No products in the cart.
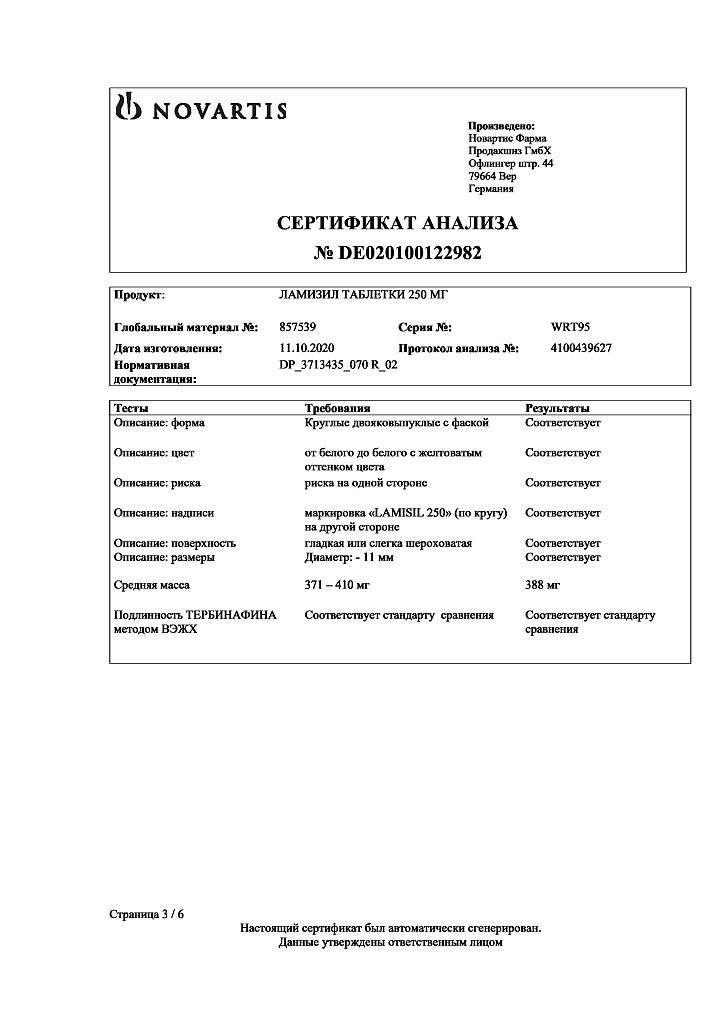
Lamisil, tablets 250 mg 14 pcs
€60.25 €52.21
Description
LAMISIL is a broad spectrum antifungal, fungistatic, fungicidal.
Pharmacodynamics
Terbinafine is an allylamine, which has a broad spectrum of action against fungi that cause skin, hair and nail diseases, including dermatophytes.Dermatophytes, such as T. rubrum, T. mentagrophytes, T. verrucosum, T. tonsurans, T. violaceum, Microsporum (such as M. canis), Epidermophyton floccosum, as well as yeasts of the Candida (such as C. albicans) and Pityrosporum. In low concentrations, terbinafine has fungicidal effect against dermatophytes, molds and some dimorphic fungi. Activity against yeast fungi, depending on their species, may be fungicidal or fungistatic.
Terbinafine specifically inhibits the early stage of sterol biosynthesis in the fungus cell. This leads to a deficit of ergosterol and to intracellular accumulation of squalene, which causes cell death of the fungus. The action of terbinafine is performed by inhibiting the squaleneepoxidase enzyme in the cell membrane of the fungus. This enzyme does not belong to the cytochrome P450 system.
When Lamisil® is administered orally, concentrations of the drug are created in the skin, hair and nails to provide fungicidal action.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration, terbinafine is well absorbed (>70%); the absolute bioavailability of terbinafine due to the first-pass effect is approximately 50%. After a single oral dose of 250 mg terbinafine, its Cmax in plasma is reached after 1.5 hours and is 1.3 µg/ml. When terbinafine was taken continuously, its Cmax increased by an average of 25% compared to a single dose; the AUC increased 2.3-fold. Based on the increase in AUC, an effective T1/2 can be calculated – 30 h. Food intake has little effect on bioavailability of the drug (AUC increased by less than 20%), therefore no correction of the dose of Lamisil® preparation is required in case of concomitant use with food.
