No products in the cart.
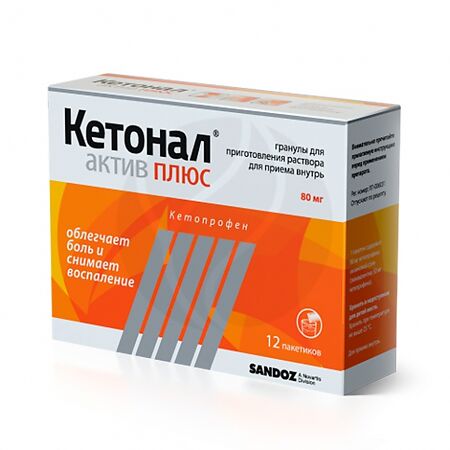
Ketonal Activ Plus, 80 mg 12 pcs
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID).
ATX code: M01AE03.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
It has anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effect. By inhibiting cyclooxygenase of types I and II, inhibits the synthesis of prostaglandins. It has anti-bradykinin activity, stabilizes lysosomal membranes and inhibits release of the enzymes from them, which contribute to destruction of tissues during chronic inflammation. It reduces release of cytokines, inhibits activity of neutrophils.
Limits morning stiffness and swelling of the joints and increases range of motion.
Ketoprofen lysine salt, unlike ketoprofen, is a rapidly soluble molecule with a neutral pH and causes almost no gastrointestinal (GI) irritation.
Pharmacokinetics
Intake
Ketoprofen is quickly and completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract when ingested, its bioavailability is about 80%. Maximal concentration in blood plasma when administered orally is observed after 0.5-2 hours and directly depends on the dose taken. Equilibrium concentration of ketoprofen is reached 24 hours after its regular use.
Distribution
Up to 99% of adsorbed ketoprofen is bound to plasma proteins, mainly to albumin. The volume of distribution is 0.1-0.2 l/kg. It easily passes through histohematic barriers and is distributed in tissues and organs. Ketoprofen penetrates well into the synovial fluid and connective tissues. Although ketoprofen concentration in synovial fluid is slightly lower than in blood plasma, it is more stable (remains up to 30 h).
Metabolism
Ketoprofen is mainly metabolized in the liver, where it undergoes glucuronidation to form glucuronic acid esters.
Elimination
The metabolites are excreted by the kidneys. The drug does not cumulate.
Indications
Indications
Inflammatory and degenerative diseases of the musculoskeletal system:
rheumatoid arthritis;
seronegative arthritis: ankylosing spondylitis (Bechterew’s disease), psoriatic arthritis, reactive arthritis (Reiter’s disease;
gout, pseudogout;
osteoarthritis;
tendonitis, bursitis, myalgia, neuralgia, radiculitis.
Pain syndrome, including mild, moderate and severe:
headache;
toothache;
post-traumatic and postoperative pain syndrome;
pain syndrome in cancer;
algodismenorrhea.
Children (over 6 years old): short-term symptomatic treatment of inflammatory processes accompanied by pain in combination with or without fever in diseases of the musculoskeletal system, otitis media.
The drug is intended for symptomatic therapy, reducing pain and inflammation at the time of use, and does not affect the progression of the disease.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID).
ATX code: M01AE03.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
It has anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effects. By inhibiting cyclooxygenase types I and II, it inhibits the synthesis of prostaglandins. It has anti-bradykinin activity, stabilizes lysosomal membranes and delays the release of enzymes from them that contribute to tissue destruction during chronic inflammation. Reduces the release of cytokines, inhibits the activity of neutrophils.
Reduces morning stiffness and swelling of joints, increases range of motion.
Ketoprofen lysine salt, unlike ketoprofen, is a rapidly soluble molecule with a neutral pH and causes almost no irritation to the gastrointestinal tract (GIT).
