No products in the cart.
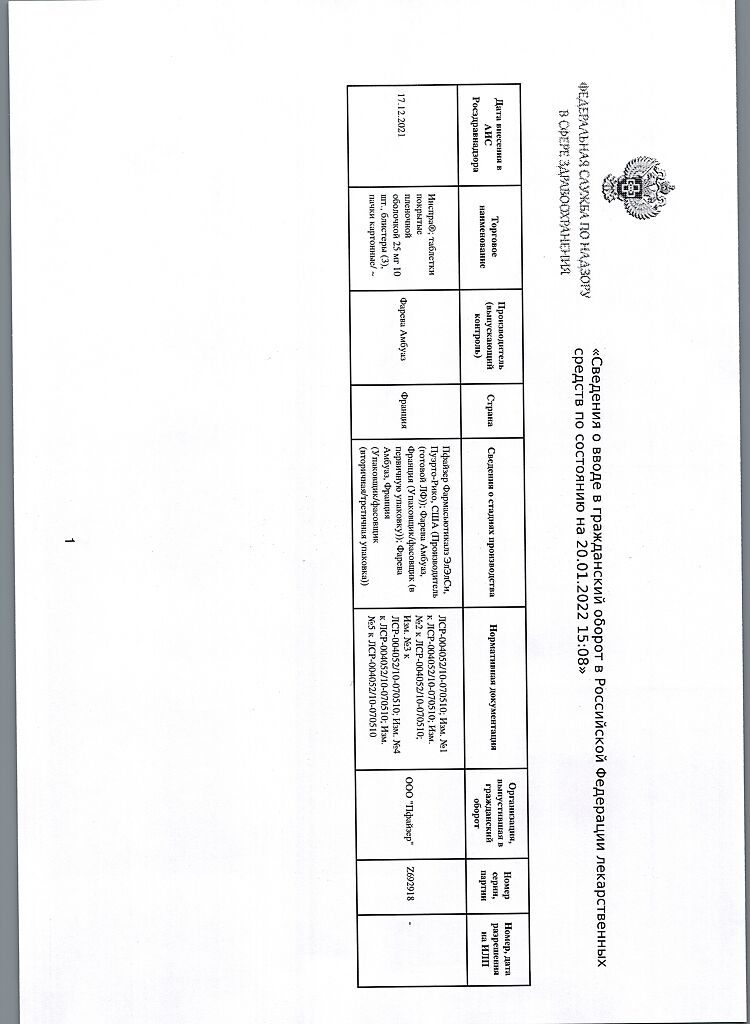
Inspra, 25 mg 30 pcs.
€39.11 €32.59
Description
Inspra is a diuretic.
Pharmacodynamics
Eplerenone is highly selective for mineralocorticoid receptors in humans as opposed to glucocorticoid, progesterone and androgen receptors and prevents binding of mineralocorticoid receptors to aldosterone, a key hormone of the RAAS that is involved in BP regulation and the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease.
Eplerenone causes a persistent increase in plasma renin and serum aldosterone concentrations. Subsequently, renin secretion is inhibited by aldosterone through a feedback mechanism. At the same time, increase of renin activity or concentration of circulating aldosterone does not affect the effects of eplerenone.
. The efficacy of eplerenone was studied in a double-blind, placebo-controlled EMPHESUS (Eplerenone Postacute Myocardial Infarction Heart failure Efficacy and Survival Study) in 6632 patients with acute myocardial infarction (MI), left ventricular (LV) dysfunction (ejection fraction (EF)
. The EMPHASIS-HF (Eplerenone in Mild Patients Hospitalization And Survival Study in Heart Failure) clinical trial enrolled 2737 patients with NYHA (New York Heart Association) functional class II (FC) CHF and severe systolic dysfunction (mean LV EF in the study was 26.1%). The average follow-up period was 21 months. In the eplerenone active treatment group, patients were taking ACE inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers (94%), β-adrenoblockers (86.6%) before inclusion. Primary end point: death from cardiovascular causes or hospitalization for heart failure. The EMPHASIS-HF clinical trial demonstrated that eplerenone at a mean dose (39.1±13.8) mg/day (25-50 mg) in patients with NYHA class II CHF reduced cardiovascular-related mortality by 37% (p
EKG
In studies examining ECG dynamics in healthy volunteers, no significant effect of eplerenone on HR, QRS interval duration, PR, or QT intervals was found.
