No products in the cart.
Ibuklin Junior, 100 mg+125 mg 20 pcs
€6.69 €5.58
Description
Pharmacodynamics
Combined drug, the action of which is due to its constituent components.
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), has analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic effect.
Inhibiting cyclooxygenase (COX) 1 and 2, disrupts arachidonic acid metabolism, reduces the number of prostaglandins (mediators of pain, inflammation and hyperthermia) both in inflammation focus and in healthy tissues, inhibits the exudative and proliferative phases of inflammation.
Paracetamol inhibits COX indiscriminately, mainly in the central nervous system, slightly affects the water-salt metabolism and the mucosa of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). It has analgesic and antipyretic effect.
In inflamed tissues peroxidase neutralizes the effect of paracetamol on COX 1 and 2, which explains the low anti-inflammatory effect.
The effectiveness of the combination is greater than that of the individual components.
Pharmacokinetics
Ibuprofen.
Absorption is high, rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract (GIT).
Time to reach maximal
concentration (TCmax) after oral intake – about 1-2 hours.
Blood plasma protein binding – more than 90%. The half-life (T1/2) is about 2 hours.
It is metabolized.
More than 90% is excreted by the kidneys (not more than 1% unchanged) and, to a lesser extent, with the bile as metabolites and their conjugates.
Paracetamol.
Absorption is high, binding to plasma proteins is less than 10% and increases slightly in overdose.
Sulfate and glucuronide metabolites do not bind to plasma proteins even in relatively high concentrations.
Cmax is 5-20 mg/ml, TCmax is 0.5-2 hours. It is evenly distributed in the body fluids.
In case of depletion of glutathione reserves in liver (in overdose) enzyme systems of hepatocytes may be blocked resulting in their necrosis.
T1/2 – 2-3 hours. It is excreted by the kidneys, mainly as glucuronide and sulfate conjugates (less than 5% – unchanged).
Less than 1% of the dose of paracetamol is penetrated into the breast milk.
The ability to form conjugates with glucuronic acid in children is lower than in adults.
Indications
Indications
Feverish syndrome.
Pain syndrome of mild or moderate intensity of various etiologies: toothache, pain during sprains, dislocations, fractures.
As an auxiliary drug for the treatment of pain and fever in sinusitis, tonsillitis, acute infectious and inflammatory diseases of the upper respiratory tract (pharyngitis, tracheitis, laryngitis).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group: combined analgesic drug (NSAID + analgesic non-narcotic drug).
ATX code: M01AE51
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
A combined drug whose effect is determined by its constituent components.
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that has analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic effects. By inhibiting cyclooxygenase (COX) 1 and 2, it disrupts the metabolism of arachidonic acid, reduces the amount of prostaglandins (mediators of pain, inflammation and hyperthermic reaction) both in the site of inflammation and in healthy tissues, suppresses the exudative and proliferative phases of inflammation.
Paracetamol indiscriminately blocks COX, mainly in the central nervous system, and has little effect on water-salt metabolism and the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). Has an analgesic and antipyretic effect. In inflamed tissues, peroxidases neutralize the effect of paracetamol on COX 1 and 2, which explains the low anti-inflammatory effect.
The effectiveness of the combination is higher than that of individual components.
Pharmacokinetics
Ibuprofen.
Absorption is high, quickly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). The time to reach maximum concentration (TCmax) after oral administration is about 1-2 hours. Communication with blood plasma proteins is more than 90%. The half-life (T1/2) is about 2 hours. It slowly penetrates into the joint cavity, accumulates in the synovial fluid, creating higher concentrations in it than in the blood plasma. After absorption, about 60% of the pharmacologically inactive R-form is slowly transformed into the active S-form. Metabolized. More than 90% is excreted by the kidneys (no more than 1% unchanged) and, to a lesser extent, with bile in the form of metabolites and their conjugates.
Paracetamol.