Pharmacokinetics
Suction
Ketoprofen, when taken orally, is quickly and fairly completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, its bioavailability is about 80%. The maximum concentration in blood plasma when taken orally is observed after 0.5-2 hours and directly depends on the dose taken. The equilibrium concentration of ketoprofen is achieved 24 hours after the start of its regular use.
Distribution
Up to 99% of adsorbed ketoprofen binds to plasma proteins, mainly albumin. Volume of distribution – 0.1-0.2 l/kg. Easily passes through histohematic barriers and is distributed in tissues and organs. Ketoprofen penetrates well into synovial fluid and connective tissue. Although the concentration of ketoprofen in synovial fluid is slightly lower than in blood plasma, it is more stable (lasts up to 30 hours).
Metabolism
Ketoprofen is mainly metabolized in the liver, where it undergoes glucuronidation to form esters with glucuronic acid.
Removal
Metabolites are excreted by the kidneys. The drug does not accumulate.
Special instructions
Special instructions
At the beginning of treatment, it is necessary to monitor the peripheral blood picture and the functional state of the liver and kidneys.
After 2 weeks of using the drug, monitoring of liver function indicators (transaminase levels) is necessary.
The use of ketoprofen by patients with bronchial asthma can lead to the development of an attack of bronchial asthma.
If it is necessary to determine 17-ketosteroids, the drug should be discontinued 48 hours before the study.
The drug can change the properties of platelets, but does not replace the preventive effects of acetylsalicylic acid in cardiovascular diseases.
Taking the drug may mask signs of infectious diseases. Elderly patients, patients with a history of gastric and duodenal ulcers, as well as patients taking low doses of acetylsalicylic acid or other drugs that may increase the risk of gastrointestinal reactions, the combined use of gastroprotective drugs (misoprostol or proton pump inhibitors) is indicated.
The use of the drug may adversely affect female fertility and is not recommended for women planning pregnancy. The use of the drug should be discontinued in women with fertility problems or undergoing fertility research.
The drug does not affect low-calorie and controlled diets and can be used in patients with diabetes.
The drug does not contain gluten, so it can be used in patients with celiac disease.
The drug does not contain aspartame, so it can be used in patients with phenylketonuria.
Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular effects
Patients with arterial hypertension and/or moderate heart failure accompanied by fluid retention and edema (history) associated with taking NSAIDs require careful monitoring and consultation with a physician.
Clinical studies and epidemiological data indicate that the use of some NSAIDs (especially at high doses over long periods of time) may be associated with a small increased risk of arterial thrombotic events (eg, myocardial infarction or stroke). There is insufficient data to exclude the above risk for ketoprofen lysine salt.
Patients with uncontrolled arterial hypertension, heart failure, established coronary artery disease, peripheral arterial disease and/or cerebrovascular disease should use ketoprofen lysine salt only after a thorough examination. Patients with risk factors for developing cardiovascular diseases (for example, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, smoking) should undergo the same examination before starting long-term treatment.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery
The drug has a limited and moderate effect on the ability to drive vehicles or operate machinery due to the possible occurrence of dizziness and drowsiness.
If drowsiness, dizziness or convulsions are observed after using the drug, you should avoid driving vehicles and machinery, as well as other activities that require concentration.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Ketoprofen
Composition
Composition
One two-volume sachet contains:
Active ingredient:
ketoprofen lysine salt – 80.0 mg (equivalent to 50.0 mg of ketoprofen);
Excipients:
mannitol – 1822.0 mg,
povidone K 30 – 40.0 mg,
mint flavor – 20.0 mg,
sodium chloride – 20.0 mg,
sodium saccharinate – 15.0 mg,
colloidal silicon dioxide – 3.0 mg.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
In the third trimester of pregnancy, the use of ketoprofen is contraindicated. In the first and second trimesters of pregnancy, the drug can be prescribed only if the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus.