Terbinafine is largely bound to blood plasma proteins (99%). It quickly penetrates through the dermal layer of the skin and concentrates in the lipophilic stratum corneum. Terbinafine also penetrates into the sebaceous gland secretion, resulting in high concentrations in hair follicles, hair and sebaceous gland-rich skin. Terbinafine has also been shown to penetrate the nail plates in the first few weeks of therapy.
Terbinafine is metabolized rapidly and to a significant extent with the participation of at least 7 cytochrome P450 isoenzymes, with CYP2C9, CYP1A2,CYP3A4, CYP2C8 and CYP2C19 playing a major role. As a result of biotransformation of terbinafine metabolites are formed that have no antifungal activity and are excreted mainly with the urine.
There were no changes in the equilibrium concentration of terbinafine in plasma depending on age.
In pharmacokinetic studies of a single dose of Lamisil® in patients with concomitant renal dysfunction (creatinine Cl
Indications
Indications
onychomycosis caused by dermatophyte fungi;
mycoses of the scalp;
fungal infections of the skin – treatment of dermatomycosis of the trunk, legs, feet, as well as yeast infections of the skin caused by fungi of the genus Candida (for example, Candida albicans) – in cases where the localization, severity or prevalence of the infection determine the advisability of oral therapy.
Note: Unlike topical Lamisil®, oral Lamisil® is not effective for tinea versicolor.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
LAMISIL – broad-spectrum antifungal, fungistatic, fungicidal.
Pharmacodynamics
Terbinafine is an allylamine that has a broad spectrum of action against fungi that cause diseases of the skin, hair and nails, incl. dermatophytes such as Trichophyton (for example T. rubrum, T. mentagrophytes, T. verrucosum, T. tonsurans, T. violaceum), Microsporum (for example M. canis), Epidermophyton floccosum, as well as yeast fungi of the genus Candida (for example C. albicans) and Pityrosporum. In low concentrations, terbinafine has a fungicidal effect against dermatophytes, molds and some dimorphic fungi. Activity against yeast fungi, depending on their type, can be fungicidal or fungistatic.
Terbinafine specifically inhibits the early stage of sterol biosynthesis in the fungal cell. This leads to ergosterol deficiency and intracellular accumulation of squalene, which causes the death of the fungal cell. Terbinafine works by inhibiting the enzyme squalene epoxidase in the cell membrane of the fungus. This enzyme does not belong to the cytochrome P450 system.
When Lamisil® is administered orally, concentrations of the drug are created in the skin, hair and nails, providing a fungicidal effect.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration, terbinafine is well absorbed (>70%); The absolute bioavailability of terbinafine due to the first pass effect is approximately 50%. After a single oral dose of terbinafine at a dose of 250 mg, its Cmax in plasma is reached after 1.5 hours and is 1.3 mcg/ml. With continuous use of terbinafine, its Cmax increased by an average of 25% compared with a single dose; AUC increased 2.3 times. Based on the increase in AUC, it is possible to calculate the effective T1/2 – 30 hours. Food intake has a slight effect on the bioavailability of the drug (AUC increases by less than 20%), therefore no dose adjustment of Lamisil® is required when taken simultaneously with food.
Terbinafine is highly bound to plasma proteins (99%). It quickly penetrates the dermal layer of the skin and concentrates in the lipophilic stratum corneum. Terbinafine also penetrates the secretions of the sebaceous glands, which leads to the creation of high concentrations in the hair follicles, hair and skin rich in sebaceous glands. Terbinafine has also been shown to penetrate the nail plates within the first few weeks after initiation of therapy.
Terbinafine is metabolized quickly and to a significant extent with the participation of at least 7 isoenzymes of cytochrome P450, with the main role being played by the isoenzymes CYP2C9, CYP1A2, CYP3A4, CYP2C8 and CYP2C19. As a result of the biotransformation of terbinafine, metabolites are formed that do not have antifungal activity and are excreted primarily in the urine.
There were no changes in the equilibrium concentration of terbinafine in plasma depending on age.
In pharmacokinetic studies of a single dose of Lamisil® in patients with concomitant renal impairment (Cl creatinine
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Terbinafine
Composition
Composition
1 tablet contains:
Active substance:
terbinafine (in the form of hydrochloride) 250 mg;
Excipients:
magnesium stearate;
anhydrous colloidal silicon dioxide;
methylhydroxypropylcellulose;
sodium starch glycolate;
MCC.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to terbinafine or any other ingredient of the drug.
