No products in the cart.
Human albumin, 20% 50 ml
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
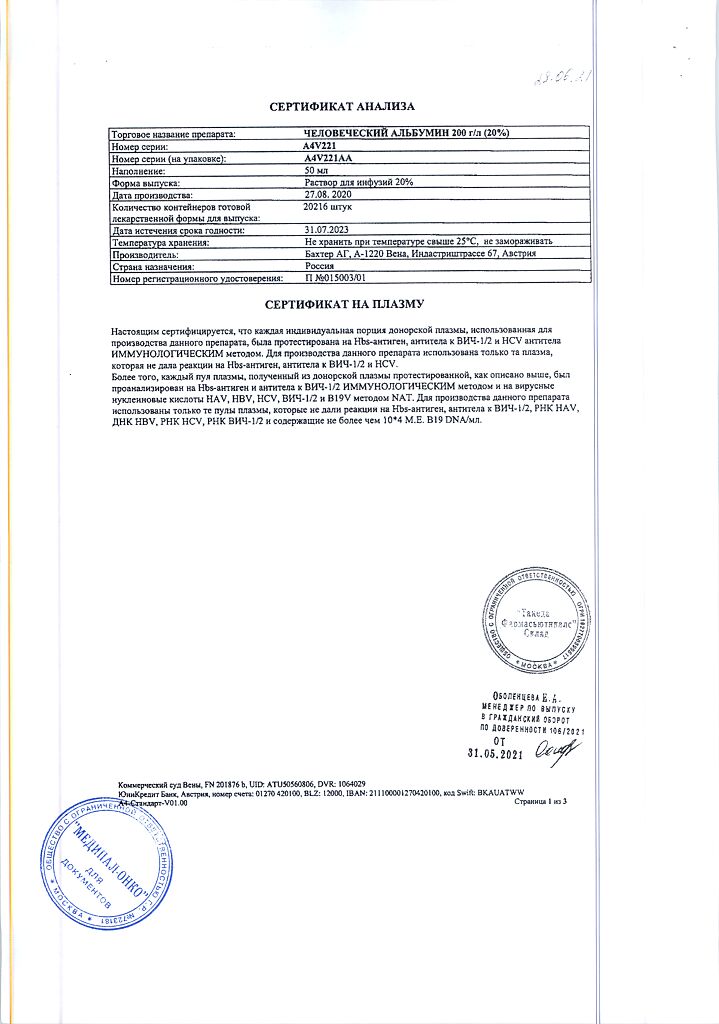
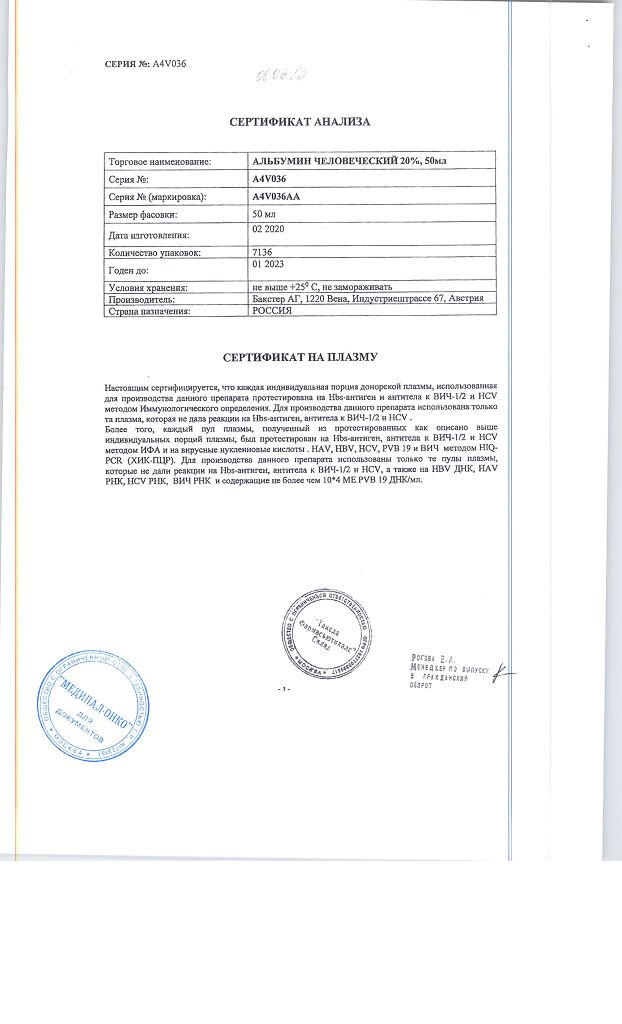
EAN: 4650081980348
SKU: 25029
Categories: Anesthesia and resuscitation, Anesthesia solutions, Medicine
Description
The drug Albumin human is recommended for restoration and maintenance of circulating blood volume when the volume and appropriateness of colloidal solutions are insufficient.
