3 (4%) children in the Levemir® FlexPen® treatment group and 3 (2%) in the isophane insulin treatment group.
Children and teenagers
The effectiveness and safety of Levemir® FlexPen® in children was studied in two controlled clinical studies lasting 12 months in adolescents and children over 2 years of age with type 1 diabetes mellitus (694 patients in total); one of these studies included a total of 82 children with type 1 diabetes in the age group of two to five years. The results of these studies demonstrated that glycemic control (HbA1c) during therapy with Levemir® FlexPen® was comparable to that during treatment with isophane insulin when administered in basal-bolus therapy. In addition, there was a lower risk of nocturnal hypoglycemia (based on self-measured plasma glucose concentrations) and no weight gain (standard deviation for age- and sex-adjusted body weight) with Levemir® FlexPen® compared with isophane insulin. One of the clinical studies was extended for an additional 12 months (a total of 24 months of clinical data were obtained) in order to obtain a more complete database to evaluate the formation of antibodies in patients during long-term treatment with Levemir® FlexPen®.
The results obtained during the study indicate that during the first year of treatment while taking the drug Levemir® FlexPen®, there was an increase in the level of antibodies to insulin detemir; however, by the end of the second year of treatment, the level of formation of antibodies to Levemir® FlexPen® decreased in patients to a level slightly higher than the initial level at the time of initiation of therapy with Levemir® FlexPen®. Thus, it has been proven that the formation of antibodies in patients with diabetes mellitus during treatment with Levemir® FlexPen® does not have a negative effect on the level of glycemic control and the dose of insulin detemir.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Cmax in serum is achieved 6–8 hours after administration. With a twice daily administration regimen, Css is achieved after 2–3 injections.
Intraindividual variability in absorption is lower with Levemir® FlexPen® compared to other basal insulin preparations. There were no clinically significant gender differences in the pharmacokinetics of Levemir® FlexPen®.
Distribution
The average Vd of Levemir® FlexPen® (approximately 0.1 l/kg) indicates that a high proportion of insulin detemir circulates in the blood.
Metabolism
Inactivation of Levemir® FlexPen® is similar to that of human insulin preparations; all metabolites formed are inactive.
Results from in vitro and in vivo protein binding studies indicate that there are no clinically significant interactions between insulin detemir and fatty acids or other protein-binding drugs.
Removal
Terminal T1/2 after subcutaneous injection is determined by the degree of absorption from the subcutaneous tissue and is 5–7 hours, depending on the dose.
Linearity
With subcutaneous administration, plasma concentrations were proportional to the administered dose (Cmax, degree of absorption). No pharmacokinetic or pharmacodynamic interaction was detected between liraglutide and Levemir® FlexPen®, at steady state, when patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus were simultaneously administered Levemir® FlexPen® at a single dose of 0.5 U/kg and liraglutide at a dose of 1.8 mg.
Special patient groups
The pharmacokinetic properties of Levemir® FlexPen® were studied in children (6–12 years old) and adolescents (13–17 years old) and compared with the pharmacokinetic properties in adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus. No differences were found.
There were no clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of Levemir® FlexPen® between elderly and young patients or between patients with impaired renal and hepatic function and healthy patients.
Preclinical safety data
In vitro studies in human cell lines, including binding studies with insulin and IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor) receptors, have shown that insulin detemir has low affinity for both receptors and has little effect on cell growth compared to human insulin. Preclinical data based on routine studies of pharmacological safety, repeated dose toxicity, genotoxicity, carcinogenic potential, and reproductive toxicity have not identified any hazard to humans.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Levemir® FlexPen® is a soluble basal insulin analogue with a prolonged action (up to 24 hours).
Unlike other insulin preparations, basal-bolus therapy with Levemir® FlexPen® does not lead to weight gain.
Treatment with the drug Levemir® FlexPen® provides less weight gain compared to the use of isophane insulin and insulin glargine.
The lower risk of nocturnal hypoglycemia compared to isophane insulin allows for more intensive dose titration in order to achieve the target blood glucose level in basal-bolus therapy.
Compared with other insulins, particularly isophane insulin, the lower risk of episodes of mild nocturnal hypoglycemia allows for more intensive dose titration to achieve target blood glucose when treated with Levemir® FlexPen® in combination with oral hypoglycemic drugs.