The drug should not be used during breastfeeding.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the active substance and other components of the drug, as well as to other NSAIDs;
complete or incomplete combination of bronchial asthma, recurrent polyposis of the nose and paranasal sinuses, and intolerance to acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs (including a history);
erosive and ulcerative lesions of the stomach and duodenum in the acute stage;
active gastrointestinal, cerebrovascular or other bleeding;
inflammatory bowel diseases (ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease) in the acute stage;
hemophilia and other bleeding disorders;
decompensated heart failure;
period after coronary artery bypass surgery;
severe liver failure or active liver disease;
severe renal failure (creatinine clearance (CC) <30 ml/min), progressive kidney disease;
confirmed hyperkalemia;
children's age (up to 6 years);
pregnancy (III trimester) and breastfeeding period.
With caution
Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, liver disease (history), hepatic porphyria, chronic renal failure (creatinine clearance 30-60 ml/min), chronic heart failure, arterial hypertension, significant decrease in circulating blood volume (including after surgery), elderly patients (including those receiving diuretics, debilitated patients and those with low body weight), bronchial asthma, simultaneous use of glucocorticosteroids (including prednisolone), anticoagulants (including warfarin), antiplatelet agents (including acetylsalicylic acid, clopidogrel), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (including citalopram, fluoxetine, paroxetine, sertraline), coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular diseases, dyslipidemia/hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, peripheral artery disease, smoking, Helicobacter pylori infection, long-term use of NSAIDs, tuberculosis, severe osteoporosis, alcoholism, severe somatic diseases, pregnancy (I, II trimester).
Side Effects
Side Effects
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), adverse reactions are classified according to their frequency as follows: very common (≥1/10), common (≥1/100, <1/10), uncommon (≥1/1000, <1/100), rare (≥1/10000, <1/1000) and very rare (<1/10000); frequency unknown (the frequency of events cannot be determined from the available data).
Blood and lymphatic system disorders:
rarely: hemorrhagic anemia;
frequency unknown: thrombocytopenia, thrombocytopenic purpura, agranulocytosis, bone marrow dysfunction, leukocytopenia, leukocytosis, inflammation of the lymphatic vessels, vasculitis.
Immune system disorders: frequency unknown: anaphylactic reactions (including anaphylactic shock).
Disorders of the nervous system and sensory organs:
uncommon: headache, dizziness, drowsiness;
rarely: paresthesia, blurred vision, tinnitus;
frequency unknown: convulsions, dysgeusia, mood changes, irritability, insomnia.
Cardiovascular disorders: frequency unknown: heart failure, tachycardia, palpitations, hypertension, hypotension, vasodilation.
Respiratory system disorders:
rarely: bronchial asthma;
frequency unknown: bronchospasm (especially in patients with documented hypersensitivity to acetylsalicylic acid and other NSAIDs), rhinitis, shortness of breath, swelling and spasm of the larynx.
Gastrointestinal disorders:
often: nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia, abdominal pain;
uncommon: constipation, diarrhea, bloating, gastritis;
rarely: stomatitis, gastric and duodenal ulcers;
frequency unknown: exacerbation of ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease, gastrointestinal bleeding, perforation, heartburn.
Disorders of the liver and biliary tract: rarely: hepatitis, increased activity of liver transaminases and increased concentration of bilirubin in the blood serum caused by impaired liver function.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders:
uncommon: rash, itching;
frequency unknown: photosensitivity reactions, alopecia, urticaria, angioedema, bullous skin reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell’s syndrome), erythema and exanthema, maculopapular rash, dermatitis.
Renal and urinary tract disorders: frequency unknown: acute renal failure, tubulointerstitial nephritis, nephritic syndrome, abnormal values of renal function tests.
Other:
uncommon: swelling, fatigue;
frequency unknown: allergic and anaphylactoid reactions, swelling of the oral mucosa, periorbital edema.
If any side effects occur, you should immediately stop taking the drug and consult a doctor.
Interaction
Interaction
Combinations to avoid
Corticosteroids: Increases the risk of gastrointestinal ulceration and gastrointestinal bleeding.