Absorption is high, binding to plasma proteins is less than 10% and increases slightly with overdose. Sulfate and glucuronide metabolites do not bind to plasma proteins even at relatively high concentrations. The Cmax value is 5-20 μg/ml, TCmax is 0.5-2 hours. Distributed fairly evenly in body fluids. Penetrates the blood-brain barrier.
About 90-95% of paracetamol is metabolized in the liver to form inactive conjugates with glucuronic acid (60%), taurine (35%) and cysteine (3%), as well as a small amount of hydroxylated and deacetylated metabolites. A small portion of the drug is hydroxylated by microsomal enzymes to form highly active N-acetyl-n-benzoquinone imine, which binds to the sulfhydryl groups of glutathione. When glutathione reserves in the liver are depleted (in case of overdose), the enzyme systems of hepatocytes can be blocked, leading to the development of their necrosis.
T1/2 – 2-3 hours. Excreted by the kidneys, mainly in the form of glucuronide and sulfate conjugates (less than 5% unchanged). Less than 1% of the administered dose of paracetamol passes into breast milk. In children, the ability to form conjugates with glucuronic acid is lower than in adults.
Special instructions
Special instructions
The advisability of using the drug as an antipyretic is decided in each case, depending on the severity, nature and tolerability of the febrile syndrome.
Ibuprofen may mask objective signs of infectious diseases, so therapy with ibuprofen in patients with infectious diseases should be prescribed with caution.
To reduce the risk of developing adverse events from the gastrointestinal tract, the minimum effective dose should be used in the shortest possible short course.
When using indirect anticoagulants simultaneously, it is necessary to monitor blood coagulation parameters.
Avoid taking Ibuklin Junior® together with other NSAIDs.
With long-term (more than 5 days) use of the drug, monitoring of peripheral blood and the functional state of the liver is necessary.
The drug may distort the results of laboratory tests when quantitatively determining glucose, uric acid in blood serum, 17-ketosteroids (the drug must be discontinued 48 hours before the test).
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery
During the treatment period, the patient should refrain from engaging in potentially hazardous activities that require increased attention and speed of psychomotor reactions
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Ibuprofen, Paracetamol
Composition
Composition
Each dispersible tablet [for children] contains:
active ingredients: ibuprofen 100 mg, paracetamol 125 mg
excipients: microcrystalline cellulose, corn starch, lactose, sodium carboxymethyl starch (type A), crimson dye (Ponceau 4R) (E124), glycerol, colloidal silicon dioxide, orange flavor DC 100 PH, pineapple flavor DC 106 PH, peppermint leaf oil, aspartame, magnesium stearate, talc
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
If it is necessary to use the drug Ibuklin Junior® during pregnancy and lactation (breastfeeding), you should carefully weigh the expected benefits of therapy for the mother and the potential risk for the fetus or child.
If use is necessary in the first trimester of pregnancy, long-term use of the drug Ibuklin Junior® should be avoided.
NSAIDs should not be used by women from the 20th week of pregnancy due to the possible development of oligohydramnios and/or kidney pathology in newborns (neonatal renal dysfunction).
If short-term use of Ibuklin Junior® is necessary during lactation, cessation of breastfeeding is usually not required.
Experimental studies have not established the embryotoxic, teratogenic and mutagenic effects of the components of the drug Ibuklin Junior®.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Increased individual sensitivity to the components of the drug (including other NSAIDs), peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum in the acute phase, complete or incomplete combination of bronchial asthma, recurrent polyposis of the nose and paranasal sinuses and intolerance to acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs (including a history), severe renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min), lesions optic nerve, genetic absence of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, diseases of the blood system, the period after coronary artery bypass surgery, progressive kidney disease, severe liver failure or active liver disease, confirmed hyperkalemia, active gastrointestinal bleeding, inflammatory bowel disease, pregnancy over 20 weeks, childhood (up to 3 years).
