No products in the cart.
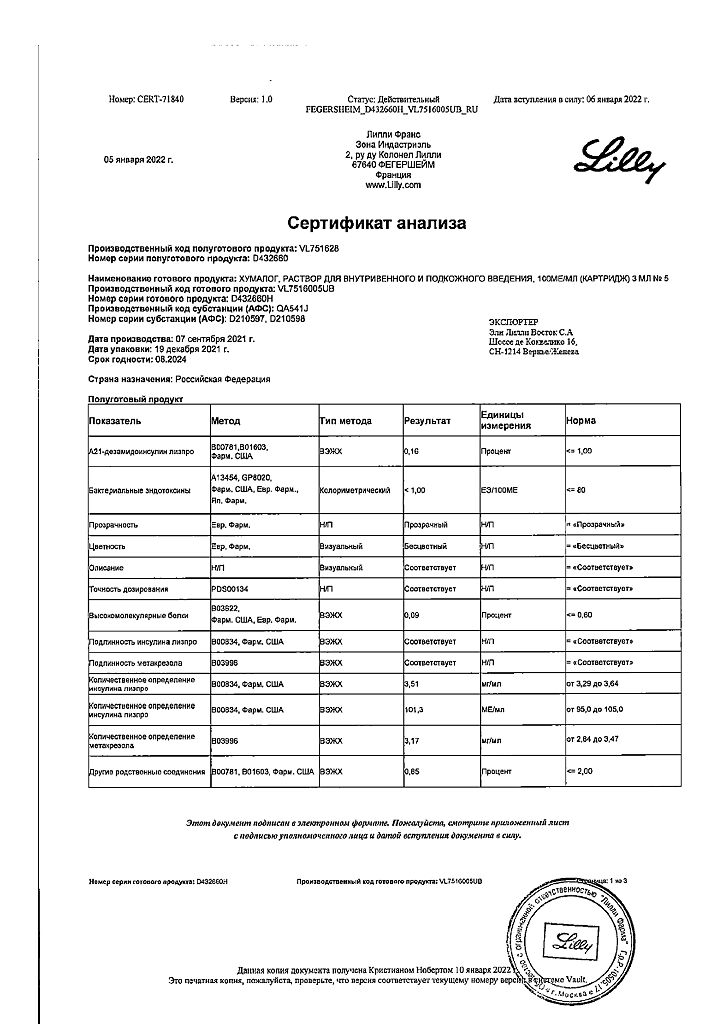
Humalog, 100 me/ml 3 ml cartridges 5 pcs
€45.30 €39.26
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Humalog is a DNA recombinant analogue of human insulin. It differs from the latter in reverse sequence of amino acids at positions 28 and 29 of the B-chain of insulin.
The main action of the drug is regulation of glucose metabolism. In addition, it has an anabolic effect. In muscle tissue there is an increase of glycogen, fatty acids, glycerol content, increased protein synthesis and increased consumption of amino acids, but there is a decrease of glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis, ketogenesis, lipolysis, protein catabolism and release of amino acids.
In patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, insulin lispro has a greater reduction in post-meal hyperglycemia compared to soluble human insulin. For patients receiving short-acting and basal insulin, the dose of both insulins should be adjusted to achieve optimal blood glucose levels throughout the day.
As with all insulin medications, the duration of action of insulin lispro can vary between patients or at different times in the same patient and depends on the dose, site of injection, blood supply, body temperature and physical activity.
The pharmacodynamic characteristics of insulin lispro in children and adolescents are similar to those seen in adults.
In patients with type 2 diabetes receiving maximum doses of sulfonylurea derivatives, the addition of insulin lispro results in a significant decrease in glycated hemoglobin.
The treatment with insulin lispro in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes is associated with a decrease in the number of episodes of nocturnal hypoglycemia.
The glucodynamic response to insulin lispro is independent of functional renal or hepatic impairment.
Lispro insulin has been shown to be equimolar to human insulin, but its action is more rapid and lasts for a shorter time.
