No products in the cart.
Lactinet-Richter, 0.075 mg 28 pcs
€36.82 €30.68
Description
Lactinet® is an oral gestagen-containing contraceptive with the active ingredient deogestrel. Like other hormonal contraceptives with only progestogen as an active ingredient, Lactinet® can be taken by women during breastfeeding and if there are contraindications to estrogens or if the use of estrogen-containing contraceptives is not desired.
In contrast to other gestagenic contraceptives, the contraceptive effect of Lactinet® is explained by ovulation inhibition, which is confirmed by absence of ovulatory follicle at ultrasound and absence of increase in serum LTH and progesterone values in the middle of menstrual cycle. At the same time, desogestrel, like other progestagens, has the property of increasing the viscosity of cervical mucus, preventing the advancement of sperm.
The Perl index (an indicator reflecting the occurrence of pregnancy in 100 women during a year of contraception) is 0.4, which is comparable to the use of combined hormonal contraceptives for oral use. The use of Lactinet® leads to a decrease in plasma estradiol to values corresponding to the early follicular phase. Progestagens affect carbohydrate and lipid metabolism.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Desogestrel is rapidly absorbed when taken orally. Tmax is reached 1.8 h after taking the tablet. The bioavailability of etonogestrel is about 70%.
Distribution
The etonogestrel is 95.5-99% bound to plasma proteins, mainly to albumin and to a lesser extent to sex hormone-binding globulin (hGBS).
Metabolism
Desogestrel is metabolized by hydroxylation and dehydrogenation to the active metabolite etonogestrel. Etonogestrel is metabolized by formation of sulfate and glucuronide conjugates.
The average T1/2 of etonogestrel is about 30 h, both with single and multiple doses. Css in plasma are established after 4-5 days. Etonogestrel and its metabolites are excreted by the kidneys and through the intestine (at a ratio of 1.5:1) as free steroids and conjugates. In breastfeeding mothers etonogestrel is excreted with breast milk at a milk/serum ratio of 0.37-0.55.
Hence, with an approximate maternal milk intake of 150 mg/kg/day, a newborn can receive etonogestrel at 0.01-0.05 µg/kg/day.
Indications
Indications
Contraception
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Lactinet® is a gestagen-containing contraceptive for oral use, the active ingredient of which is desogestrel. Like other hormonal contraceptives, which contain exclusively progestogen as an active component, Lactinet® can be taken by women during breastfeeding, as well as if there are contraindications to estrogens or reluctance to use estrogen-containing contraceptives.
Unlike other gestagenic contraceptives, the contraceptive effect of Lactinet® is explained by inhibition of the ovulation process, which is confirmed by the absence of an ovulatory follicle on ultrasound and the absence of an increase in LTG and progesterone values in the blood serum in the middle of the menstrual cycle. At the same time, desogestrel, like other progestogens, has the property of increasing the viscosity of cervical mucus, preventing the advancement of sperm.
The Pearl index (an indicator reflecting the onset of pregnancy in 100 women during a year of contraception) is 0.4, which is comparable to the use of combined hormonal contraceptives for oral use. The use of the drug Lactinet® leads to a decrease in the content of estradiol in the blood plasma to values corresponding to the early follicular phase. Progestogens affect carbohydrate and lipid metabolism.
Pharmacokinetics
Suction
When taken orally, desogestrel is rapidly absorbed. Tmax is reached 1.8 hours after taking the tablet. The bioavailability of etonogestrel is about 70%.
Distribution
Etonogestrel is 95.5–99% bound to plasma proteins, mainly albumin and to a lesser extent sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG).
Metabolism
Desogestrel is metabolized by hydroxylation and dehydrogenation to the active metabolite etonogestrel. Etonogestrel is metabolized by the formation of sulfate and glucuronide conjugates.
Removal
The average T1/2 of etonogestrel is about 30 hours, both with single and multiple doses. Css in blood plasma are established after 4–5 days. Etonogestrel and its metabolites are excreted by the kidneys and through the intestines (in a ratio of 1.5:1) in the form of free steroids and conjugates. In nursing mothers, etonogestrel is excreted in breast milk in a milk/serum ratio of 0.37–0.55.
Thus, with an estimated maternal milk intake of 150 mg/kg/day, the newborn may receive etonogestrel in amounts of 0.01–0.05 mcg/kg/day.