Side Effects
Side Effects
In therapeutic doses, the drug is usually well tolerated.
From the digestive system: rarely – dyspeptic symptoms, with long-term use in high doses – hepatotoxic effect.
From the hematopoietic system: rarely – thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, pancytopenia, neutropenia, agranulocytosis.
Allergic reactions: rarely – skin rash, itching, urticaria.
If side effects occur, you should stop taking the drug and consult a doctor.
Interaction
Interaction
When using the drug Ibuklin Junior® simultaneously with drugs, various interaction effects may develop.
Long-term combined use with paracetamol increases the risk of nephrotoxic effects.
Combination with ethanol, glucocorticosteroids, corticotropin increases the risk of erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract.
Ibuprofen enhances the effect of direct (heparin) and indirect (coumarin and indanedione derivatives) anticoagulants, thrombolytic agents (alteplase, anistreplase, streptokinase, urokinase), antiplatelet agents, colchicine – the risk of developing hemorrhagic complications increases.
Enhances the hypoglycemic effect of insulin and oral hypoglycemic drugs.
Weakens the effects of antihypertensive drugs and diuretics (by inhibiting the synthesis of renal prostaglandins).
Increases the blood concentration of digoxin, lithium and methotrexate.
Caffeine enhances the analgesic effect of ibuprofen.
Cyclosporine and gold preparations increase nephrotoxicity.
Cefamandole, cefoperazone, cefotetan, valproic acid, plicamycin increase the incidence of hypoprothrombinemia.
Antacids and cholestyramine reduce the absorption of the drug.