Lispro has a rapid onset (approximately 15 minutes) because it is highly absorbed, so it can be injected immediately before a meal (0-15 minutes before a meal) versus regular short-acting insulin (30-45 minutes before a meal). Insulin lispro has a shorter duration of action (2 to 5 hours) compared to regular human insulin.
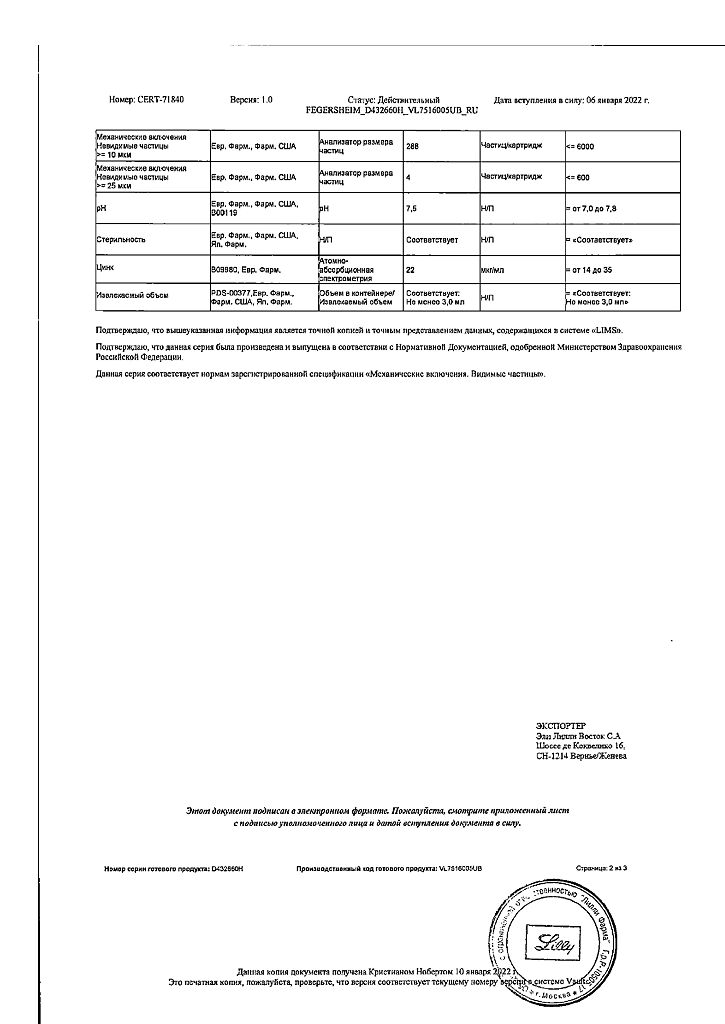
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption and distribution
Lispro insulin is rapidly absorbed after subcutaneous administration and reaches Cmax in blood plasma after 30-70 minutes. The Vd of insulin lispro and regular human insulin are identical and range from 0.26-0.36 L/kg.
The T1/2 of insulin lispro is about 1 hour when administered subcutaneously. Patients with renal and hepatic impairment retain a higher rate of absorption of insulin lispro compared to regular human insulin.
Indications
Indications
Diabetes mellitus in adults and children, requiring insulin therapy to maintain normal glucose levels.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Humalog is a DNA recombinant analogue of human insulin. It differs from the latter in the reverse sequence of amino acids at positions 28 and 29 of the insulin B chain.
The main effect of the drug is the regulation of glucose metabolism. In addition, it has an anabolic effect. In muscle tissue, there is an increase in the content of glycogen, fatty acids, glycerol, increased protein synthesis and an increase in amino acid consumption, but at the same time there is a decrease in glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis, ketogenesis, lipolysis, protein catabolism and amino acid release.
In patients with diabetes mellitus types 1 and 2, the use of insulin lispro significantly reduces postprandial hyperglycemia compared with soluble human insulin. For patients receiving rapid-acting insulin and basal insulin, it is necessary to adjust the dose of both insulins to achieve optimal blood glucose levels throughout the day.