Pharmacokinetics
Eplerenone absorption and distribution
The absolute bioavailability of eplerenone is 69% after oral administration of 100 mg of eplerenone as tablets. Tmax is approximately 2 h. Cmax and AUC are linearly dose-dependent between 10 and 100 mg and nonlinearly dose-dependent above 100 mg. The equilibrium state is reached within 2 days. Food intake has no effect on absorption.
Eplerenone is approximately 50% bound to plasma proteins, predominantly to the α1-acid group of glycoproteins. The calculated Vd in equilibrium is (50±7) liters. Eplerenone does not bind to erythrocytes.
Metabolism and excretion
The metabolism of eplerenone is primarily by the CYP3A4 isoenzyme. Active metabolites of eplerenone have not been identified in blood plasma.
Less than 5% of the dose of eplerenone is excreted unchanged through the kidneys and intestines. After a single oral administration of labeled eplerenone, about 32% of the dose was excreted through the intestine and about 67% through the kidneys. T1/2 of eplerenone is about 3-5 h, blood plasma clearance is about 10 l/h.
Particular groups
Age, sex and race. The pharmacokinetics of eplerenone at a dose of 100 mg once daily have been studied in elderly patients (older than 65 years), men and women. Eplerenone pharmacokinetics was not significantly different in men and women. At equilibrium, older patientsCmax and AUC were 22% and 45% higher, respectively, than younger patients (18-45 years old).
Renal insufficiency. The pharmacokinetics of eplerenone were studied in patients with renal insufficiency of various degrees of severity and in patients on hemodialysis. Compared with patients in control group, in patients with severe renal failure equilibrium AUC and Cmax were increased by 38 and 24%, respectively, and in patients on hemodialysis – their decrease by 26 and 3%. No correlation was found between eplerenone plasma clearance and creatinine clearance. Eplerenone is not eliminated by hemodialysis.
Hepatic failure. The pharmacokinetics of eplerenone at a dose of 400 mg were compared in patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score 7-9) and healthy volunteers. The equilibrium Cmax and AUC of eplerenone were increased by 3.6% and 42%, respectively. Eplerenone has not been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment, so its use in this group of patients is not indicated.
Heart failure. Pharmacokinetics of eplerenone at a dose of 50 mg was studied in patients with heart failure (II-IV FC). Equilibrium AUC and Cmax in patients with heart failure were 38 and 30% higher, respectively, than in healthy volunteers matched for age, body weight, and sex. The clearance of eplerenone in patients with heart failure was similar to that of healthy older adults.
Indications
Indications
– Myocardial infarction: in addition to standard therapy, to reduce the risk of cardiovascular mortality and morbidity in patients with stable left ventricular dysfunction (ejection fraction ≤ 40%) and clinical signs of heart failure after myocardial infarction.
– Chronic heart failure: in addition to standard therapy, to reduce the risk of cardiovascular mortality and morbidity in patients with chronic heart failure of NYHA functional class II, with left ventricular dysfunction (ejection fraction ≤ 35%).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Eplerenone has high selectivity for mineralocorticoid receptors in humans, in contrast to glucocorticoid, progesterone and androgen receptors, and prevents the binding of mineralocorticoids to aldosterone, a key hormone of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), which is involved in the regulation of blood pressure (BP) and the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases.
Eplerenone causes a persistent increase in the activity of renin in the blood plasma and aldosterone in the serum. Subsequently, renin secretion is suppressed by aldosterone via a feedback mechanism. However, an increase in renin activity or circulating aldosterone concentration does not affect the effects of eplerenone.
