No products in the cart.
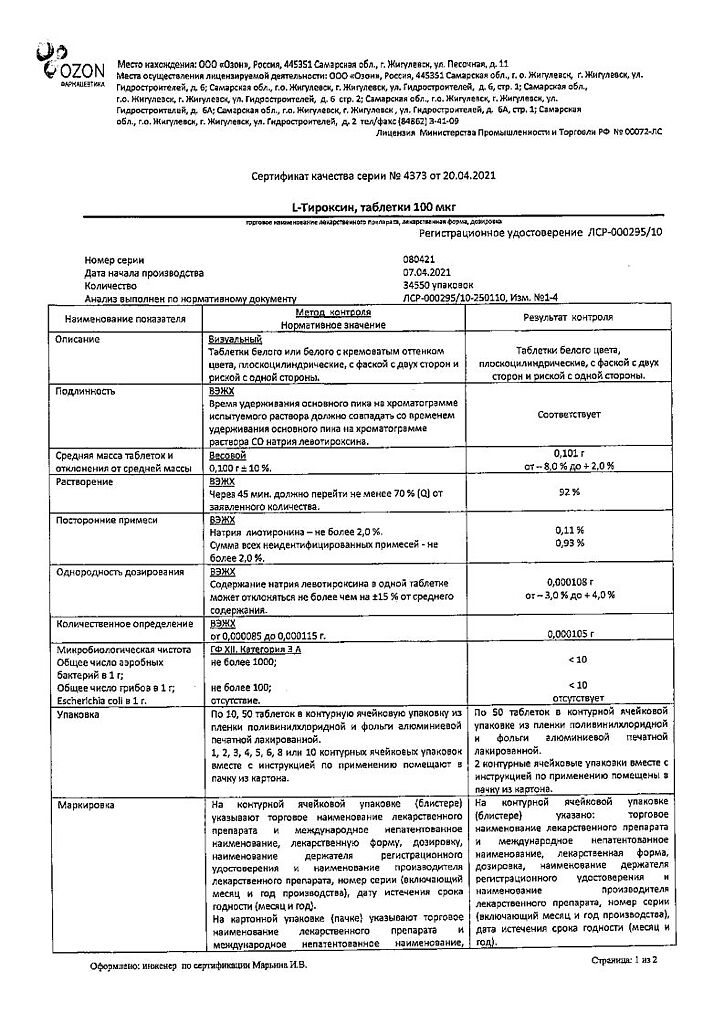
L-Tyroxine, tablets 100 mcg 100 pcs
€4.55 €4.04
Description
Levothyroxine sodium
Indications
Indications
hypothyroidism;
euthyroid goiter;
as replacement therapy and for the prevention of goiter recurrence after resection of the thyroid gland;
thyroid cancer (after surgical treatment);
diffuse toxic goiter: after achieving a euthyroid state with thyreostatics (in the form of combination or monotherapy);
as a diagnostic tool when performing a thyroid suppression test.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Thyroid agent
Pharmacological action
Synthetic levorotatory isomer of thyroxine. After partial conversion into triiodothyronine (in the liver and kidneys) and passage into the cells of the body, it affects the development and growth of tissues and metabolism. In small doses it has an anabolic effect on protein and fat metabolism. In medium doses, it stimulates growth and development, increases the need for oxygen in tissues, stimulates the metabolism of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, and increases the functional activity of the cardiovascular system and central nervous system. In large doses, it inhibits the production of thyrotropin-releasing hormone of the hypothalamus and thyroid-stimulating hormone of the pituitary gland.
The therapeutic effect is observed after 7-12 days, during the same time the effect persists after discontinuation of the drug. The clinical effect for hypothyroidism appears after 3-5 days. Diffuse goiter decreases or disappears within 3-6 months.
Pharmacokinetics
When taken orally, levothyroxine sodium is absorbed almost exclusively in the upper small intestine. Up to 80% of the dose taken is absorbed. Eating reduces the absorption of levothyroxine sodium. Cmax is reached approximately 5-6 hours after oral administration. After absorption, more than 99% of the drug binds to serum proteins (thyroxine-binding globulin, thyroxine-binding prealbumin and albumin). Approximately 80% of levothyroxine sodium is monodeiodinated in various tissues to form triiodothyronine (T3) and inactive products. Thyroid hormones are metabolized mainly in the liver, kidneys, brain and muscles. A small amount of the drug undergoes deamination and decarboxylation, as well as conjugation with sulfuric and glucuronic acids (in the liver). Metabolites are excreted by the kidneys and through the intestines. The half-life of the drug is 6-7 days. With thyrotoxicosis, the half-life is shortened to 3-4 days, and with hypothyroidism it is extended to 9-10 days.