As with all insulin products, the duration of action of insulin lispro may vary between patients or over time within the same patient and is dependent on the dose, injection site, blood supply, body temperature and physical activity.
The pharmacodynamic profile of insulin lispro in children and adolescents is similar to that observed in adults.
In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus receiving maximum doses of sulfonylureas, the addition of insulin lispro results in a significant decrease in glycated hemoglobin.
Treatment of patients with diabetes mellitus types 1 and 2 with insulin lispro is accompanied by a decrease in the number of episodes of nocturnal hypoglycemia.
The glucodynamic response to isulin lispro is independent of renal or hepatic impairment.
Insulin lispro has been shown to be equimolar to human insulin, but its action is more rapid and lasts for a shorter time.
Insulin lispro has a rapid onset of action (about 15 minutes), because has a high absorption rate, and this allows it to be administered immediately before meals (0-15 minutes before meals) in contrast to regular short-acting insulin (30-45 minutes before meals). Insulin lispro has a shorter duration of action (2 to 5 hours) compared to regular human insulin.
Pharmacokinetics
Suction and distribution
After subcutaneous administration, insulin lispro is rapidly absorbed and reaches Cmax in the blood plasma within 30-70 minutes. Vd of insulin lispro and regular human insulin are identical and range from 0.26-0.36 l/kg.
Removal
When administered subcutaneously, T1/2 of insulin lispro is about 1 hour. In patients with renal and hepatic impairment, the absorption rate of insulin lispro remains higher than that of regular human insulin.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Transferring a patient to another type or brand of insulin should be done under strict medical supervision. Changes in potency, brand (manufacturer), type (eg, Regular, NPH, Lente), species (animal, human, human insulin analogue) and/or production method (DNA recombinant insulin or animal insulin) may require a dose change.
Conditions in which early warning symptoms of hypoglycemia may be nonspecific and less severe include long-term diabetes mellitus, intensive insulin therapy, nervous system disease associated with diabetes mellitus, or use of medications such as beta-blockers.
In patients with hypoglycemic reactions after switching from animal insulin to human insulin, early symptoms of hypoglycemia may be less severe or different from those they experienced with their previous insulin. Uncorrected hypoglycemic or hyperglycemic reactions can cause loss of consciousness, coma, or death.
Use in inadequate doses or discontinuation of treatment, especially in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, can lead to hyperglycemia and diabetic ketoacidosis, conditions that are potentially life-threatening to the patient.
Insulin requirements may be reduced in patients with renal failure, as well as in patients with liver failure, as a result of decreased gluconeogenesis and insulin metabolism. However, in patients with chronic liver failure, increased insulin resistance may lead to increased insulin requirements.
The need for insulin may increase with infectious diseases, emotional stress, and with an increase in the amount of carbohydrates in the diet.
Dose adjustment may also be required if the patient increases physical activity or changes the usual diet. Exercise immediately after eating increases the risk of hypoglycemia. A consequence of the pharmacodynamics of rapid-acting insulin analogs is that if hypoglycemia occurs, it may occur sooner after injection than with injection of soluble human insulin.
The patient should be warned that if the doctor has prescribed insulin with a concentration of 40 IU/ml in a vial, then insulin should not be drawn from a cartridge with an insulin concentration of 100 IU/ml using a syringe for administering insulin with a concentration of 40 IU/ml.
If it is necessary to take other medications at the same time as Humalog, the patient should consult a doctor.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
In case of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia associated with an inadequate dosage regimen, the ability to concentrate and the speed of psychomotor reactions may be impaired. This can become a risk factor during potentially hazardous activities (including driving vehicles or working with machinery).