Anticoagulants (parenteral heparin, warfarin) increase the risk of bleeding caused by inhibition of platelet function and damage to the gastrointestinal mucosa. NSAIDs may enhance the effects of anticoagulants such as warfarin.
Antiplatelet agents (clopidogrel, ticlopidine) and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors: increases the risk of bleeding caused by inhibition of platelet aggregation and damage to the gastrointestinal mucosa. Patients should be monitored if coadministration cannot be avoided.
Other NSAIDs, including high doses of salicylates (>3 g/day): Concomitant use of multiple NSAIDs may increase the risk of GI ulceration and GI bleeding due to a synergistic effect.
Lithium: NSAIDs increase plasma lithium levels (decreased renal excretion of lithium), which may reach toxic levels. This parameter must be monitored at the beginning of treatment, when adjusting the dose and after stopping treatment with ketoprofen.
Methotrexate in high doses (more than 15 mg per week): the hematotoxicity of methotrexate increases, as its excretion by the kidneys decreases when taking anti-inflammatory drugs. When used concomitantly with low-dose methotrexate (less than 15 mg per week), a complete blood count should be performed once a week for the first few weeks of treatment. It is imperative to conduct more frequent monitoring of the patient’s clinical condition in the presence of even a slight deterioration in renal function, as well as in elderly patients.
Hydantoin and sulfonamides: the toxic effects of these substances may be enhanced.
Combinations that require precautions
Diuretics, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor antagonists: NSAIDs may reduce their effectiveness. In patients with impaired renal function (eg, dehydrated patients or elderly patients), concomitant use of ACE inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor antagonists with drugs that inhibit the cyclooxygenase system may cause additional impairment of renal function, including acute renal failure, which is usually reversible. Patients should be adequately hydrated before concomitant therapy is initiated and renal function should be monitored after initiation of therapy.
Pentoxifylline: increased risk of bleeding. It is imperative to monitor the patient’s clinical condition more frequently and monitor blood clotting times.
Zidovudine: There is an increased risk of red blood cell toxicity via effects on reticulocytes with the development of severe anemia one week after starting NSAID treatment. It is necessary to conduct a complete blood count and monitor the reticulocyte count 1-2 times a week after starting NSAID treatment.
Sulfonylurea: NSAIDs may enhance the hypoglycemic effect of sulfonylurea by reducing its binding to plasma proteins.
Combinations to take into account
Beta blockers: NSAIDs may reduce the hypotensive effects of beta blockers due to inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis.
Cyclosporine and tacrolimus: NSAIDs may increase nephrotoxicity due to renal prostaglandin-related effects. When used together, it is necessary to monitor renal function.
Thrombolytics: increased risk of bleeding.
Probenecid: the concentration of ketoprofen in the blood plasma may increase. This increase may be due to an inhibitory mechanism at the site of renal tubular secretion and glucuronoconjugation and requires dose adjustment of ketoprofen.
Overdose
Overdose
Cases of overdose have been reported when taking a dose of 2.5 g of ketoprofen. In most cases, symptoms were limited to lethargy, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting and epigastric pain.
Measures to help with overdose
A specific antidote is unknown. As symptomatic measures to ensure vital functions (stabilization of blood circulation, respiration, elimination of acidosis), drugs and procedures that reduce resorption and accelerate elimination (medical charcoal, forced diuresis) are indicated.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years. Do not use the drug after the expiration date indicated on the package.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Fine Foods & Pharmaceuticals N.T.M. S.P.A., Italy
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years. Do not use the drug after the expiration date stated on the package. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. Keep out of reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Fine Foods & Pharmaceuticals N.T.M. S.P.A., Italy |
| Medication form | granules for preparation of oral solution |
| Brand | Fine Foods & Pharmaceuticals N.T.M. S.P.A. |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Ketonal Activ Plus, 80 mg 12 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.