The effectiveness of eplerenone was studied in the double-blind, placebo-controlled EPHESUS study (Eplerenone Postacute myocardial infarction Heart failure Efficacy and Survival Study) in 6632 patients with acute myocardial infarction (MI), left ventricular (LV) dysfunction (ejection fraction (EF) <40%) and clinical signs of heart failure. For 3–14 days (mean 7 days) after acute myocardial infarction, patients were prescribed eplerenone or placebo in addition to standard therapy. Treatment was started at 25 mg once daily and increased to 50 mg once daily at the end of 4 weeks if serum potassium remained less than 5.0 mmol/L. During the study, patients received standard therapy using acetylsalicylic acid (92%), angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors (90%), beta-blockers (83%), nitrates (72%), loop diuretics (66%) or 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase (HMG) inhibitors KoA reductase) (60%). The primary endpoint of the study was overall mortality, and the composite endpoint was death or hospitalization for cardiovascular disease. Eplerenone treatment reduced the risk of all-cause mortality by 15% (relative risk, 0.85; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.75-0.96; P=0.008) compared with placebo, primarily due to a reduction in cardiovascular mortality. The risk of death or hospitalization for cardiovascular disease was reduced by 13% with eplerenone (relative risk, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.79 to 0.95; P=0.002). The absolute risk reductions for the two endpoints—all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality/hospitalization—were 2.3% and 3.3%, respectively.
The clinical trial EMPHASIS-HF (Eplerenone in Mild Patients Hospitalization And SurvIval Study in Heart Failure) included 2,737 patients with chronic heart failure (CHF) functional class II according to the NYHA (New York Heart Association) classification and severe systolic dysfunction (the average LVEF in the study was 26.1%). The average follow-up period was 21 months. In the group of active treatment with eplerenone, before enrollment, patients were taking ACE inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers (94%), beta-blockers (86.6%). Primary endpoint: death from cardiovascular causes or hospitalization for heart failure (HF). The EMPHASIS-HF clinical trial demonstrated that the use of eplerenone at an average dose of 39.1±13.8 mg/day (25-50 mg) in patients with NYHA class II CHF reduced mortality associated with cardiovascular diseases by 37% (p<0.001). Clinical efficacy has been demonstrated primarily with eplerenone in patients under 75 years of age.
The effectiveness of therapy in patients over 75 years of age has not been studied.
Electrocardiography
In studies examining the dynamics of the electrocardiogram (ECG) in healthy volunteers, no significant effect of eplerenone on heart rate (HR), the duration of the QRS, PR or QT intervals was detected.
Suction and distribution
The absolute bioavailability of eplerenone is 69% after oral administration of 100 mg eplerenone in tablet form. The maximum concentration in blood plasma (Cmax) is achieved in approximately 1.5-2 hours. Cmax and area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) depend linearly on the dose in the range from 10 to 100 mg and nonlinearly at doses greater than 100 mg. The equilibrium state is achieved within 2 days. Eating does not affect absorption. Eplerenone is approximately 50% bound to plasma proteins, predominantly to the alpha1-acid group of glycoproteins. The estimated volume of distribution at steady state is 42-90 l. Eplerenone does not bind to red blood cells.
Metabolism and excretion
Eplerenone is metabolized mainly by the CYP3A4 isoenzyme.
Active metabolites of eplerenone in blood plasma have not been identified.
Less than 5% of the eplerenone dose is excreted unchanged through the kidneys and intestines. After a single oral dose of labeled eplerenone, about 32% of the dose was excreted through the intestines and about 67% through the kidneys. The half-life of eplerenone is approximately 3-6 hours, plasma clearance is approximately 10 l/h.
Special groups
Age, gender and race: The pharmacokinetics of eplerenone 100 mg once daily have been studied
in elderly patients (over 65 years), men and women. The pharmacokinetics of eplerenone did not differ significantly between men and women. At steady state, Cmax and AUC were 22% and 45% higher in elderly patients, respectively, than in younger patients
(18-45 years old).
Kidney failure
The pharmacokinetics of eplerenone were studied in patients with renal failure of varying severity and in patients on hemodialysis. Compared with patients in the control group, patients with severe renal failure showed an increase in steady-state AUC and Cmax by 38% and 24%, respectively, and in patients on hemodialysis, their decrease by 26% and 3%. No correlation was found between plasma clearance of eplerenone and creatinine clearance. Eplerenone is not removed by hemodialysis.