Patients should be careful to avoid hypoglycemia while driving. This is especially important for patients who have reduced or absent awareness of the warning signs of hypoglycemia, or who experience frequent episodes of hypoglycemia. In these circumstances, it is necessary to evaluate the advisability of driving a vehicle. Patients with diabetes can independently relieve perceived mild hypoglycemia by taking glucose or eating high carbohydrate foods (it is recommended to always have at least 20 g of glucose with you). The patient should inform the attending physician about hypoglycemia.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Insulin lispro
Composition
Composition
1 ml of solution for intravenous and subcutaneous administration contains:
active ingredient:
insulin lispro 100 IU,
excipients:
glycerol (glycerin) – 16 mg,
metacresol – 3.15 mg,
zinc oxide (q.s. for Zn2+ content 0.0197 μg),
sodium hydrogen phosphate heptahydrate – 1.88 mg,
hydrochloric acid solution 10% and/or sodium hydroxide solution 10% – q.s. up to pH 7.0-8.0,
water for injection – q.s. up to 1 ml.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
To date, no adverse effects of insulin lispro on pregnancy or fetal/newborn health have been identified. No relevant epidemiological studies have been conducted.
The goal of insulin therapy during pregnancy is to maintain adequate glucose control in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus or gestational diabetes. Insulin requirements usually decrease in the first trimester and increase in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. During and immediately after childbirth, the need for insulin may decrease dramatically.
Women of childbearing age with diabetes should inform their doctor about an existing or planned pregnancy. During pregnancy, patients with diabetes require careful monitoring of blood glucose levels, as well as general clinical supervision.
In patients with diabetes mellitus, adjustment of the insulin dose and/or diet may be required during breastfeeding.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypoglycemia; hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Side effect associated with the main effect of the drug: hypoglycemia. Severe hypoglycemia can lead to loss of consciousness (hypoglycemic coma) and, in exceptional cases, death.
Allergic reactions: local allergic reactions are possible – redness, swelling or itching at the injection site (usually disappear within a few days or weeks); systemic allergic reactions (occur less frequently, but are more serious) – generalized itching, urticaria, angioedema, fever, shortness of breath, decreased blood pressure, tachycardia, increased sweating. Severe cases of systemic allergic reactions can be life-threatening.
Local reactions: lipodystrophy at the injection site.
Interaction
Interaction
The hypoglycemic effect of Humalog is reduced by oral contraceptives, corticosteroids, thyroid hormone preparations, danazol, beta2-adrenergic agonists (including ritodrine, salbutamol, terbutaline), tricyclic antidepressants, thiazide diuretics, chlorprothixene, diazoxide, isoniazid, lithium carbonate, nicotinic acid, phenothiazine derivatives.
The hypoglycemic effect of Humalog is enhanced by beta-blockers, ethanol and ethanol-containing drugs, anabolic steroids, fenfluramine, guanethidine, tetracyclines, oral hypoglycemic drugs, salicylates (for example, acetylsalicylic acid), sulfonamides, MAO inhibitors, ACE inhibitors (captopril, enalapril), octreotide, angiotensin II receptor antagonists.
Humalog should not be mixed with animal insulin preparations.
Humalog can be used (under medical supervision) in combination with longer-acting human insulin or in combination with oral sulfonylurea hypoglycemic agents.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: hypoglycemia, accompanied by the following symptoms: lethargy, increased sweating, tachycardia, headache, vomiting, confusion.
Treatment: Mild hypoglycemia is usually treated by ingesting glucose or other sugars or eating sugar-containing foods.
Moderately severe hypoglycemia can be corrected with intramuscular or subcutaneous glucagon followed by oral carbohydrate once the patient’s condition has stabilized. For patients who do not respond to glucagon, a dextrose (glucose) solution is given intravenously.
If the patient is in a comatose state, then glucagon should be administered intramuscularly or subcutaneously. In the absence of glucagon or if there is no reaction to its administration, it is necessary to administer a dextrose (glucose) solution intravenously. Immediately after regaining consciousness, the patient should be given food rich in carbohydrates.
Further maintenance carbohydrate intake and patient monitoring may be required as a relapse of hypoglycemia may occur.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At 2–8 °C (do not freeze)
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Lilly France, France
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At 2-8 °C (do not freeze) |
| Manufacturer | Lilly France, France |
| Medication form | solution |
| Brand | Lilly France |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Humalog, 100 me/ml 3 ml cartridges 5 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.