Special instructions
Special instructions
If there is any condition or risk factor, the doctor must weigh the risks and benefits of using Lactinet® individually for each woman before starting hormonal contraception. If any undesirable effect or risk factor occurs, you must immediately notify your doctor to decide on the advisability of further taking the drug. Women with diabetes mellitus should be closely monitored during the first months of using Lactinet®.
Taking the drug Lactinet® reduces the serum estradiol content to a value corresponding to the early follicular phase. The protective effect of traditional progestogen-only contraceptives in terms of preventing ectopic pregnancy is not as pronounced as that of combined oral contraceptives, which is associated with ovulation that occurs relatively frequently when taking progestogen-only drugs.
Despite the fact that Lactinet®, as a rule, inhibits ovulation, the possibility of ectopic pregnancy should be kept in mind in the differential diagnosis when a woman develops amenorrhea or abdominal pain. Chloasma can sometimes occur, especially in women with a history of chloasma during pregnancy.
Women prone to chloasma should avoid exposure to sunlight and ultraviolet radiation while taking Lactinet®. Patients with lactose intolerance should keep in mind that one film-coated tablet Lactinet® contains 67.445 mg of lactose monohydrate. Patients with rare hereditary diseases such as lactose intolerance, lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption should not take the drug.
Impact on the ability to drive a car or other operating mechanisms. Does not affect the ability to drive a car or operate machinery.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Desogestrel
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient:
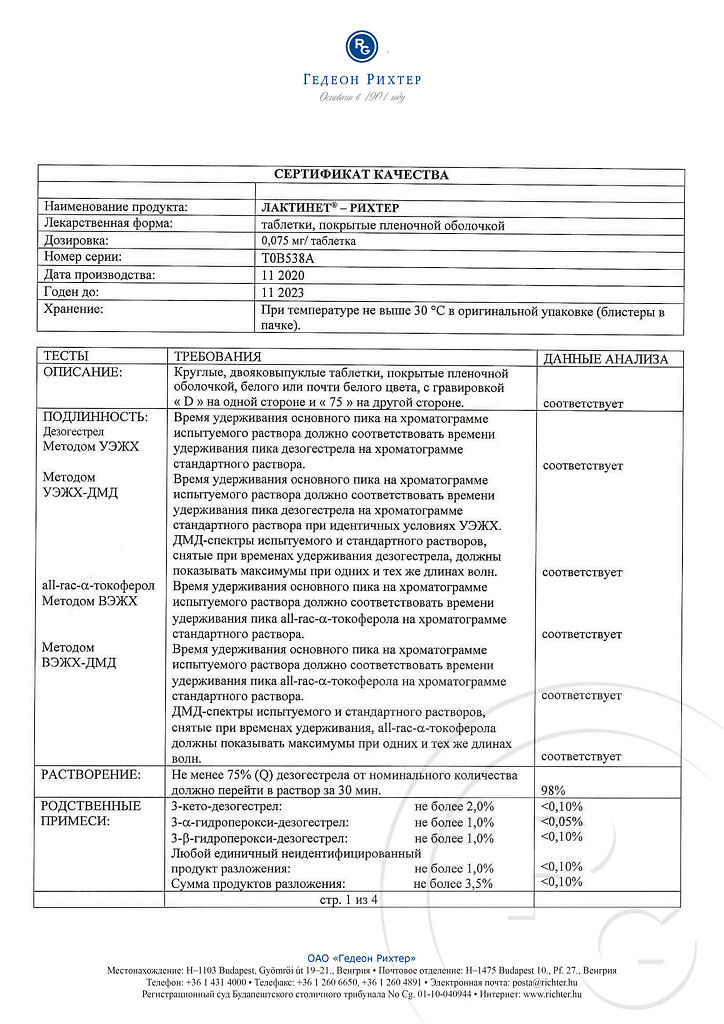
desogestrel 0.075 mg;
Excipients:
core: D,L-α-tocopherol – 0.08 mg;
colloidal silicon dioxide – 0.8 mg;
stearic acid – 0.8 mg;
magnesium stearate – 0.4 mg;
potato starch – 8 mg;
povidone K30 – 2.4 mg;
lactose monohydrate – 67.445 mg;
Film shell:
Opadry II white (titanium dioxide (E171) Cl 77891 – 0.25 mg, talc – 0.148 mg, macrogol 3000 – 0.202 mg, polyvinyl alcohol – 0.4 mg) – 1 mg;
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
During pregnancy, the use of the drug is contraindicated. In preclinical studies, when very high doses of progestogen were administered, masculinization of the female fetus was observed.