Myelotoxic drugs contribute to the manifestation of hematotoxicity of the drug.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: gastrointestinal disorders (abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, pain in the epigastric region), increased prothrombin time, bleeding after 12-48 hours, lethargy, drowsiness, depression, headache, tinnitus, impaired consciousness, heart rhythm disturbances, decreased blood pressure, manifestations of hepato- and nephrotoxicity, convulsions, possibly development of hepatonecrosis.
Treatment: gastric lavage during the first 4 hours; alkaline drinking, forced diuresis; activated carbon orally, administration of SH-group donors and precursors for the synthesis of glutathione – methionine 8-9 hours after an overdose and N-acetylcysteine orally or intravenously – after 12 hours, antacid drugs; hemodialysis; symptomatic therapy. The need for additional therapeutic measures (further administration of methionine, intravenous administration of N-acetylcysteine) is determined depending on the concentration of paracetamol in the blood, as well as the time elapsed after its administration.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
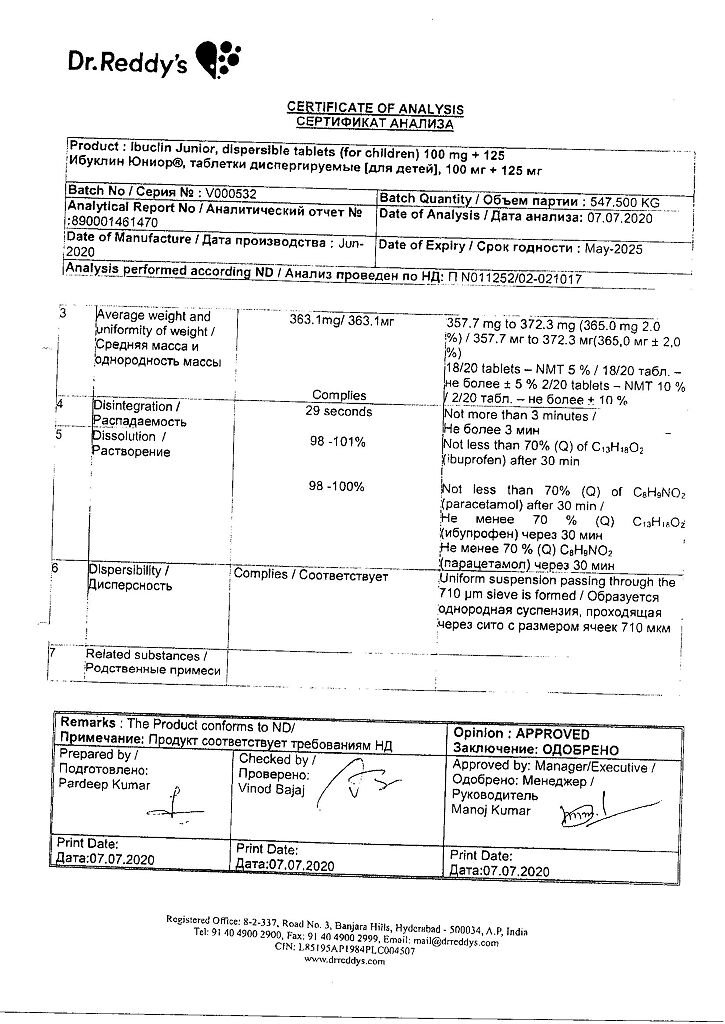
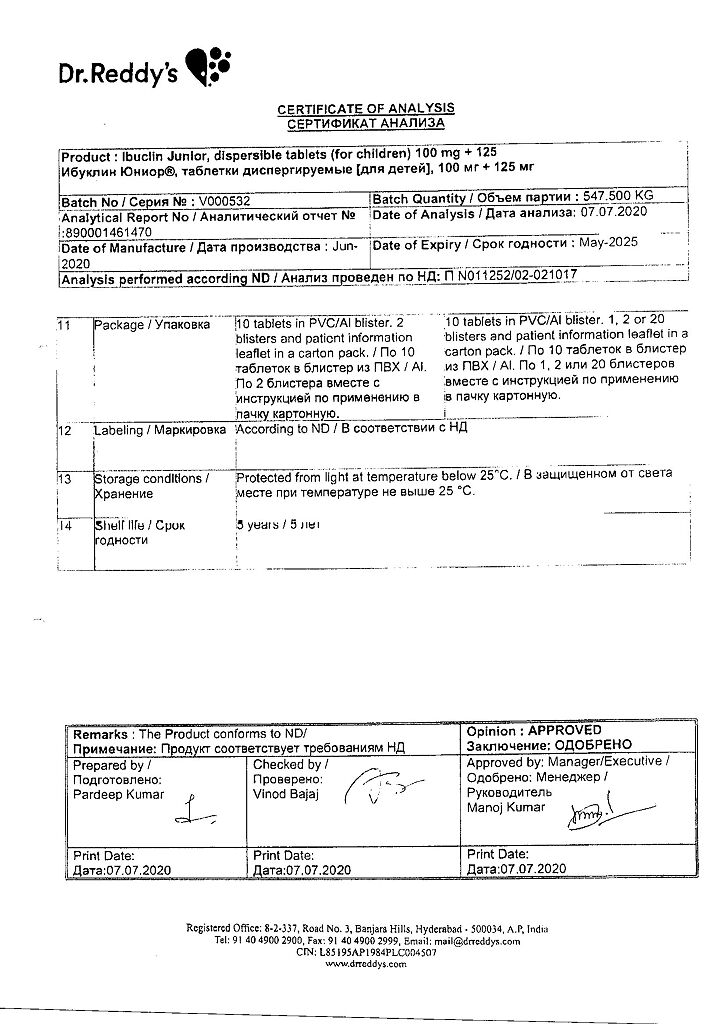
In the original packaging (blister in a pack) at a temperature not exceeding 25 ºС.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
5 years. Do not use after the expiration date stated on the package.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Ltd, India
Additional information
| Shelf life | 5 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, light-protected place, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C |
| Manufacturer | Dr. Reddy's, India |
| Medication form | dispersible tablets |
| Brand | Dr. Reddy's |
Related products
Buy Ibuklin Junior, 100 mg+125 mg 20 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.