Levemir® FlexPen® provides better glycemic control (based on fasting plasma glucose concentrations) compared to the use of isophane insulin.
Before traveling for long periods of time due to jet lag, the patient should consult with their physician, as jet lag means that the patient must eat and take insulin at different times.
Insufficient dosage of the drug or discontinuation of treatment, especially in type 1 diabetes mellitus, can lead to the development of hyperglycemia or diabetic ketoacidosis. Typically, the first symptoms of hyperglycemia appear gradually, over several hours or days. These symptoms include thirst, increased urination, nausea, vomiting, drowsiness, redness and dryness of the skin, dry mouth, loss of appetite, and the smell of acetone in the exhaled air. In type 1 diabetes, untreated hyperglycemia leads to diabetic ketoacidosis and can lead to death.
Hypoglycemia can occur when the insulin dose is too high relative to insulin needs, when meals are skipped, or when unplanned intense physical activity occurs. After compensation of carbohydrate metabolism, for example, with intensified insulin therapy, patients may experience changes in their typical symptoms that are precursors of hypoglycemia, of which patients should be informed.
The usual warning symptoms may disappear with prolonged diabetes mellitus.
Concomitant diseases, especially infectious ones and those accompanied by fever, usually increase the body’s need for insulin.
Dose adjustment of the drug may also be required if the patient has concomitant diseases of the kidneys, liver or dysfunction of the adrenal glands, pituitary gland or thyroid gland.
Transferring the patient from other insulin preparations. Transferring a patient to a new type or insulin preparation from another manufacturer should occur under strict medical supervision. If the concentration, manufacturer, type, type (human, analogue of human insulin) and/or method of its production changes, dose adjustment may be required. Patients switching to treatment with Levemir® FlexPen® from another type of insulin may require a dose change compared to the doses of previously used insulin preparations.
Dose adjustments may be made at the time of the first dose or during the first few weeks or months of treatment.
Reactions at the injection site. As with treatment with other insulin drugs, reactions may develop at the injection site, which is manifested by pain, redness, urticaria, inflammation, hematomas, swelling and itching. Regularly changing the injection site in the same anatomical area may reduce symptoms or prevent the development of a reaction. The reactions usually disappear within a few days to a few weeks. In rare cases, injection site reactions require discontinuation of treatment.
Concomitant use of drugs of the thiazolidinedione group and insulin drugs. Cases of the development of chronic heart failure have been reported when treating patients with thiazolidinediones in combination with insulin drugs, especially if such patients have risk factors for the development of chronic heart failure. This fact should be taken into account when prescribing combination therapy with thiazolidinediones and insulin drugs to patients. When prescribing such combination therapy, it is necessary to conduct medical examinations of patients to identify signs and symptoms of chronic heart failure, weight gain and the presence of edema. If patients’ symptoms of heart failure worsen, treatment with thiazolidinediones should be discontinued.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery. Patients’ ability to concentrate and react quickly may be impaired due to hypoglycemia, which can be dangerous in situations where these abilities are especially necessary (for example, when driving or operating machinery). Patients should be advised to take measures to prevent the development of hypoglycemia when driving vehicles and operating machinery. This is especially important for patients with no or decreased severity of symptoms that are warning signs of developing hypoglycemia or who suffer from frequent episodes of hypoglycemia. In these cases, the advisability of driving or performing similar work should be considered.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Insulin detemir
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient:
insulin detemir 100 units;
Excipients:
glycerol;
phenol;
metacresol;
zinc acetate;
sodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate;
sodium chloride;
hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide;
water for injections;
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
When using Levemir® FlexPen® during pregnancy, it is necessary to consider how the benefits of its use outweigh the possible risks.
One randomized controlled clinical trial in pregnant women with type 1 diabetes mellitus, which examined the efficacy and safety of combination therapy with Levemir® FlexPen® with insulin aspart (152 pregnant women) compared with isophane insulin therapy in combination with insulin aspart (158 pregnant women), found no difference in the overall safety profile during pregnancy, in pregnancy outcomes or the impact on the health of the fetus and newborn (see. “Pharmacodynamics”, “Pharmacokinetics”).
Additional data on the effectiveness and safety of treatment with Levemir® FlexPen®, obtained from approximately 300 pregnant women during post-marketing use, indicate the absence of unwanted side effects of insulin detemir leading to congenital malformations and malformative or feto/neonatal toxicity.