Epidemiological studies have not revealed an increased risk of teratogenic effects and congenital developmental defects among children whose mothers took oral hormonal contraceptives before pregnancy or unintentionally in early pregnancy.
Like other drugs containing only progestogen, Lactinet® does not affect the quality and quantity of breast milk, but a small amount of desogestrel metabolite (etonogestrel) is excreted in breast milk and amounts to approximately 0.01–0.05 mcg/kg/day (with an amount of breast milk consumed of 150 ml/kg/day).
The results of a 7-month follow-up did not reveal increased risks for breastfed children when assessing their growth, psychomotor and physical development. However, careful dynamic monitoring of the development and growth of the child during breastfeeding is necessary if a woman uses Lactinet® for contraception.
Contraindications
Contraindications
hypersensitivity to desogestrel or any other component of the drug;
the presence or history of venous thromboembolism (including deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities, pulmonary embolism);
severe liver disease currently or in history (until normalization of liver function indicators);
liver failure currently or in history;
established or suspected malignant hormone-dependent tumors (including breast cancer);
liver cancer;
bleeding from the vagina of unknown etiology;
established or suspected pregnancy;
lactose intolerance, lactase deficiency, glucose-galactose malabsorption;
long-term immobilization, incl. associated with surgery or disease (risk of venous thromboembolism).
With caution: resistant arterial hypertension developing while taking the drug, incl. if antihypertensive therapy is ineffective; chloasma, especially if there is a history of chloasma during pregnancy; diabetes mellitus (due to the possible effect of progestogens on peripheral insulin resistance and glucose tolerance); porphyria; systemic lupus erythematosus; herpes (history of pregnancy during pregnancy).
Side Effects
Side Effects
Often – acne, nausea, mood changes, decreased libido, breast tenderness, menstrual irregularities, headache, weight gain.
Uncommon: alopecia, fatigue, vomiting, discomfort when wearing contact lenses, vaginitis, dysmenorrhea, ovarian cysts.
Rarely – redness of the skin, rash, urticaria, erythema nodosum.
Interaction
Interaction
Concomitant use of inducers of microsomal liver enzymes may cause breakthrough bleeding and a decrease in the contraceptive effect of the drug. These drugs are hydantoin derivatives (including phenytoin), rifabutin, barbiturates, primidone, carbamazepine and rifampicin, as well as oxcarbazepine, topiramate, felbamate and griseofulvin.
No specialized studies have been conducted on the interaction of desogestrel with other drugs. Maximum induction of microsomal liver enzymes is achieved no earlier than 2–3 weeks after the start of use of the corresponding inducer and continues until 4 weeks after its discontinuation. Antibiotics (such as ampicillin and tetracycline) reduce the effectiveness of oral contraceptives.
Women taking medications that induce liver microsomal enzymes should be advised to temporarily additionally use barrier or other non-hormonal methods of contraception.
When using the above drugs simultaneously with desogestrel, it is recommended to use a barrier method of contraception throughout the entire course of treatment and for 7 days (for rifampicin – 28 days) after the end of therapy.
When treated with activated charcoal, the absorption of steroids, and therefore contraceptive effectiveness, may decrease. In this case, you should follow the recommendations given in the “Method of administration and dosage” section regarding missed doses of the drug.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: nausea, vomiting, spotting/bleeding from the vagina.
