No products in the cart.
Janumet, 500 mg+50 mg 56 pcs.
€95.43 €82.70
Description
Manumet is a combination of two hypoglycemic drugs with a complementary mechanism of action designed to improve glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes: sitagliptin, an inhibitor of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 enzyme (DPP-4), and metformin, a representative of the biguanide class.
Sitagliptin is an orally active, highly selective DPP-4 inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. The pharmacological effects of the class of DPP-4 inhibitor drugs are mediated by the activation of incretins.
Inhibiting DPP-4, sitagliptin increases the concentration of two known active hormones of the incretin family: glucagon-like peptide 1 (GFP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). Incretins are part of the internal physiological system of glucose homeostasis regulation. At normal or elevated blood glucose concentrations, GFP-1 and GIP contribute to increased insulin synthesis and secretion by pancreatic beta cells. GFP-1 also inhibits glucagon secretion by pancreatic alpha cells, thus reducing glucose synthesis in the liver. This mechanism of action differs from the mechanism of action of sulfonylurea derivatives, which stimulate insulin release even at low blood glucose concentrations, which is fraught with development of sulfonyl-induced hypoglycemia not only in patients with type 2 diabetes but also in healthy individuals.
As a highly selective and effective inhibitor of DPP-4 enzyme, sitagliptin in therapeutic concentrations does not inhibit activity of related enzymes DPP-8 or DPP-9. Sitagliptin differs in chemical structure and pharmacological action from PPP-1 analogues, insulin, sulfonylurea or meglitinide derivatives, biguanides, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonists (PPARy), alpha-glycosidase inhibitors and amylin analogues.
Metformin is a hypoglycemic drug that increases glucose tolerance in patients with type 2 diabetes by reducing basal and postprandial blood glucose concentrations. Its pharmacological mechanisms of action are different from the mechanisms of action of oral hypoglycemic drugs of other classes. Metformin reduces glucose synthesis in the liver, reduces glucose absorption in the intestine and increases insulin sensitivity through glucose capture and utilization.
Indications
Indications
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
One tablet contains:
Active ingredients:
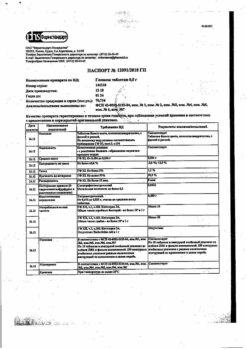
Metformin hydrochloride – 500 mg;
Sitagliptin phosphate monohydrate – 50 mg .
Auxiliary components:
Cellulose microcrystalline;
Povidone;
Sodium stearyl fumarate;
Sodium lauryl sulfate.
Composition of the shell:
Opadray II Pink, 85 F 94203;
Polyvinyl alcohol;
Titanium dioxide (E171);
Macrogol-3350;
Talc;
Red iron oxide (E172);
Black iron oxide (E172).
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
The dosing regimen of the drug Janumet should be chosen individually, based on the current therapy, efficacy and tolerability, but not exceeding the maximum recommended daily dose of sitagliptin 100 mg.
Janumet is usually administered in a twice-daily regimen with meals, with gradual dose increases to minimize possible gastrointestinal (GI) side effects characteristic of metformin.
The starting dose of Janumet depends on the current hypoglycemic therapy.
Interaction
Interaction
Sitagliptin and metformin
Simultaneous administration of multiple doses of sitagliptin (50 mg 2 times daily) and metformin (1000 mg 2 times daily) was not accompanied by significant changes in the pharmacokinetic parameters of sitagliptin or metformin in type 2 diabetic patients.
There have been no studies of interdrug effects on the pharmacokinetic parameters of Janumet, but a sufficient number of such studies have been performed for each of the drug components, sitagliptin and metformin.
Sitagliptin
In drug interaction studies, sitagliptin had no clinically significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of the following drugs: metformin, rosiglitazone, glibenclamide, simvastatin, warfarin, oral contraceptives. Based on these data, sitagliptin does not inhibit the CYP isoenzymes of the cytochrome system CYP3A4,2C8 or 2C9. In vitro data indicate that sitagliptin also does not inhibit the CYP2D6,1A2,2C19, and 2B6 isoenzymes and does not induce CYP3A4. According to population pharmacokinetic analysis of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, concomitant therapy had no clinically significant effect on sitagliptin pharmacokinetics.
The study evaluated a number of drugs most commonly used by patients with type 2 diabetes, including: hypocholesterolemic drugs (statins, fibrates, ezetimibe), antiaggregants (clopidogrel), hypotensive drugs (ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists, beta-adrenoblockers, “slow” calcium channel blockers, hydrochlorothiazide, analgesics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (naproxen, diclofenac, celecoxib), antidepressants (bupropion, fluoxetine, sertraline), antihistamines (cetirizine), proton pump inhibitors (omeprazole, lansoprazole) and drugs to treat erectile dysfunction (sildenafil).
Like an increase in AUC (11%) as well as mean C mah (18%) of digoxin when coadministered with sitagliptin was noted. This increase is not considered clinically significant, but patient monitoring is recommended when concomitant administration of digoxin. There was an increase in AUC and C mah of sitagliptin by 29% and 68%, respectively, when co-administering a single oral dose of JANUVIA at 100 mg and cyclosporine (a potent inhibitor of p-glycoprotein) at a dose of 600 mg. These changes in the pharmacokinetic parameters of sitagliptin are not clinically significant.
Metformin
Glyburide – No changes in the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic parameters of metformin were observed in an interdrug interaction study of single doses of metformin and glyburide in type 2 diabetic patients. Changes in the AUC and Stach values of glyburide were highly variable. Insufficient information (single administration) and inconsistency of plasma concentration of glyburide with the observed pharmacodynamic effects call into question the clinical significance of this interaction.
