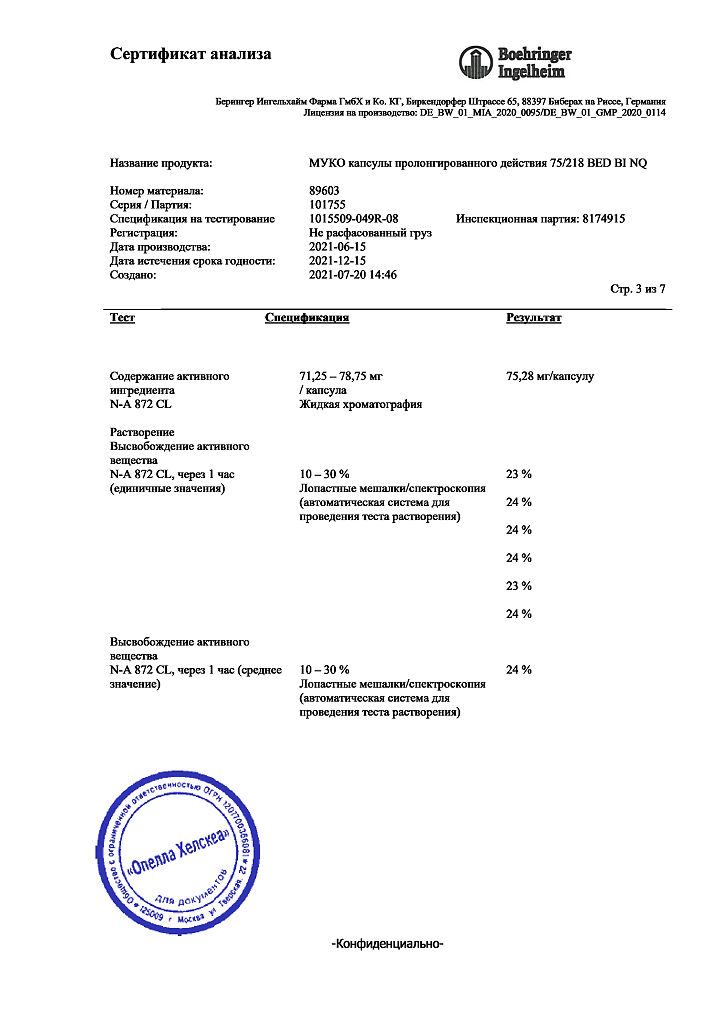
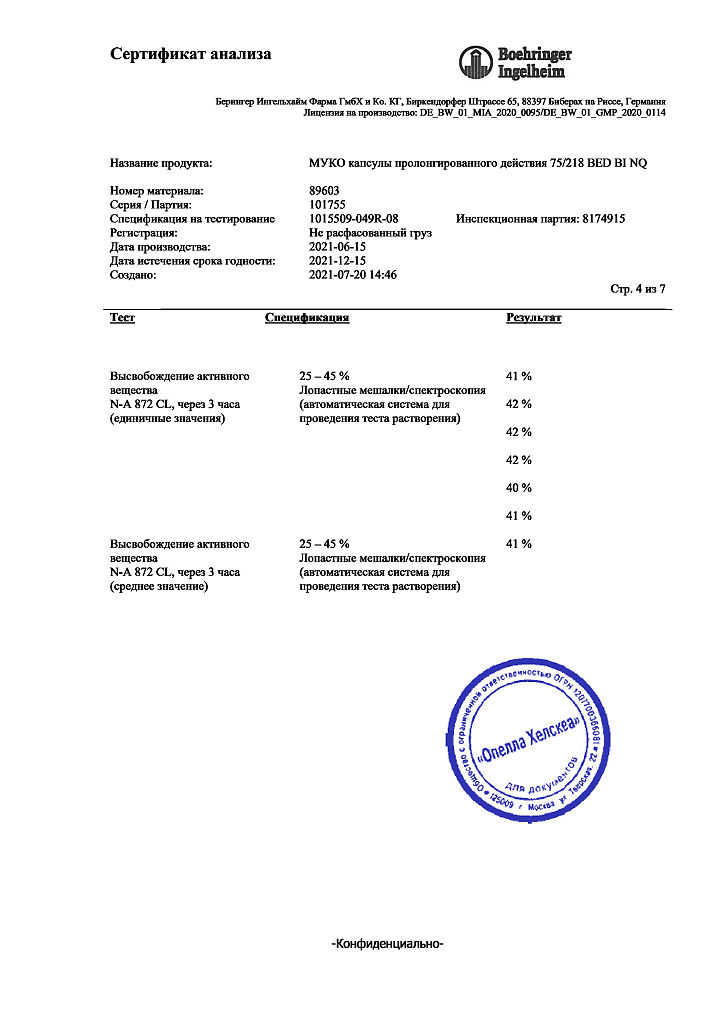
No products in the cart.