Treatment: symptomatic, there is no specific antidote.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
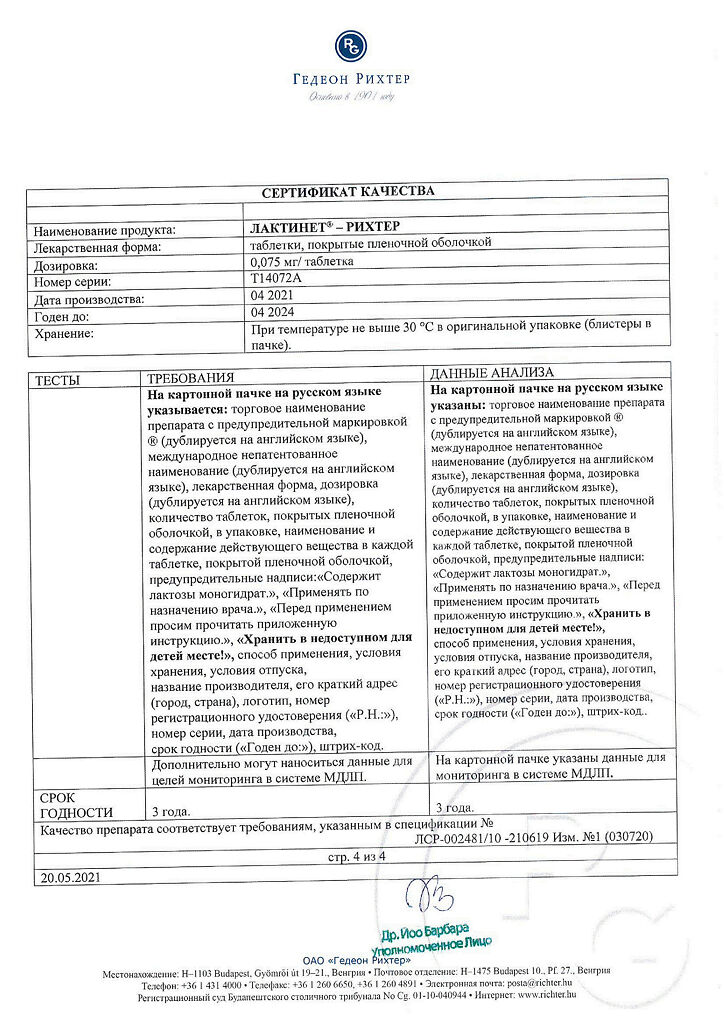
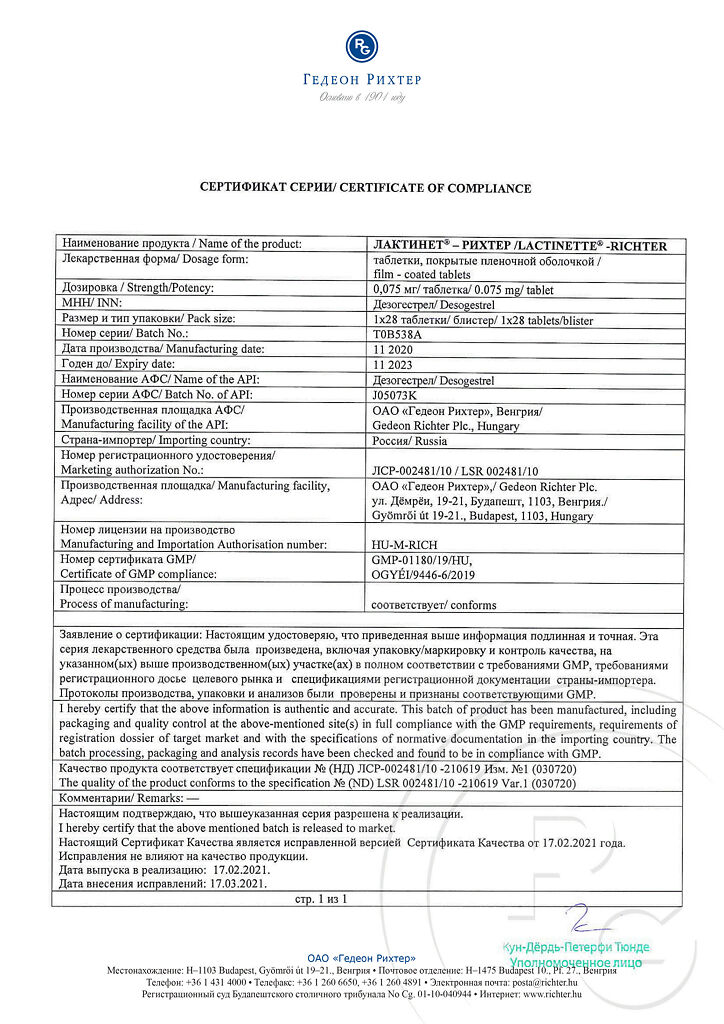
At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C, in original packaging
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Gedeon Richter, Hungary
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C, in the original package |
| Manufacturer | Gedeon Richter, Hungary |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Gedeon Richter |
Related products
Buy Lactinet-Richter, 0.075 mg 28 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.