Furosemide – In an interdrug interaction study of single-dose metformin and furosemide in healthy volunteers, changes in the pharmacokinetic parameters of both drugs were observed. Furosemide increased the value of metformin C mah concentration in plasma and whole blood by 22%, the AUC value of metformin in whole blood by 15%, without changing renal clearance of the drug. The C mah and AUC values of furosemide, in turn, decreased by 31% and 12%, respectively, and the elimination half-life decreased by 32%, without significant changes in renal clearance of furosemide. There is no information on interdrug interactions between the two drugs in long-term concomitant use.
Nifedipine – the study of interdrug interaction between nifedipine and metformin after a single drug administration in healthy volunteers showed an increase in plasma C mah and AUC of metformin by 20% and 9%, respectively, as well as an increase in metformin renal excretion. T mah and metformin elimination half-life were unchanged. The basis is an increase in metformin absorption in the presence of nifedipine. The effect of metformin on the pharmacokinetics of nifedipine is minimal.
Cationic drugs are cationic drugs (ie. amiloride, digoxin, morphine, procainamide, quinidine, quinine, ranitidine, triamterene, trimethoprim, or vancomycin) excreted by tubular secretion could theoretically interact with metformin by competing for the shared renal tubular transport system.
Such competition was observed when metformin and cimetidine were administered simultaneously to healthy volunteers in single- and multiple-dose studies, with a 60% increase in plasma and whole blood C mah concentration of metformin and a 40% increase in plasma and whole blood AUC of metformin. The metformin elimination half-life was not altered in the single-dose study. Metformin did not affect the pharmacokinetics of cimetidine. Although the above interdrug interactions are mainly theoretical (with the exception of cimetidine), close patient monitoring and dose adjustment of Janumet and/or the above cationic drugs excreted by proximal renal tubules are recommended in cases of concomitant administration.
Some drugs have hyperglycemic potential and may interfere with established glycemic control. These include thiazide and other diuretics, glucocorticosteroids, phenothiazines, thyroid medications, estrogens, oral contraceptives, phenytoin, nicotinic acid, sympathomimetics, slow calcium channel blockers, and isoniazid. When prescribing the above drugs, close monitoring of glycemic control parameters is recommended for a patient receiving Janumet.
No changes in the pharmacokinetic parameters of these drugs were observed when metformin and propranololol or metformin and ibuprofen were administered simultaneously in healthy volunteers.
. Only a small proportion of metformin binds to plasma proteins; therefore, interdrug interactions between metformin and drugs that actively bind to plasma proteins (salicylates, sulfonamides, chloramphenicol and probenecid) are unlikely, unlike sulfonylurea derivatives, which also actively bind to plasma proteins.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
Application in the elderly with Janumet: Because the primary route of excretion of sitagliptin and metformin is through the kidneys, and because renal excretory function decreases with age, the precautions for prescribing Janumet increase in proportion to age.
In elderly patients, careful dose selection and regular monitoring of renal function are necessary.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Side effects
Side effects
Gastrointestinal system disorders:at the beginning of treatment – anorexia, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, flatulence, abdominal pain (reduced with meals); metallic taste in the mouth (3%).
Cardiovascular system and blood (hematopoiesis, hemostasis):in single cases – megaloblastic anemia (result of impaired absorption of vitamin B12 and folic acid).
From the metabolic side: hypoglycemia; in rare cases, lactate acidosis (weakness, drowsiness, hypotension, resistant bradyarrhythmia, respiratory disorders, abdominal pain, myalgia, hypothermia).
Skin side:rash, dermatitis.
Overdose
Overdose
Sitagliptin: In healthy volunteers, single doses up to 800 mg were generally well tolerated. When using 800 mg in a clinical trial, a slight prolongation of the Q-Tc interval was observed, which was not considered to be clinically significant. There is no experience of using the drug in doses exceeding 800 mg. No dose-related adverse reactions have been reported in studies when using 600 mg/day for 10 days and 400 mg for 28 days. Sitagliptin is poorly dialyzed: according to clinical studies, only 13.5% of the dose was excreted during 3-4-hour hemodialysis session. Prolonged hemodialysis is prescribed in case of clinical necessity. There are no data on the effectiveness of peritoneal dialysis of sitagliptin.
Metformin: There have been cases of metformin overdose, including administration in amounts greater than 50 g. Hypoglycemia was detected in about 10% of all overdoses, but a causal association with metformin overdose has not been established. Lactacidosis has been reported in about 32% of all metformin overdoses. Emergency hemodialysis (metformin is dialyzed at a rate up to 170 ml/min in good hemodynamics) should be performed to accelerate excretion of excess metformin in cases of suspected overdose. In case of Janumet overdose, standard supportive measures should be initiated: removal from the GI tract of residual drug that has not yet been absorbed, monitoring of vital signs, including ECG, hemodialysis, and administration of supportive therapy if necessary.
Pregnancy use
Pregnancy use
No adequately controlled studies of the drug Janumet or its components have been conducted in pregnant women; therefore, there are no data on the safety of its use in pregnant women.
The drug Janumet, like other oral hypoglycemic drugs, is not recommended for use during pregnancy.
There have been no experimental studies of the combined drug Janumet to evaluate its effect on reproductive function.
Only data available from studies of sitagliptin and metformin are cited.
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. |
| Manufacturer | Akrihin HFC JSC, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Akrihin HFC JSC |
Related products
Buy Janumet, 500 mg+50 mg 56 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.