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the hematopoietic system: very rarely – neutropenia, agranulocytosis, pancytopenia. In very rare cases, when using the drug, the development of qualitative or quantitative changes in blood cells (neutropenia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia) was observed. If qualitative or quantitative changes in blood cells develop, the cause of the disturbances should be established and consideration should be given to reducing the dose of the drug or, if necessary, stopping therapy with Lamisil®.
From the immune system: very rarely – anaphylactoid reactions (including angioedema), cutaneous and systemic lupus erythematosus.
From the nervous system: often – headache; sometimes – disturbances in taste, including their loss (usually recovery occurs within a few weeks after stopping treatment); very rarely – dizziness, paresthesia, hypoesthesia. There are isolated reports of cases of long-term disturbances in taste. In some cases, while taking the drug, there was a decrease in food consumption, which led to a significant decrease in weight.
From the hepatobiliary system: rarely – hepatobiliary dysfunction (mainly cholestatic in nature), including very rare cases of severe liver failure (some fatal or requiring liver transplantation). In most cases where liver failure developed, patients had serious concomitant systemic diseases and the causal relationship of liver failure with taking Lamisil® was questionable.
From the digestive system: very often – a feeling of fullness in the stomach, loss of appetite, dyspepsia, nausea, mild abdominal pain, diarrhea.
From the skin and subcutaneous tissue: very often – mild skin reactions (rash, urticaria); very rarely – serious skin reactions (including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis); psoriasis-like skin rashes or exacerbations of psoriasis. Very rarely, cases of hair loss have been reported, although the cause-and-effect relationship of this phenomenon with taking the drug has not been established. If a progressive skin rash develops, treatment should be discontinued.
From the musculoskeletal system: very often – arthralgia, myalgia.
Other: very rarely – feeling of fatigue.
Interaction
Interaction
Effect of other drugs on terbinafine. Plasma Cl of terbinafine can be accelerated under the influence of drugs that are metabolic inducers, and suppressed under the influence of cytochrome P450 inhibitors. If it is necessary to use the above drugs and Lamisil® simultaneously, an appropriate adjustment of the dosage regimen of the latter may be required.
Cimetidine may enhance the effect of terbinafine or increase its plasma concentration. Cimetidine reduces the Cl of terbinafine by 33%.
Rifampicin may weaken the effect of terbinafine or reduce its plasma concentration. Rifampicin increases the Cl of terbinafine by 100%.
Effect of terbinafine on other drugs. Results from studies conducted in vitro and in healthy volunteers indicate that terbinafine has little potential to suppress or increase Cl of most drugs that are metabolized by the cytochrome P450 system (for example, terfenadine, triazolam, tolbutamide or oral contraceptives), with the exception of those metabolized by CYP2D6.
Terbinafine does not affect the Cl of antipyrine or digoxin.
There have been reports of several cases of menstrual irregularities in patients taking Lamisil® in combination with oral contraceptives, although the frequency of these disorders does not exceed the average frequency of such disorders in patients taking only oral contraceptives.
Terbinafine may enhance the effects of caffeine or increase its plasma concentration. Terbinafine reduces caffeine Cl when administered intravenously by 19%.
Terbinafine has been shown to inhibit metabolism mediated by enzyme 2D6 (CYP2D6) in in vivo and in vitro studies. These data may be clinically significant for those drugs that are predominantly metabolized by this enzyme: tricyclic antidepressants, beta-blockers, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, class 1A, 1B and 1C antiarrhythmic drugs and MAO B inhibitors, if the concomitant drug has a small therapeutic concentration range.
Terbinafine reduces desipramine Cl by 82%.
Terbinafine may weaken the effect of cyclosporine and reduce its plasma concentration. Terbinafine increases the Cl of cyclosporine by 15%.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: there are reports of several cases of overdose (the dose taken was up to 5 g), in which headache, nausea, pain in the epigastric region and dizziness were noted.
Treatment: symptomatic and supportive therapy, measures to remove the drug, primarily by prescribing activated charcoal and gastric lavage.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a place protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 30 °C
Shelf life
Shelf life
5 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Novartis Pharma Productions GmbH, Germany
Additional information
| Shelf life | 5 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a light-protected place, at a temperature not exceeding 30 °C |
| Manufacturer | Novartis Pharma Productions GmbH, Germany |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Novartis Pharma Productions GmbH |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Lamisil, tablets 250 mg 14 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.