Liver failure
The pharmacokinetics of eplerenone at a dose of 400 mg were compared in patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score 7-9) and healthy volunteers. Steady-state Cmax and AUC of eplerenone were increased by 3.6% and 42%, respectively. Eplerenone has not been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment and is therefore not indicated for use in this group of patients.
Heart failure
The pharmacokinetics of eplerenone at a dose of 50 mg was studied in patients with heart failure (FC II-IV). Steady-state AUC and Cmax in patients with heart failure were 38 and 30% higher, respectively, than in healthy volunteers matched by age, body weight and gender. The clearance of eplerenone in patients with heart failure is similar to that in healthy elderly people.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Hyperkalemia
When treated with Inspra®, hyperkalemia may develop, which is due to its mechanism of action. At the beginning of treatment and when changing the dose of the drug in all patients, potassium levels in the blood serum should be monitored. In the future, periodic monitoring of potassium levels is recommended for patients with an increased risk of developing hyperkalemia, for example, the elderly, patients with renal failure and diabetes mellitus. Given the increased risk of hyperkalemia, administration of potassium supplements after initiation of eplerenone treatment is not recommended. Reducing the dose of Inspra® leads to a decrease in potassium levels in the blood serum. In one study, adding hydrochlorothiazide to eplerenone prevented increases in serum potassium.
Renal dysfunction
In patients with impaired renal function, including diabetic microalbuminuria, it is recommended to regularly monitor serum potassium levels. The risk of developing hyperkalemia increases with decreased renal function. Although the number of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and microalbuminuria in the studies was limited, an increase in the incidence of hyperkalemia was noted in this small sample. In this regard, treatment should be carried out with caution in such patients. Inspra® is not removed by hemodialysis. The use of Inspra® is contraindicated in severe renal failure.
Liver dysfunction
In patients with mild or moderate liver dysfunction (5-6 and 7-9 points according to the Child-Pugh classification), an increase in serum potassium levels of more than 5.5 mmol/l was not detected. Due to increased exposure to eplerenone in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment, frequent and regular monitoring of serum potassium levels should be performed, especially in elderly patients. Eplerenone has not been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment and is therefore contraindicated.
Inducers of the CYP3A4 isoenzyme
Concomitant use of Inspra® with strong inducers of the CYP3A4 isoenzyme is not recommended.
Cyclosporine, tacrolimus, drugs containing lithium
The use of these drugs should be avoided during treatment with Inspra®.
Lactose
Inspra® tablets contain lactose, so they should not be prescribed to patients with rare hereditary diseases such as lactose intolerance, lactase deficiency and glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Eplerenone
Composition
Composition
1 tablet contains:
active substance: eplerenone 25 mg or 50 mg;
excipients: lactose monohydrate 35.700/ 71.400 mg, microcrystalline cellulose 15.375/ 30.750 mg, croscarmellose sodium 4.250/ 8.500 mg, hypromellose 2.550/ 5.100 mg, sodium lauryl sulfate 0.850/ 1.700 mg, talc 0.850/1.700 mg, magnesium stearate 0.425/0.850 mg;
film coating: Opadry yellow YS-1-12524-A 3.825/ 5.10 mg [hypromellose, titanium dioxide, macrogol, polysorbate-80, iron oxide yellow, iron oxide red].
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
There is no information on the use of the drug in pregnant women. The drug should be used with caution and only in cases where the expected benefit to the mother significantly outweighs the possible risk to the fetus/child.
There is no information on the excretion of eplerenone after oral administration in breast milk. The possible adverse effects of eplerenone on breastfed newborns are unknown, so it is advisable to either stop breastfeeding or discontinue the drug, depending on its importance to the mother.