The choice of the drug Albumin human instead of synthetic colloidal solutions is determined by the clinical condition of the patient, as well as the standards of medical care.
The drug Albumin human may be used for the following clinical conditions:
- shock – in emergency therapy in case of shock and other similar conditions when urgent restoration of circulating blood volume is required;
- Burns – to prevent severe hemoconcentration and maintain the necessary electrolyte balance (drug Albumin human in an isotonic solution (5% solution of dextrose or 0.9% sodium chloride solution);hypoproteinemia with or without edema – in clinical situations usually associated with low plasma protein concentrations and resulting in reduced circulating blood volume;
- hypoalbuminemia – when albumin deficiency has resulted from insufficient synthesis, excessive catabolism, loss due to burns, trauma or due to redistribution within the body.
.
Indications
Indications
The drug Albumin human is recommended for restoring and maintaining circulating blood volume in case of insufficient volume and the advisability of using colloidal solutions.
The choice of the drug Albumin human instead of synthetic colloidal solutions is determined by the clinical condition of the patient, as well as the standards of medical care.
The drug Albumin human can be used for the following clinical conditions:
shock – for emergency treatment in case of shock and other similar conditions when urgent restoration of circulating blood volume is required;
burns – to prevent severe hemoconcentration and maintain the required electrolyte balance (human Albumin in an isotonic solution (5% dextrose solution or 0.9% sodium chloride solution));
hypoproteinemia with or without edema – in clinical situations usually associated with low plasma protein concentrations and leading to a decrease in circulating blood volume;
hypoalbuminemia – when albumin deficiency is the result of insufficient synthesis, excessive catabolism, loss due to burns, injuries, or as a result of redistribution within the body.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group: plasma replacement agent
Special instructions
Special instructions
INFLUENCE ON THE ABILITY TO DRIVE VEHICLES AND OPERATE MACHINERY
There are no data on the effect of human albumin on the ability to drive a car and perform work with other machines and mechanisms that require increased attention.
SPECIAL INSTRUCTIONS AND PRECAUTIONS FOR USE
Allergic reactions/anaphylactic shock
If an allergic or anaphylactic reaction is suspected, the drug should be stopped immediately and appropriate treatment should be initiated. In case of shock, antishock therapy should be initiated in accordance with current standards of treatment.
Hemodynamics
The drug Albumin human should be administered subject to careful monitoring of hemodynamic parameters for the development of symptoms of cardiac or respiratory failure, renal failure or increased intracranial pressure.
Hypervolemia/hemodilution
The drug Albumin human should be used with caution in conditions where hypervolemia and its consequences or hemodilution may pose a particular risk to the patient, in particular with decompensated heart failure, arterial hypertension, esophageal varices, pulmonary edema, hemorrhagic diathesis, severe anemia, renal and postrenal anuria.
The colloid-osmotic effect of a human albumin solution at a concentration of 200 g/l is approximately four times higher than that of blood plasma. Therefore, when administering a concentrated albumin solution, the patient should be adequately hydrated. Careful monitoring is necessary to prevent cardiovascular overload and overhydration.
The rate of administration of the drug Albumin human should be selected taking into account the concentration of the infusion solution and hemodynamic parameters. If the infusion rate does not correspond to the patient’s condition, hypervolemia and pulmonary edema may develop. When the first clinical signs of overload of the cardiovascular system appear (headache, shortness of breath, swelling of the jugular veins), with an increase in blood pressure, an increase in central venous pressure, or with the development of pulmonary edema, the infusion should be stopped immediately.
Large volumes
If it is necessary to replace relatively large volumes of fluid, it is necessary to monitor coagulation parameters and hematocrit. Adequate replacement of other blood components (clotting factors, electrolytes, platelets and red blood cells) should be ensured and hemodynamic parameters should be strictly monitored.
Before administering large volumes, the drug should be warmed to room temperature or body temperature.
Electrolyte status
When administering the drug Albumin human, it is necessary to monitor the patient’s electrolyte status (see section “Dosage and Administration”) and take appropriate measures to restore and maintain electrolyte balance. The drug Albumin human contains sodium in the amount of 100-130 mmol/l, which must be taken into account when using it in patients on a low-salt diet.
Blood pressure
An increase in blood pressure after an infusion of Human Albumin requires careful monitoring of the patient who has undergone trauma or surgery to detect damaged blood vessels that might not bleed at lower blood pressure and take appropriate action.
Prevention of infections
Standard measures to prevent infections arising from the use of medicinal products derived from human plasma or blood include donor selection, screening of individual donations and plasma pools for specific markers of infection, and the use of effective virus inactivation/removal measures during the manufacturing process. Despite this, when administering medicinal products produced from human blood or plasma, the possibility of transmitting an infectious agent cannot be completely excluded. This also applies to unknown or new viruses and other pathogens.