Studies of reproductive function in animals did not reveal the toxic effect of the drug on the reproductive system (see “Pharmacodynamics”, “Pharmacokinetics”).
In general, careful monitoring of pregnant women with diabetes is necessary throughout pregnancy, as well as when planning pregnancy. The need for insulin usually decreases in the first trimester of pregnancy, then increases in the second and third trimesters. Shortly after birth, insulin requirements quickly return to pre-pregnancy levels.
It is not known whether insulin detemir is excreted in breast milk. It is assumed that insulin detemir does not affect the metabolic reactions in the body of newborns/infants during breastfeeding, since it belongs to a group of peptides that are easily broken down into amino acids in the digestive tract and absorbed by the body.
Breastfeeding women may require adjustments in insulin dosage and diet.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Increased individual sensitivity to insulin detemir or any of the components of the drug; It is not recommended to use Levemir® FlexPen® in children under 2 years of age, because Clinical studies have not been conducted in children under 2 years of age.
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the immune system: allergic reactions, potentially allergic reactions, urticaria, skin rash, skin rashes; anaphylactic reactions;
Metabolism and nutrition: hypoglycemia;
From the nervous system: peripheral neuropathy (acute painful neuropathy);
From the organ of vision: refractive errors; diabetic retinopathy;
From the skin and subcutaneous tissues: lipodystrophy;
General disorders and administration site disorders: injection site reactions; swelling;
Interaction
Interaction
There are a number of drugs that affect the need for insulin.
The hypoglycemic effect of insulin is enhanced by oral hypoglycemic drugs, MAO inhibitors, ACE inhibitors, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, non-selective beta-blockers, bromocriptine, sulfonamides, anabolic steroids, tetracyclines, clofibrate, ketoconazole, mebendazole, pyridoxine, theophylline, cyclophosphamide, fenfluramine, drugs lithium, salicylates.
The hypoglycemic effect of insulin is weakened by oral contraceptives, corticosteroids, iodine-containing thyroid hormones, somatropin, thiazide diuretics, heparin, tricyclic antidepressants, sympathomimetics, danazol, clonidine, CCB, diazoxide, morphine, phenytoin, nicotine.
Octreotide/lanreotide can either increase or decrease the body’s need for insulin.
Beta blockers may mask symptoms of hypoglycemia and delay recovery from hypoglycemia.
Alcohol can either increase or decrease the hypoglycemic effect of insulin.
Incompatibility
Some drugs, for example those containing thiol or sulfite groups, when added to Levemir® Flexpen®, can cause the destruction of insulin detemir. Levemir®Flexpen® should not be added to infusion solutions. This drug should not be mixed with other drugs.
Overdose
Overdose
There is no specific dose that causes insulin overdose, but hypoglycemia can develop gradually if the dose is too high for a particular patient.
Treatment: the patient can eliminate mild hypoglycemia himself by ingesting glucose, sugar or carbohydrate-rich foods. Therefore, patients with diabetes are recommended to constantly carry sugar, sweets, cookies or sweet fruit juice with them.
In case of severe hypoglycemia, when the patient is unconscious, 0.5 to 1 mg of glucagon should be administered IM or SC (can be administered by a trained person) or IV dextrose (glucose) solution (can only be administered by a healthcare professional). It is also necessary to administer dextrose intravenously if the patient does not regain consciousness 10–15 minutes after the administration of glucagon. After regaining consciousness, the patient is advised to eat a meal rich in carbohydrates to prevent recurrence of hypoglycemia.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a place protected from light, at a temperature of 2–8 °C (do not freeze). To protect from light, the pen syringe should be stored with the cap on. When used or carried as a spare syringe pen with the drug, it should be stored at a temperature
Shelf life
Shelf life
30 months
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Novo Nordisk, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 30 months |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store in a light-protected place at 2-8 °C (do not freeze). Keep the syringe pen with the cap on to protect it from light. Keep the syringe pen with the drug in a safe place at a temperature of 2-8 °C (do not freeze) to protect it from light. |
| Manufacturer | Novo Nordisk A/S, Denmark |
| Medication form | solution |
| Brand | Novo Nordisk A/S |
Related products
Buy Levemir FlexPen, 100 me/ml 3 ml cartridges in syringe pens 5 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.