Special instructions
Special instructions
In case of hypothyroidism caused by damage to the pituitary gland, it is necessary to find out whether there is simultaneous insufficiency of the adrenal cortex. In this case, replacement therapy with glucocorticosteroids should be started before treatment of hypothyroidism with thyroid hormones is started in order to avoid the development of acute adrenal insufficiency.
It is recommended to periodically determine the concentration of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) in the blood, an increase in which indicates an insufficient dose.
The drug does not affect activities associated with driving vehicles and operating machinery.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Levothyroxine sodium
Composition
Composition
Active substance: levothyroxine sodium
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
During pregnancy and breastfeeding, therapy with the drug prescribed for hypothyroidism should continue. During pregnancy, an increase in the dose of the drug is required due to an increase in the level of thyroxine-binding globulin. The amount of thyroid hormone secreted in breast milk during lactation (even when treated with high doses of the drug) is not sufficient to cause any problems in the child.
The use of the drug in combination with antithyroid drugs during pregnancy is contraindicated, since taking levothyroxine sodium may require an increase in the dose of antithyroid drugs. Since antithyroid drugs, unlike levothyroxine sodium, can penetrate the placenta, the fetus may develop hypothyroidism.
During breastfeeding, the drug should be taken with caution, strictly in recommended doses under medical supervision.
Contraindications
Contraindications
increased individual sensitivity to the drug;
untreated thyrotoxicosis;
acute myocardial infarction, acute myocarditis;
untreated adrenal insufficiency;
hereditary galactose intolerance, lactase deficiency or impaired absorption of glucose and lactose.
With caution: the drug should be prescribed for diseases of the cardiovascular system: coronary heart disease (atherosclerosis, angina pectoris, history of myocardial infarction), arterial hypertension, arrhythmia; for diabetes mellitus, severe long-term hypothyroidism, malabsorption syndrome (dose adjustment may be required).
Side Effects
Side Effects
When L-thyroxine is used correctly under medical supervision, no side effects are observed.
If you are hypersensitive to the drug, allergic reactions may occur. The development of other side effects is due to an overdose of the drug
Interaction
Interaction
Levothyroxine sodium enhances the effect of indirect anticoagulants, which may require a reduction in their dose. The use of tricyclic antidepressants with levothyroxine sodium may lead to increased effects of the antidepressants. Thyroid hormones may increase the need for insulin and oral hypoglycemic agents. More frequent monitoring of blood glucose concentrations is recommended during periods of initiation of treatment with levothyroxine sodium, as well as when changing its dosage regimen. Levothyroxine sodium reduces the effect of cardiac glycosides. With simultaneous use of cholestyramine, colestipol and aluminum hydroxide, they reduce the plasma concentration of levothyroxine sodium by inhibiting its absorption in the intestine. When used simultaneously with anabolic steroids, asparaginase, tamoxifen, pharmacokinetic interaction is possible at the level of protein binding. When used simultaneously with phenytoin, salicylates, clofibrate, furosemide in high doses, the content of levothyroxine sodium and thyroxine (T4) not bound to blood plasma proteins increases. Taking estrogen-containing medications increases thyroxine-binding globulin levels, which may increase the need for levothyroxine sodium in some patients. Somatotropin, when used simultaneously with levothyroxine sodium, can accelerate the closure of epiphyseal growth zones. Taking phenobarbital, carbamazepine and rifampicin may increase the clearance of levothyroxine sodium and require an increase in dose.
The distribution and metabolism of the drug is influenced by amiodarone, aminoglutethimide, PAS, ethionamide, antithyroid drugs, beta-blockers, carbamazepine, chloral hydrate, diazepam, levodopa, dopamine, metoclopramide, lovastatin, somatostatin.
When used simultaneously with phenytoin, salicylates, furosemide (in high doses), clofibrate, the concentration of the drug in the blood increases.
Phenytoin reduces the amount of protein bound levothyroxine and T4 concentration by 15 and 25%, respectively.
Overdose
Overdose
In case of an overdose of the drug, symptoms characteristic of thyrotoxicosis are observed: palpitations, cardiac arrhythmias, heart pain, anxiety, tremor, sleep disturbance, increased sweating, increased appetite, weight loss, diarrhea. Depending on the severity of symptoms, the doctor may recommend reducing the daily dose of the drug, a break in treatment for several days, or prescribing beta-blockers. After side effects disappear, treatment should be started with caution at a lower dose.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Ozon, Russia
Additional information
| Manufacturer | Ozon, Russia |
|---|---|
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Ozon |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy L-Tyroxine, tablets 100 mcg 100 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.