There have been no reports of transmission of the virus from Albumin human manufactured according to European Pharmacopoeia specifications using standard processes.
Whenever Albumin Human is administered, it is strongly recommended that the trade name and lot number of the drug be recorded to understand the relationship between the patient and the specific lot of product.
Pharmaceutical incompatibility
The drug Albumin human should not be mixed with other drugs (except for the recommended solvents indicated in the section “Method of administration and dosage”), whole blood and red blood cells. Human albumin should also not be mixed with protein hydrolysates, particularly parenteral nutrition solutions or solutions containing alcohol, as this may result in protein precipitation.
Application and disposal
If the solution becomes cloudy, the seal of the bottle is broken, or if a leak is detected, the drug should not be used. Before use, preparations for parenteral administration should be visually checked for the presence of mechanical inclusions and color changes, if the color of the solution and the material of the container allow this. The drug Albumin human does not contain preservatives, therefore the contents of the bottle should be used immediately after opening. The unused remainder of the drug should be destroyed in accordance with local requirements.
When using sterile water for injection to reconstitute Human Albumin at concentrations of 20% or higher, there is a potential risk of fatal hemolysis and acute renal failure. Suitable diluents are 5% dextrose solution or 0.9% sodium chloride solution.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Human albumin
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient:
Human albumin – solution contains 200 g/l total protein (at least 95% albumin) produced from human plasma.
Excipients:
Caprylic acid 16 mmol/l
N-acetyltryptophan 16 mmol/l
Water for injections up to 1 l
Total sodium ion content 100 – 130 mmol/l
The solution is hyperoncotic.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
The safety of human albumin when used in pregnant women and breastfeeding women has not been studied in controlled clinical studies. However, clinical experience with human albumin, a natural component of human blood, suggests no harmful effects on pregnancy, the fetus or the newborn.
The effect of human albumin on fertility has not been studied in controlled clinical trials.
Animal reproductive studies have not been conducted using human albumin.
To assess the safety of a human albumin preparation in relation to reproductive function, embryonic or fetal development, the course of pregnancy, as well as peri- and postnatal development, the results of experimental studies in animals are insufficient. Before prescribing, the doctor in each specific case must carefully assess the possible risks and benefits of using human albumin.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to human albumin or any other component of the drug.
WITH CAUTION
The drug Albumin human should be used with caution in conditions where hypervolemia and its consequences or hemodilution may pose a particular risk to the patient, in particular with decompensated heart failure, arterial hypertension, esophageal varices, pulmonary edema, hemorrhagic diathesis, severe anemia, renal and postrenal anuria.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Adverse effects observed in clinical studies
In controlled clinical trials of the drug Albumin human, sponsored by the company, there was no data on the development of adverse adverse reactions.
Adverse effects observed during post-registration use
During post-marketing use of Albumin Human, the following adverse reactions were observed, listed according to system organ classification (SOC) using the preferred Medical Dictionary of Regulatory Activities (MedDRA) terms in descending order of severity.
Immune system disorders: anaphylactic shock, anaphylactic reactions, hypersensitivity/allergic reactions
Nervous system disorders: headache, dysgeusia
Cardiovascular system disorders: myocardial infarction, atrial fibrillation, tachycardia, hypotension, hyperemia
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: pulmonary edema, shortness of breath
Gastrointestinal disorders: vomiting, nausea
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: urticaria, rash, itching
General disorders and reactions at the injection site: hyperthermia, chills
Safety information regarding vector-borne agents is provided in the “Special Instructions and Precautions for Use” section.
Interaction
Interaction
Human albumin should not be mixed with other drugs (with the exception of isotonic solutions, for example, 5% dextrose solution or 0.9% sodium chloride solution), blood or red blood cells.
Specific interactions of human albumin with other drugs are unknown.
Overdose
Overdose
If you use too high a dose of the drug Albumin human or exceed the rate of its infusion, hypervolemia may develop. When the first clinical signs of cardiovascular overload (headache, shortness of breath, jugular vein distension), increased blood pressure, increased central venous pressure and/or pulmonary edema appear, the infusion should be stopped immediately and the patient’s hemodynamic parameters should be carefully monitored.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C in the original packaging. Do not freeze.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years
Do not use after the expiration date stated on the package.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Baxter Pharmaceutical Solutions LLC, USA
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years Do not use after the expiration date stated on the package. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C in the original container. Do not freeze. Keep out of the reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Baxter Pharmaceutical Solutions LLC, USA |
| Medication form | solution for infusion |
| Brand | Baxter Pharmaceutical Solutions LLC |
Related products
Buy Human albumin, 20% 50 ml with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.