Lasolvan Max, capsules 75 mg 10 pcs
€6.98 €6.11
Description
Medications to relieve symptoms of colds and coughs.
Hypnotics. Mucolytics. Ambroxol.
ATC code R05CB06
Pharmacological action
/b>
Pharmacokinetics
absorption. Absorption is high and almost complete, linearly dependent on the therapeutic dose. Maximum plasma concentration is reached within 6.5 hours. The relative bioavailability is 95%.
Distribution Distribution is rapid and extensive, with the highest concentrations in lung tissue. The volume of distribution is approximately 552 L. The binding to plasma proteins is approximately 90%.
Metabolism and excretion. Approximately 30% of the ingested dose is subjected to a “first pass” effect through the liver.
CYP3A4 is the main enzyme responsible for the metabolism of ambroxol, under the action of which, mainly in the liver, conjugates are formed.
The elimination half-life is 10 hours. Total clearance is within 660 ml/min, renal clearance is 83 % of total clearance. It is excreted by the kidneys: 26% in the form of conjugates, 6% – as free form.
The excretion of ambroxol is reduced with hepatic dysfunction, which leads to an increase in plasma levels by 1.3-2 times, but does not require dose adjustment.
Gender and age have no clinically significant effect on ambroxol pharmacokinetics and do not require dose adjustment.
Eating has no effect on the bioavailability of ambroxol hydrochloride.
Pharmacodynamics
The drug has secretolytic and expectorant action; stimulates serous cells of glands of mucous membrane of bronchi, increases the content of mucous secretion and secretion of surfactant in alveoli and bronchi; normalizes the disturbed ratio of serous and mucous components of sputum.
Activating hydrolyzing enzymes and increasing the release of lysosomes from Clara cells, reduces the viscosity of sputum. Increases motor activity of the cilia of the atomizing epithelium and increases mucociliary transport of sputum. Increasing secretion and mucociliary clearance improves sputum discharge and relieves coughing.
In patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) the result of long-term treatment (6 months) was a significant reduction in exacerbations after 2 months of treatment. In addition, there was a decrease in disease symptoms such as difficult sputum discharge, cough, dyspnea, and auscultatory signs compared to placebo. It was also noted that the course of the disease and the need for antibiotic therapy were shorter compared to placebo.
The local anesthetic effect of ambroxol has been shown to be due to a dose-dependent blockade of neuronal sodium channels. Under the influence of ambroxol the release of cytokines from blood as well as from tissue mononuclears and polymorphonuclear cells is significantly reduced.
Clinical studies on patients with sore throat have shown a significant reduction in soreness and redness in the throat.
Indications
Indications
Secretolytic therapy of acute and chronic bronchopulmonary diseases characterized by impaired secretion and difficult sputum discharge
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Medicines to relieve symptoms of colds and coughs.
Expectorants. Mucolytics. Ambroxol.
ATX code R05CB06
Pharmacological action
Pharmacokinetics
Suction. Absorption is high and almost complete, linearly dependent on the therapeutic dose. Maximum plasma concentration is achieved within 6.5 hours. Relative bioavailability – 95%.
Distribution. Distribution is rapid and widespread, with highest concentrations in lung tissue. Distribution volume approximately 552 l. The binding to plasma proteins is approximately 90%.
Metabolism and excretion. Approximately 30% of an ingested dose undergoes a first-pass effect through the liver.
CYP3A4 is the main enzyme responsible for the metabolism of ambroxol, under the influence of which conjugates are formed, mainly in the liver.
The half-life is 10 hours. The total clearance is within 660 ml/min, renal clearance is 83% of the total clearance. Excreted by the kidneys: 26% in the form of conjugates, 6% in free form.
The excretion of ambroxol is reduced in case of liver dysfunction, which leads to an increase in plasma levels by 1.3-2 times, but does not require dose adjustment.
Gender and age do not have a clinically significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of ambroxol and do not require dose adjustment.
Food intake does not affect the bioavailability of ambroxol hydrochloride.