Contraindications
Contraindications
– hypersensitivity to eplerenone or other components of the drug;
– clinically significant hyperkalemia;
– potassium content in blood serum at the beginning of treatment > 5.0 mmol/l;
– severe renal failure (creatinine clearance (CC) < 30 ml/min);
– severe liver failure (more than 9 points according to the Child-Pugh classification);
– simultaneous use of potassium-sparing diuretics or potent inhibitors of the CYP3A4 isoenzyme, for example, itraconazole, ketoconazole, ritonavir, nelfinavir, clarithromycin, telithromycin and nefazodone (see section “Interaction with other drugs”);
– rare hereditary diseases such as lactose intolerance, lactase deficiency and glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome (see section “Special instructions”);
– there is no experience in using the drug in children under 18 years of age, therefore its use in patients of this age group is not recommended.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Listed below are adverse events that may be related to treatment, as well as serious adverse events, the incidence of which is comparable to the incidence of adverse and serious adverse events in the placebo group. Adverse events are distributed according to body systems and frequency: often > 1/100, 1/1000, < 1/100; frequency unknown (cannot be calculated from available data).
From the hematopoietic and lymphatic systems
Uncommon: eosinophilia.
Metabolic and nutritional disorders
Common: hyperkalemia, hypertriglyceridemia, dehydration, hypercholesterolemia.
Uncommon: hyponatremia, hypothyroidism.
Mental disorders
Uncommon: insomnia.
Neurological disorders
Common: fainting, dizziness.
Uncommon: headache, hypoesthesia.
From the side of the heart
Common: myocardial infarction.
Uncommon: left ventricular failure, atrial fibrillation, tachycardia.
Vascular disorders
Often: marked decrease in blood pressure.
Uncommon: orthostatic hypotension, thrombosis of the arteries of the lower extremities.
From the respiratory system, chest and mediastinum
Often: cough.
Uncommon: pharyngitis.
From the gastrointestinal tract
Common: diarrhea, nausea, constipation.
Uncommon: flatulence, vomiting.
From the liver and biliary tract
Uncommon: cholecystitis.
From the skin and subcutaneous fat
Common: skin itching.
Uncommon: increased sweating, rash.
Frequency unknown: angioedema.
From the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue
Common: cramps in the calf muscles of the legs, musculoskeletal pain.
Uncommon: back pain.
From the kidneys and urinary tract
Common: renal dysfunction.
General and local
Uncommon: asthenia, malaise.
Laboratory indicators
Uncommon: increased concentration of residual urea nitrogen, creatinine, decreased expression of epidermal growth factor receptor, increased concentration of glucose in the blood serum.
Infections
Uncommon: pyelonephritis, gynecomastia.
Interaction
Interaction
Pharmacodynamic interactions Potassium-sparing diuretics and potassium supplements: Given the increased risk of hyperkalemia, eplerenone should not be administered to patients receiving potassium-sparing diuretics and potassium supplements. Potassium-sparing diuretics may enhance the effects of antihypertensives and other diuretics.
Preparations containing lithium: The interaction of eplerenone with lithium preparations has not been studied. However, in patients receiving lithium preparations in combination with diuretics and ACE inhibitors, cases of increased concentrations and lithium intoxication have been described. If such a combination is necessary, it is advisable to monitor plasma lithium concentrations.
Cyclosporine, tacrolimus: Cyclosporine and tacrolimus may cause renal impairment and increase the risk of hyperkalemia. Concomitant use of eplerenone and cyclosporine or tacrolimus should be avoided. If cyclosporine or tacrolimus is required during treatment with eplerenone, careful monitoring of serum potassium and renal function is recommended.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Treatment with NSAIDs can lead to acute renal failure due to direct suppression of glomerular filtration, especially in patients at risk (elderly patients and/or patients with dehydration). When using these drugs together, it is necessary to ensure adequate hydration and monitor renal function before and during treatment.
Trimethoprim: Concomitant use of trimethoprim with eplerenone increases the risk of hyperkalemia. It is recommended to monitor serum potassium levels and renal function, especially in patients with renal failure and in elderly patients.
ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor antagonists: When using eplerenone with ACE inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor antagonists, serum potassium levels should be carefully monitored. Such a combination may lead to an increased risk of developing hyperkalemia, especially in patients with impaired renal function, incl. in elderly patients. The triple combination of an ACE inhibitor and angiotensin II receptor antagonist with eplerenone should not be used. Alpha1-blockers (prazosin, alfuzosin): with simultaneous use of alpha1-blockers with eplerenone, the antihypertensive effect and/or the risk of developing orthostatic hypotension may increase, and therefore, blood pressure control is recommended, especially when changing body position.
Tricyclic antidepressants, antipsychotics, amifostine, baclofen: when used simultaneously with eplerenone, the antihypertensive effect may be enhanced or the risk of orthostatic hypotension may increase. Glucocorticoids, tetracosactide: simultaneous use of these drugs with eplerenone may lead to sodium and fluid retention.
Pharmacokinetic interactions
In vitro studies indicate that eplerenone does not inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2C19, CYP2C9, CYP2D6 or CYP3A4. Eplerenone is not a substrate or inhibitor of P glycoprotein
Digoxin: The AUC of digoxin when administered concomitantly with eplerenone increased by 16% (90% CI: 4% – 30%). Caution must be exercised if digoxin is used at doses close to the maximum therapeutic dose.
Warfarin: No clinically significant pharmacokinetic interaction with warfarin has been identified. Caution must be exercised if warfarin is used in doses close to the maximum therapeutic dose.
Substrates of the CYP3A4 isoenzyme: in special studies, no signs of pharmacokinetic interaction of eplerenone with substrates of the CYP3A4 isoenzyme, for example, midazolam and cisapride, were identified.
CYP3A4 isoenzyme inhibitors
Strong inhibitors of the CYP3A4 isoenzyme: when using eplerenone with drugs that inhibit the CYP3A4 isoenzyme, significant pharmacokinetic interaction is possible. A strong inhibitor of the CYP3A4 isoenzyme (ketoconazole 200 mg twice daily) caused an increase in eplerenone AUC by 441%. Concomitant use of eplerenone with strong inhibitors of the CYP3A4 isoenzyme, such as ketoconazole, itraconazole, ritonavir, nelfinavir, clarithromycin, telithromycin and nefazadone, is contraindicated.
Weak and moderate inhibitors of the CYP3A4 isoenzyme: simultaneous use with erythromycin, saquinavir, amiodarone, diltiazem, verapamil and fluconazole was accompanied by significant pharmacokinetic interactions (the degree of increase in AUC ranged from 98% to 187%). When these drugs are used simultaneously with eplerenone, the dose of the latter should not exceed 25 mg per day.
Inducers of the CYP3A4 isoenzyme
Simultaneous administration of drugs containing St. John’s Wort (St John’s Wort, a strong inducer of the CYP3A4 isoenzyme) with eplerenone caused a decrease in the AUC of the latter by 30%. When using stronger inducers of the CYP3A4 isoenzyme, such as rifampicin, a more pronounced decrease in the AUC of eplerenone is possible. Given the possible decrease in the effectiveness of eplerenone, the simultaneous use of strong inducers of the CYP3A4 isoenzyme (rifampicin, carbamazepine, phenytoin, phenobarbital, drugs containing St. John’s wort) is not recommended.
Antacids: Based on a pharmacokinetic clinical study, there is no significant interaction between antacids and eplerenone when used concomitantly.
Overdose
Overdose
There are no cases of eplerenone overdose in humans.
Symptoms: the most likely manifestations of an overdose may be a pronounced decrease in blood pressure and hyperkalemia.
Treatment: if a pronounced decrease in blood pressure develops, maintenance treatment should be prescribed. If hyperkalemia develops, standard therapy is indicated. Eplerenone is not removed by hemodialysis. It has been established that eplerenone actively binds to activated carbon.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At a temperature not exceeding 30 ºС.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years
Do not use after the expiration date stated on the package.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Pfizer Pharmaceuticals LLC, Puerto Rico
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature not exceeding 30 °C |
| Manufacturer | Pfizer Pharmaceuticals LLC, Puerto Rico |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Pfizer Pharmaceuticals LLC |
Related products
Buy Inspra, 25 mg 30 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.