Pharmacodynamics
The drug has a secretolytic and expectorant effect; stimulates the serous cells of the glands of the bronchial mucosa, increases the content of mucous secretions and the release of surfactant in the alveoli and bronchi; normalizes the disturbed ratio of serous and mucous components of sputum.
By activating hydrolyzing enzymes and enhancing the release of lysosomes from Clara cells, it reduces the viscosity of sputum. Increases the motor activity of the cilia of the ciliated epithelium, increases the mucociliary transport of sputum. Increasing secretion and mucociliary clearance improves sputum production and relieves cough.
In patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) resulting from long-term treatment (6 months), a significant reduction in exacerbations was observed after 2 months of treatment. In addition, there was a weakening of symptoms of the disease such as difficult sputum discharge, cough, shortness of breath, and auscultatory signs compared to placebo. In addition, it was noted that the course of the disease and the need for antibiotic therapy were shorter compared to placebo.
It has been proven that the local anesthetic effect of ambroxol is due to dose-dependent blockade of sodium channels of neurons. Under the influence of ambroxol, the release of cytokines from the blood, as well as from tissue mononuclear cells and polymorphonuclear cells, is significantly reduced.
Clinical studies on patients with sore throat have shown a significant reduction in sore throat and redness.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Very rare cases of severe skin lesions such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis have been reported with the use of ambroxol hydrochloride. They are mainly due to the severity of the underlying disease and concomitant treatment.
In addition, in the early stages of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis, patients may show signs of the onset of a nonspecific disease with the following symptoms: fever, pain throughout the body, rhinitis, cough and sore throat.
The appearance of these signs may lead to unnecessary symptomatic treatment with cold medications. If skin lesions appear, the patient is immediately examined by a doctor, and ambroxol hydrochloride is discontinued.
For patients with decompensated renal failure, the use of the drug is indicated only after consultation with a doctor.
Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
Ambroxol hydrochloride penetrates the placental barrier. Preclinical studies have not shown direct or indirect negative effects on pregnancy, fetal development, childbirth or postnatal development.
It is not recommended to use the drug during the first trimester of pregnancy. Use with caution in the II–III trimesters of pregnancy and lactation.
Ambroxol hydrochloride passes into breast milk, however, when prescribed in therapeutic doses, it does not have a negative effect on the child.
Preclinical studies have not shown direct or indirect negative effects on fertility.
Features of the effect of the drug on the ability to drive a vehicle or potentially dangerous mechanisms
There are no reports of cases of the drug affecting the ability to drive a car or use machinery during the post-marketing period. No studies have been conducted.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Ambroxol
Composition
Composition
Active substances:
ambroxol hydrochloride 75 mg;
Excipients:
crospovidone 12.55 mg,
carnauba wax 18.31 mg,
stearyl alcohol 110.94 mg,
magnesium stearate 1.20 mg;
composition of the capsule shell:
gelatin 52.307 mg, purified water 9.135 mg, titanium dioxide (E171) 1.008 mg, red iron oxide dye (E172) 0.150 mg, yellow iron oxide dye (E172) 0.398 mg;
ink composition:
shellac, titanium dioxide.
Contraindications
Contraindications
hypersensitivity to ambroxol hydrochloride or other components of the drug
childhood and adolescence up to 12 years
Side Effects
Side Effects
Gastrointestinal disorders
Common (≥ 1/100 – < 1/10):
nausea, change in taste, decreased sensitivity in the mouth and pharynx (oral and pharyngeal hyposthesia)
Uncommon(≥ 1/1,000 – < 1/100):
vomiting, diarrhea, dyspepsia, abdominal pain, dry mouth
Rarely (≥ 1/10,000 – < 1/1,000):
dry throat
Immune system disorders
Not known:
anaphylactic reactions, including anaphylactic shock
Disorders of the skin and subcutaneous tissue
Rarely (≥ 1/10,000 – < 1/1,000):
rash, hives,
Not known:
itching and other hypersensitivity reactions, angioedema.
Interaction
Interaction
No clinically significant adverse interactions with other drugs have been reported.
Combined use with antitussive drugs leads to difficulty in sputum discharge due to cough suppression.
Increases the penetration and concentration in bronchial secretions of amoxicillin, cefuroxime and erythromycin.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dyspepsia.
Treatment: symptomatic therapy.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Sanofi Winthrop Industries, France
Additional information
| Manufacturer | Sanofi Winthrop Industry, France |
|---|---|
| Medication form | slow-release capsules |
| Brand | Sanofi Winthrop Industry |
Related products
Buy Lasolvan Max, capsules 75 mg 10 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.